Asthma - child - discharge
Pediatric asthma - discharge; Wheezing - discharge; Reactive airway disease - dischargeYour child has asthma, which causes the airways of the lungs to swell and narrow. Now that your child is going home from the hospital, follow your health care provider's instructions on how to care for your child. Use the information below as a reminder.
Asthma
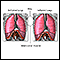
Asthma is a chronic disease that causes the airways of the lungs to swell and become narrow. It leads to breathing difficulty such as wheezing, shor...

When You're in the Hospital
In the hospital, your provider helped your child breathe better. This likely involved giving oxygen through a mask and medicines to open the lung airways.
What to Expect at Home
Your child will probably still have asthma symptoms after leaving the hospital. These symptoms include:
-
Wheezing and coughing that may last up to 5 days
Wheezing
Wheezing is a high-pitched whistling sound during breathing. It occurs when air moves through narrowed breathing tubes in the lungs.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Sleeping and eating that may take up to a week to return to normal
You may need to take time off work to care for your child.
Take Charge of Your Child's Asthma at Home
Make sure you know the asthma symptoms to watch out for in your child.
Asthma symptoms
If you do not know whether or not you have asthma, these 4 symptoms could be signs that you do:Coughing during the day or coughing that may wake you ...
You should know how to take your child's peak flow reading and understand what it means.
Peak flow reading
A peak flow meter is a small device that helps you check how well your asthma is controlled. Peak flow meters are most helpful if you have moderate ...

- Know your child's personal best peak flow reading.
- Know your child's peak flow reading that tells you if their asthma is getting worse.
- Know your child's peak flow reading that means you need to contact your child's provider.
Keep the phone number (or other contact information) of your child's provider with you.
Triggers may make asthma symptoms worse. Know which triggers make your child's asthma worse and what to do when this happens. Common triggers include:
Triggers
It is important to know what things make your asthma worse. These are called asthma "triggers. " Avoiding them is your first step toward feeling bet...

- Pets
- Smells from chemicals and cleaners
- Grass and weeds
- Smoke
-
Dust
Dust
In people who have sensitive airways, allergy and asthma symptoms can be triggered by breathing in substances called allergens, or triggers. It is i...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Cockroaches
- Rooms that are moldy or damp
Moldy or damp
In people who have sensitive airways, allergy and asthma symptoms can be triggered by breathing in substances called allergens, or triggers. It is i...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article
Know how to prevent or treat asthma symptoms that arise when your child is active. These things might also trigger your child's asthma:
- Cold or dry air.
- Smoky or polluted air.
- Grass that has just been mowed.
- Starting and stopping an activity too fast. Try to make sure your child warms up before being very active and cools down after.
Understand your child's asthma medicines and how they should be taken. These include:
-
Asthma control medicines that your child takes every day
Asthma control medicines
Control medicines for asthma are medicines you take to control your asthma symptoms. You must use these medicines every day for them to work well. ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Quick-relief asthma medicines when your child has symptoms
Quick-relief asthma medicines
Asthma quick-relief medicines work fast to control asthma symptoms. You take them when you are coughing, wheezing, having trouble breathing, or havi...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Keep Smoking Away From Your Child
No one should smoke in your house. This includes you, your visitors, your child's babysitters, and anyone else who comes to your house.
Smokers should smoke outside and wear a coat. The coat will keep smoke particles from sticking to clothes, so it should be left outside or away from the child.
Ask people who work at your child's day care, preschool, school, and anyone else who takes care of your child, if they smoke. If they do, make sure they smoke away from your child.
School and Asthma
Children with asthma may need a lot of support at school. They may need help from school staff to keep their asthma under control and to be able to do school activities.
Support at school
Children with asthma may need extra support at school. They may need help from school staff to keep their asthma under control and to be able to do ...
There should be an asthma action plan at school. The people who should have a copy of the plan is based on the school's policy, but may include:
- Your child's teacher
- The school nurse
- The school office
- Gym teachers and coaches
Your child should be able to take asthma medicines at school when needed.
School staff should know your child's asthma triggers. Your child should be able to go to another location to get away from asthma triggers, if needed.
When to Call the Doctor
Contact your child's provider if your child is having any of the following:
- Hard time breathing
- Chest muscles are pulling in with each breath
Pulling in
Intercostal retractions occur when the muscles between the ribs pull inward. The movement is most often a sign that the person has a breathing probl...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Breathing faster than 50 to 60 breaths per minute (when not crying)
- Making a grunting noise
- Sitting with shoulders hunched over
- Skin, nails, gums, lips, or area around the eyes is bluish or grayish
- Extremely tired
- Not moving around very much
- Limp or floppy body
- Nostrils are flaring out when breathing
Flaring out
Nasal flaring occurs when the nostrils widen while breathing. It is often a sign of trouble breathing.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Also contact your provider if your child:
- Loses their appetite
- Is irritable
- Has trouble sleeping
References
Jackson DJ, Lemanske RF, Bacharier LB. Management of asthma in infants and children. In: Burks AW, Holgate ST, O'Hehir RE, et al, eds. Middleton's Allergy: Principles and Practice. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 50.
Liu AH, Bacharier LB, Fitzpatrick Am, Sicherer SH. Childhood asthma. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 22nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 185.
National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute website. Asthma Management Guidelines: Focused Updates 2020. www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/asthma-management-guidelines-2020-updates. Updated February 4, 2021. Accessed April 10, 2024.
-
Asthma control drugs - illustration
Control drugs for asthma must be taken every day in order for them to work. You may need to take them more than once daily. Take them as prescribed by your health care provider.
Asthma control drugs
illustration
Review Date: 4/1/2024
Reviewed By: Charles I. Schwartz, MD, FAAP, Clinical Assistant Professor of Pediatrics, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, General Pediatrician at PennCare for Kids, Phoenixville, PA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.


