Atelectasis
Partial lung collapseAtelectasis is the collapse of part or, much less commonly, all of a lung.
Causes
Atelectasis is caused by a blockage of the air passages (bronchus or bronchioles) or by pressure on the outside of the lung. Atelectasis is not the same as another type of collapsed lung called pneumothorax, which occurs when air escapes from the lung. The air then fills the space outside of the lung, between the lung and chest wall. In atelectasis, there is usually fluid between the lung and the chest wall and the air sacs within the lung fill with fluid.
Pneumothorax
A collapsed lung occurs when air escapes from the lung. The air then can fill the space outside of the lung between the lung and chest wall. This b...

Common situations in people with atelectasis include:
- There is fluid or a tumor that compresses the lung.
- There is a blockage in the airway not allowing air into the air sacs of the lung.
- The air sacs collapse when the lung has a condition that decreases production of a protein, called surfactant that normally keeps the air sacs open.
Atelectasis is common after surgery or in people who are or were in the hospital.
Risk factors for developing atelectasis include:
- Anesthesia
- Use of a breathing tube
Breathing tube
Endotracheal intubation is a medical procedure in which a tube is placed into the windpipe (trachea) through the mouth or nose. In most emergency si...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Foreign object in the airway (most common in children)
-
Lung disease
Lung disease
Lung disease is any problem in the lungs that prevents the lungs from working properly. There are three main types of lung disease:Airway diseases -...
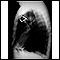 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Mucus that plugs the airway
- Pressure on the lung caused by a buildup of fluid between the ribs and the lungs (called a pleural effusion)
Pleural effusion
A pleural effusion is a buildup of fluid between the layers of tissue that line the lungs and chest cavity.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Prolonged bed rest with few changes in position
- Shallow breathing (may be caused by painful breathing or muscle weakness as in people who have had surgery)
-
Tumors that block an airway
Tumors
A tumor is an abnormal growth of body tissue. Tumors can be cancerous (malignant) or noncancerous (benign).
Read Article Now Book Mark Article
Symptoms
Symptoms may include any of the following:
-
Breathing difficulty
Breathing difficulty
Breathing difficulty may involve:Difficult breathing Uncomfortable breathingFeeling like you are not getting enough air
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Chest pain
Chest pain
Chest pain is discomfort or pain that you feel anywhere along the front of your body between your neck and upper abdomen.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Cough
Cough
Coughing is an important way to keep your throat and airways clear. But too much coughing may mean you have a disease or disorder. Some coughs are d...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
There are no symptoms if atelectasis is mild.
Exams and Tests
To confirm if you have atelectasis and determine its cause, the following tests will likely be done to view the lungs and airways:
- Physical exam by auscultating (listening) or percussing (tapping) the chest
-
Bronchoscopy
Bronchoscopy
Bronchoscopy is a test to view the airways and diagnose lung disease. It may also be used during the treatment of some lung conditions.
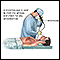 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Chest CT or MRI scan
Chest CT
A chest CT (computed tomography) scan is an imaging method that uses x-rays to create cross-sectional pictures of the chest and upper abdomen....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleMRI
A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan is an imaging test that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the body. It does not us...
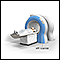 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Chest x-ray
Chest x-ray
A chest x-ray is an x-ray of the chest, lungs, heart, large arteries, ribs, and diaphragm.
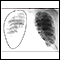 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Ultrasound of the chest
Ultrasound
Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to make images of organs and structures inside the body.
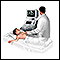 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
The goal of treatment is to treat the underlying cause and re-expand the collapsed lung tissue. If fluid is putting pressure on the lung, removing the fluid may allow the lung to expand.
Treatments include one or more of the following:
- Clap (percussion) on the chest to loosen mucus plugs in the airway.
Percussion
Percussion is a method of tapping body parts with fingers, hands, or small instruments as part of a physical examination. It is done to determine:Th...
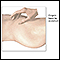 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Deep breathing exercises (with the help of incentive spirometry devices).
Incentive spirometry devices
Your health care provider may recommend that you use an incentive spirometer after surgery or when you have a lung illness, such as pneumonia. The s...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Remove or relieve any blockage in the airways by bronchoscopy.
Bronchoscopy
Bronchoscopy is a test to view the airways and diagnose lung disease. It may also be used during the treatment of some lung conditions.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Tilt the person so the head is lower than the chest (called postural drainage). This allows mucus to drain more easily.
- Treat a tumor or other condition.
- Turn the person to lie on the healthy side, allowing the collapsed area of lung to re-expand.
- Use inhaled medicines to open the airway.
- Use other devices that help increase positive pressure in the airways and clear fluids.
- Be physically active if possible
Outlook (Prognosis)
In an adult, atelectasis in a small area of the lung is usually not life threatening. The rest of the lung can make up for the collapsed area, bringing in enough oxygen for the body to function.
Large areas of atelectasis may be life threatening, often in a baby or small child, or in someone who has another lung disease or illness.
The collapsed lung usually reinflates slowly if the airway blockage has been removed. Scarring or damage may remain.
The outlook depends on the underlying disease. For example, people with extensive cancer often don't do well, while those with simple atelectasis after surgery have a very good outcome.
Possible Complications
Pneumonia may develop quickly after atelectasis in the affected part of the lung.
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is inflamed or swollen lung tissue due to infection with a germ. This article covers community-acquired pneumonia (CAP). This type of pneu...

When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your health care provider right away if you develop symptoms of atelectasis.
Prevention
To prevent atelectasis:
- Encourage movement and deep breathing in anyone who is bedridden for long periods.
- Keep small objects out of the reach of young children.
- Maintain deep breathing after anesthesia.
References
Frohlich M, Prentice B, Jaffé A. Air and fluid in the pleural space, and atelectasis. In: Bush A, Deterding R, Li AM, et al. Kendig and Wilmott's Disorders of the Respiratory Tract in Children. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 81.
O'Donnell AE. Bronchiectasis, atelectasis, and cavitary or cystic lung diseases. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 78.
Rozenfeld RA. Atelectasis. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 22nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 459.
-
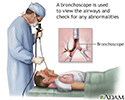
Bronchoscopy - illustration
Bronchoscopy is a surgical technique for viewing the interior of the airways. Using sophisticated flexible fiber optic instruments, surgeons are able to explore the trachea, main stem bronchi, and some of the small bronchi. In children, this procedure may be used to remove foreign objects that have been inhaled. In adults, the procedure is most often used to take samples of (biopsy) suspicious lesions and for culturing specific areas in the lung.
Bronchoscopy
illustration
-
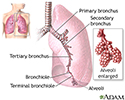
Lungs - illustration
The major features of the lungs include the bronchi, the bronchioles and the alveoli. The alveoli are the microscopic blood vessel-lined sacks in which oxygen and carbon dioxide gas are exchanged.
Lungs
illustration
-
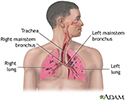
Respiratory system - illustration
Air is breathed in through the nasal passageways, travels through the trachea and bronchi to the lungs.
Respiratory system
illustration
-
Bronchoscopy - illustration
Bronchoscopy is a surgical technique for viewing the interior of the airways. Using sophisticated flexible fiber optic instruments, surgeons are able to explore the trachea, main stem bronchi, and some of the small bronchi. In children, this procedure may be used to remove foreign objects that have been inhaled. In adults, the procedure is most often used to take samples of (biopsy) suspicious lesions and for culturing specific areas in the lung.
Bronchoscopy
illustration
-
Lungs - illustration
The major features of the lungs include the bronchi, the bronchioles and the alveoli. The alveoli are the microscopic blood vessel-lined sacks in which oxygen and carbon dioxide gas are exchanged.
Lungs
illustration
-
Respiratory system - illustration
Air is breathed in through the nasal passageways, travels through the trachea and bronchi to the lungs.
Respiratory system
illustration
Review Date: 8/19/2024
Reviewed By: Allen J. Blaivas, DO, Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care, and Sleep Medicine, VA New Jersey Health Care System, Clinical Assistant Professor, Rutgers New Jersey Medical School, East Orange, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.