Sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis is a disease in which inflammation occurs in the lymph nodes, lungs, liver, eyes, skin, and other tissues.
Causes
The exact cause of sarcoidosis is unknown. What is known is that when a person has the disease, tiny clumps of abnormal tissue (granulomas) form in certain organs of the body. Granulomas are clusters of immune cells and are a type of inflammation.
The disease can affect almost any organ. It most commonly affects the lungs.
Health experts think that having certain genes makes it more likely for a person to develop sarcoidosis. Things that may trigger the disease include infections with bacteria or viruses. Contact with dust or chemicals may also be triggers.
The disease is more common in African Americans and White people of Scandinavian heritage. More women than men have the disease.
The disease often begins between ages 20 and 40. Sarcoidosis is rare in young children.
A person with a close blood relative who has sarcoidosis is nearly 5 times as likely to develop the condition.
Symptoms
There may be no symptoms. When symptoms do occur, they can involve almost any body part or organ system.
Almost all people affected by sarcoidosis have lung or chest symptoms:
-
Chest pain (most often behind the breast bone)
Chest pain
Chest pain is discomfort or pain that you feel anywhere along the front of your body between your neck and upper abdomen.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Dry cough
Cough
Coughing is an important way to keep your throat and airways clear. But too much coughing may mean you have a disease or disorder. Some coughs are d...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Shortness of breath
Shortness of breath
Breathing difficulty may involve:Difficult breathing Uncomfortable breathingFeeling like you are not getting enough air
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Coughing up blood (rare, but serious)
Coughing up blood
Coughing up blood is the spitting up of blood or bloody mucus from the lungs and throat (respiratory tract). Hemoptysis is the medical term for cough...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Symptoms of general discomfort may include:
-
Fatigue
Fatigue
Fatigue is a feeling of weariness, tiredness, or lack of energy.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Fever
Fever
Fever is the temporary increase in the body's temperature in response to a disease or illness. A child has a fever when the temperature is at or abov...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Joint ache or pain (arthralgia)
-
Weight loss
Weight loss
Unexplained weight loss is a decrease in body weight, when you did not try to lose the weight on your own. Many people gain and lose weight. Uninten...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article
Skin symptoms may include:
-
Hair loss
Hair loss
Partial or complete loss of hair is called alopecia.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Raised, red, firm skin sores (erythema nodosum), almost always on the front part of the lower legs
Erythema nodosum
Erythema nodosum is an inflammatory disorder. It involves tender, red bumps (nodules) under the skin.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Rash
Rash
Rashes involve changes in the color, feeling or texture of your skin.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Scars that become raised or inflamed
Nervous system symptoms may include:
-
Headache
Headache
A headache is pain or discomfort in the head, scalp, or neck. Serious causes of headaches are rare. Most people with headaches can feel much better...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Seizures
Seizures
A seizure is the physical changes in behavior that occurs during an episode of specific types of abnormal electrical activity in the brain. The term ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Weakness on one side of the face
Eye symptoms may include:
-
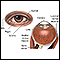
Burning, itching, discharge from the eye
Burning, itching, discharge from the ey
Eye burning with discharge is burning, itching, or drainage from the eye of any substance other than tears.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
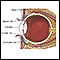
Dry eyes
Dry eyes
You need tears to moisten your eyes and to wash away particles that have gotten into your eyes. A healthy tear film on the eye is necessary for good...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
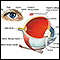
Pain
Pain
Pain in the eye may be described as a burning, throbbing, aching, or stabbing sensation in or around the eye. It may also feel like you have a forei...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Vision loss
Other symptoms of this disease may include:
-
Dry mouth
Dry mouth
Dry mouth occurs when you don't make enough saliva. This causes your mouth to feel dry and uncomfortable. Dry mouth that is ongoing may be a sign o...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Fainting spells, if the heart is involved
Fainting spells
Fainting is a brief loss of consciousness due to a drop in blood flow to the brain. The episode most often lasts less than a couple of minutes and y...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Nosebleed
Nosebleed
A nosebleed is loss of blood from the tissue lining the nose. Bleeding most often occurs from one nostril only.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Swelling in the upper part of the abdomen
-
Liver disease
Liver disease
The term "liver disease" applies to many conditions that stop the liver from working or prevent it from functioning well. Abdominal pain or swelling...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Swelling of the legs if heart and lungs are involved
- Abnormal heart rhythm if the heart is involved
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will perform a physical exam and ask about the symptoms.
Different imaging tests may help diagnose sarcoidosis:
-
Chest x-ray to see if the lungs are involved or lymph nodes are enlarged
Chest x-ray
A chest x-ray is an x-ray of the chest, lungs, heart, large arteries, ribs, and diaphragm.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
CT scan of the chest
CT scan
A chest CT (computed tomography) scan is an imaging method that uses x-rays to create cross-sectional pictures of the chest and upper abdomen....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Lung gallium scan (rarely done now)
Lung gallium scan
Lung gallium scan is a type of nuclear scan that uses radioactive gallium to identify inflammation in the lungs.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Imaging tests of the brain and liver
Brain
A head MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is an imaging test that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the brain and surrounding...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleLiver
Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to make images of organs and structures inside the body.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - PET scan of the whole body (or specific body parts)
-
Echocardiogram or MRI of the heart
Echocardiogram
An echocardiogram is a test that uses sound waves to create pictures of the heart. The picture and information it produces is more detailed than a s...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleMRI
Heart magnetic resonance imaging is an imaging method that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the heart. It does not use ra...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
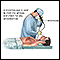
To diagnose this condition, a biopsy is often needed. A biopsy of the lung using bronchoscopy sometimes with an ultrasound to enable a biopsy of a lymph node in or near the lung is done. Biopsies of other body tissues may also be done.
Biopsy
A biopsy is the removal of a small piece of tissue for lab examination.
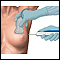
Bronchoscopy
Bronchoscopy is a test to view the airways and diagnose lung disease. It may also be used during the treatment of some lung conditions.
The following lab tests may be done:
- Calcium levels (urine,
blood)
Urine
This test measures the amount of calcium in the urine. All cells need calcium in order to work. Calcium helps build strong bones and teeth. It is ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleBlood
The calcium blood test measures the level of calcium in the blood. This article discusses the test to measure the total amount of calcium in your blo...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
CBC
CBC
A complete blood count (CBC) test measures the following:The number of white blood cells (WBC count)The number of red blood cells (RBC count)The numb...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Immunoelectrophoresis
Immunoelectrophoresis
Serum immunoelectrophoresis is a lab test that measures proteins called immunoglobulins in the blood. Immunoglobulins are proteins that function as ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
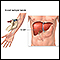
Liver function tests
Liver function tests
Liver function tests are common tests that are used to see how well the liver is working. Tests include:AlbuminAlpha-1 antitrypsinAlkaline phosphata...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Quantitative immunoglobulins
Quantitative immunoglobulins
Quantitative nephelometry is a lab test to quickly and accurately measure levels of certain proteins called immunoglobulins in the blood. Immunoglob...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Phosphorus (blood)
Phosphorus
The phosphorus blood test measures the amount of phosphate in the blood.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE)
Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE)
The ACE test measures the level of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) in the blood.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
Sarcoidosis symptoms will often get better without treatment, especially if there are only small lung abnormalities.
If the eyes, heart, nervous system, or lungs are affected, corticosteroids are usually prescribed. This medicine may need to be taken for 1 to 2 years.
Medicines that suppress the immune system are sometimes also needed.
In rare cases, people with very severe heart or lung damage (end-stage disease) may need an organ transplant.
With sarcoidosis that affects the heart, an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) may be needed to treat heart rhythm problems.
ICD
An implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) is a device that detects a life-threatening, rapid heartbeat. This abnormal heartbeat is called an a...
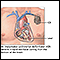
Outlook (Prognosis)
Many people with sarcoidosis are not seriously ill, and get better without treatment. Up to half of all people with the disease get better in 3 years without treatment. People whose lungs are affected may develop lung damage.
Overall the death rate from sarcoidosis is less than 5%. Causes of death include:
- Bleeding from the lung tissue
- Heart damage, leading to heart failure and abnormal heart rhythms
- Lung scarring (pulmonary fibrosis)
Possible Complications
Sarcoidosis may lead to these health problems:
- Fungal lung infections (aspergillosis)
Aspergillosis
Aspergillosis is an infection or allergic response due to the aspergillus fungus.
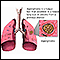 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Glaucoma and blindness from uveitis (rare)
Glaucoma
Glaucoma is a group of eye conditions that can damage the optic nerve. This nerve sends the images you see to your brain. Most often, optic nerve da...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleUveitis
Uveitis is swelling and inflammation of the uvea. The uvea is the middle layer of the wall of the eye. The uvea supplies blood for the iris at the ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Kidney stones from high calcium levels in the urine
Kidney stones
A kidney stone is a solid mass made up of tiny crystals. One or more stones can be in the kidney or ureter at the same time.
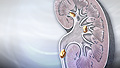 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Osteoporosis and other complications of taking corticosteroids for long periods of time
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a disease in which bones become fragile and more likely to break (fracture).
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
High blood pressure in the arteries of the lungs (pulmonary hypertension)
Pulmonary hypertension
Pulmonary hypertension is high blood pressure in the pulmonary arteries of the lungs. It makes the right side of the heart work harder than normal....
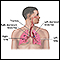 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider promptly if you have:
-
Difficulty breathing
Difficulty breathing
Breathing difficulty may involve:Difficult breathing Uncomfortable breathingFeeling like you are not getting enough air
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Irregular heartbeat
Irregular heartbeat
Palpitations are feelings or sensations that your heart is pounding or racing. They can be felt in your chest, throat, or neck. You may:Have an unpl...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Vision changes
- Other symptoms of this disorder
References
Crouser ED, Maier LA, Wilson KC, et al. Diagnosis and detection of sarcoidosis. an official American Thoracic Society clinical practice guideline. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020;201(8):e26-e51. PMID: 32293205 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32293205/.
Iannuzzi MC. Sarcoidosis. Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 83.
Judson MA, Koth LL, Baughman RP. Sarcoidosis. In: Broaddus VC, Ernst JD, King TE, et al, eds. Murray & Nadel's Textbook of Respiratory Medicine. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 93.
-
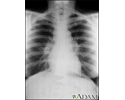
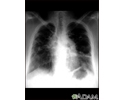
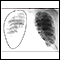
Sarcoid, stage I - chest X-ray - illustration
Sarcoid is primarily a lung (pulmonary) disease. In the early stages, a chest film may show enlargement of lymph nodes in the center of the chest near the heart (mediastinum).
Sarcoid, stage I - chest X-ray
illustration
-
Sarcoid, stage II - chest X-ray - illustration
Sarcoid causes damage to the lung tissue that heals by scarring. The film shows a diffuse milky and granular appearance in the normally dark lung areas. This individual has marked decrease in lung function.
Sarcoid, stage II - chest X-ray
illustration
-
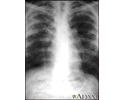
Sarcoid, stage IV - chest x-ray - illustration
This film shows advanced sarcoid, scarring of the lungs (the light streaking), and cavity formation (the dark areas in the upper right side of the picture).
Sarcoid, stage IV - chest x-ray
illustration
-
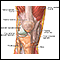
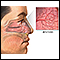
Sarcoid - close-up of the skin lesions - illustration
Sarcoid - close-up of the skin lesions. 20 to 25 percent of individuals with sarcoidosis have skin manifestations as seen in this picture. The extent of the skin manifestations is difficult to predict, but the most common are red papules that are translucent as seen here.
Sarcoid - close-up of the skin lesions
illustration
-
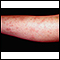
Erythema nodosum associated with sarcoidosis - illustration
This picture shows reddish-purple, hard (indurated), painful nodules (erythema nodosum) that occur most commonly on the shins. These lesions may be anywhere on the body and may be associated with tuberculosis (TB), sarcoidosis, coccidioidomycosis, systemic lupus erythematosis (SLE), fungal infections, or in response to medications.
Erythema nodosum associated with sarcoidosis
illustration
-
Sarcoidosis - close-up - illustration
Typical sarcoid lesions consist of red, raised lesions (papules) and patches (plaques) with minimal surrounding skin change.
Sarcoidosis - close-up
illustration
-
Sarcoidosis on the elbow - illustration
These lesions of sarcoidosis are located on the elbow and are red, elevated patches (plaques). The cause of sarcoidosis remains unknown.
Sarcoidosis on the elbow
illustration
-
Sarcoidosis on the nose and forehead - illustration
These are sarcoid lesions on the face. These lesions often appear in scars, as is seen in this photograph.
Sarcoidosis on the nose and forehead
illustration
-
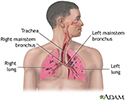
Respiratory system - illustration
Air is breathed in through the nasal passageways, travels through the trachea and bronchi to the lungs.
Respiratory system
illustration
-
Sarcoid, stage I - chest X-ray - illustration
Sarcoid is primarily a lung (pulmonary) disease. In the early stages, a chest film may show enlargement of lymph nodes in the center of the chest near the heart (mediastinum).
Sarcoid, stage I - chest X-ray
illustration
-
Sarcoid, stage II - chest X-ray - illustration
Sarcoid causes damage to the lung tissue that heals by scarring. The film shows a diffuse milky and granular appearance in the normally dark lung areas. This individual has marked decrease in lung function.
Sarcoid, stage II - chest X-ray
illustration
-
Sarcoid, stage IV - chest x-ray - illustration
This film shows advanced sarcoid, scarring of the lungs (the light streaking), and cavity formation (the dark areas in the upper right side of the picture).
Sarcoid, stage IV - chest x-ray
illustration
-
Sarcoid - close-up of the skin lesions - illustration
Sarcoid - close-up of the skin lesions. 20 to 25 percent of individuals with sarcoidosis have skin manifestations as seen in this picture. The extent of the skin manifestations is difficult to predict, but the most common are red papules that are translucent as seen here.
Sarcoid - close-up of the skin lesions
illustration
-
Erythema nodosum associated with sarcoidosis - illustration
This picture shows reddish-purple, hard (indurated), painful nodules (erythema nodosum) that occur most commonly on the shins. These lesions may be anywhere on the body and may be associated with tuberculosis (TB), sarcoidosis, coccidioidomycosis, systemic lupus erythematosis (SLE), fungal infections, or in response to medications.
Erythema nodosum associated with sarcoidosis
illustration
-
Sarcoidosis - close-up - illustration
Typical sarcoid lesions consist of red, raised lesions (papules) and patches (plaques) with minimal surrounding skin change.
Sarcoidosis - close-up
illustration
-
Sarcoidosis on the elbow - illustration
These lesions of sarcoidosis are located on the elbow and are red, elevated patches (plaques). The cause of sarcoidosis remains unknown.
Sarcoidosis on the elbow
illustration
-
Sarcoidosis on the nose and forehead - illustration
These are sarcoid lesions on the face. These lesions often appear in scars, as is seen in this photograph.
Sarcoidosis on the nose and forehead
illustration
-
Respiratory system - illustration
Air is breathed in through the nasal passageways, travels through the trachea and bronchi to the lungs.
Respiratory system
illustration
Review Date: 4/10/2025
Reviewed By: Allen J. Blaivas, DO, Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care, and Sleep Medicine, VA New Jersey Health Care System, Clinical Assistant Professor, Rutgers New Jersey Medical School, East Orange, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.