Multimedia Gallery
Pregnancy care
It's always important to take good care of your health, but never more so than when you're pregnant. You're not only caring for your own body, you're also nurturing and growing a new human being. Let's talk about pregnancy care.
During the nine or so months of your pregnancy, you'll see a lot of your ob/gyn. In fact, you should visit your doctor once a month during the first seven months of your pregnancy. Then you should see your doctor once every 2 or 3 weeks until your ninth month, and finally every week until you deliver. You might also see your regular doctor, a nurse midwife, or, if you have any complications, a perinatologist who specializes in high-risk pregnancies.
That might sound like a lot of visits, but the goal is to keep a close eye on both you and your growing baby. Your doctor will check your baby's heart rate, and measure how quickly you're gaining weight. You'll likely have at least one ultrasound, where you can actually get to see your baby and find out the gender, unless you want it to be a surprise. Throughout your pregnancy, your doctor will monitor you for any health problems, such as high blood pressure or diabetes.
At your regular prenatal visits, your doctor can give you advice about what to eat and how much to exercise. You can also ask about all those weird symptoms you've been having, like morning sickness, food cravings, and the constant urge to use the bathroom.
There are a few things you need to do while you're pregnant to make sure you and your baby are healthy. First, you have to take 400 micrograms of folic acid every day. Folic acid is especially important right before you get pregnant, and during the first trimester of your pregnancy because it helps your baby's brain and spinal cord form. Taking folic acid can help prevent birth defects like spina bifida.
One thing you need to avoid is alcohol. When you're craving a glass of wine or beer, have some sparkling water, grape juice, or ginger ale instead. Alcohol can be very dangerous for your baby. Also don't take any medicines without talking to your doctor first. That includes over-the-counter medicines like aspirin and cold relievers. Caffeine is okay, but only in moderation. Limit yourself to one cup of coffee, instead of your regular two or three. Don't smoke and stay away from anyone who is smoking. Cigarette smoke deprives your baby of oxygen. It can stunt your child's growth, and lead to birth defects such as a cleft lip or palate.
If you're pregnant and you haven't seen a doctor yet, now is the time to call. The sooner you get prenatal care, the more likely that your baby will be born healthy. Let your doctor know if you have a condition like diabetes, seizures, or high blood pressure, or if you've been exposed to a sexually transmitted infection, chemicals, or radiation.
Get medical help right away during your pregnancy if you have a fever, painful urination, vaginal bleeding, or severe stomach pain. Call if your water breaks, or you're not feeling your baby moving and it's near the end of your pregnancy.
Pregnancy care
Review Date: 2/3/2025
Reviewed By: Peter J. Chen, MD, FACOG, Associate Professor of OBGYN at Cooper Medical School at Rowan University, Camden, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Animations
- Breast engorgement
- Cell division
- Cesarean section
- Conception - general
- Conception - pregnancy
- Conception of identical twins
- C-section
- Early labor
- Egg cell production
- Egg production
- Endometriosis
- Fetal ear development
- Formation of twins
- Human face formation
- Infant formulas
- Kids - How big is the baby?
- Kids - How does the baby co...
- Kids - Is it a girl or boy?
- Kids - Umbilical cord
- Kids - Where do babies come...
- Newborn jaundice
- NICU consultants and suppor...
- Ovulation
- Placenta delivery
- Placenta formation
- Preeclampsia
- Pregnancy
- Pregnancy care
- Sperm production
- Sperm release pathway
- Storing breast milk
- The role of amniotic fluid
- Twin-to-twin transfusion sy...
- Ultrasound
- Vaginal delivery
Illustrations
- 24-week fetus
- Abnormal discharge from the...
- Abnormal menstrual periods
- Absence of menstruation (am...
- Amniocentesis
- Amniocentesis
- Amniotic fluid
- Amniotic fluid
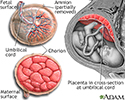
- Anatomy of a normal placenta
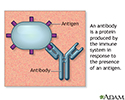
- Antibodies
- Baby burping position
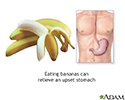
- Bananas and nausea
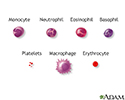
- Blood cells
- Blood test
- Breast infection
- Breastfeeding
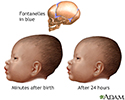
- Bulging fontanelles
- Candida - fluorescent stain
- Caput succedaneum
- Cesarean section
- Cesarean section
- Cesarean section
- Childbirth
- Chorionic villus sampling
- Congenital hip dislocation
- Congenital toxoplasmosis
- Crying - excessive (0 to 6 ...
- Delivery presentations
- Developmental milestones
- Early weeks of pregnancy
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Emergency Childbirth
- Emergency Childbirth
- Endocrine glands
- Endometriosis
- Endometritis
- Erythroblastosis fetalis - ...
- Female breast
- Female reproductive anatomy
- Female reproductive anatomy
- Female reproductive anatomy...
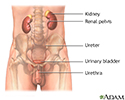
- Female urinary tract
- Fetal blood testing
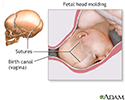
- Fetal head molding
- Fetus at 10 weeks
- Fetus at 12 weeks
- Fetus at 16 weeks
- Fetus at 26 to 30 weeks
- Fetus at 3.5 weeks
- Fetus at 30 to 32 weeks
- Fetus at 7.5 weeks
- Fetus at 8.5 weeks
- First trimester of pregnancy
- Folic acid
- Folic acid benefits
- Folic acid source
- Follicle development
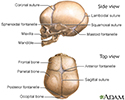
- Fontanelles
- Foreskin
- Gestational ages
- Gestational diabetes
- Gonadotropins
- Head circumference
- Heat rash
- Height/weight chart
- Hormonal effects in newborns
- Humidifiers and health
- Hysterectomy
- Infant blood sample
- Infant care following delivery
- Infant diaphragmatic hernia
- Infant heat rash
- Infant intestines
- Infant jaundice
- Infantile reflexes
- Influenza vaccines
- Intraductal papilloma
- Intrauterine transfusion
- Jaundiced infant
- Large fontanelles
- Large fontanelles (lateral view)
- Macrosomia
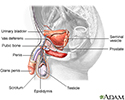
- Male reproductive anatomy
- Male reproductive anatomy
- Male urinary tract
- Mammary gland
- Meconium
- Morning sickness
- Moro reflex
- Newborn head molding
- Newborn test
- Normal female breast anatomy
- Normal uterine anatomy (cut...
- Ovarian cyst
- Ovarian hypofunction
- Overproductive ovaries
- Pelvic adhesions
- Pelvic laparoscopy
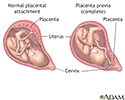
- Placenta
- Placenta
- Placenta
- Placenta previa
- Polyhydramnios
- Preeclampsia
- Pregnancy test
- Primary amenorrhea
- Primary infertility
- Secondary amenorrhea
- Secondary infection
- Side sectional view of fema...
- Single palmar crease
- Skull of a newborn
- Slit-lamp exam
- Sperm
- Stein-Leventhal syndrome
- Sunken fontanelles (superio...
- Tobacco health risks
- Transvaginal ultrasound
- Ultrasound in pregnancy
- Ultrasound, color - normal ...
- Ultrasound, normal fetus - ...
- Ultrasound, normal fetus - ...
- Ultrasound, normal fetus - ...
- Ultrasound, normal fetus - face
- Ultrasound, normal fetus - ...
- Ultrasound, normal fetus - foot
- Ultrasound, normal fetus - ...
- Ultrasound, normal fetus - ...
- Ultrasound, normal fetus - ...
- Ultrasound, normal fetus - ...
- Ultrasound, normal placenta...
- Ultrasound, normal relaxed ...
- Umbilical cord healing
- Uterus
- Vaginal bleeding during pre...
- Well baby visits
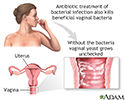
- Yeast infections

 Bookmark
Bookmark