Multimedia Gallery
Sperm production
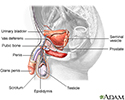
Sperm are produced, stored, and delivered by the male reproductive system. Here, you can see the parts of the male reproductive system -- the testes, urethra, vas deferens, prostate, seminal vesicle, and penis.
The testes contain coiled structures called seminiferous tubules, which are the sites of sperm production. A woman’s ovaries need only produce one egg per month, but a man’s seminiferous tubules produce over 12 billion sperm per month.
The structure on top of the seminiferous tubules is the epididymis. The immature sperm migrate there to mature, and then are stored there afterwards. This trip usually takes about 20 days.
Before intercourse, the penis fills with blood and becomes erect. Then, with sufficient stimulation, an ejaculatory process begins.
Here you can see the mature sperm traveling from the epididymis through the vas deferens, which is a narrow, muscular tube about 18 inches long. Its smooth muscle contractions propel the sperm forward. They arrive first at the ampulla, the widest part of the vas deferens, and then pass into the ejaculatory ducts. Here, a liquid secretion from the seminal vesicles mixes with the sperm. Seminal fluid contains fructose sugar, which the sperm use as fuel. It also has alkalines, which help to counteract the naturally acidic environment of the vagina and uterus so the sperm have a better chance for survival.
From there, the liquid mixture is propelled forward through the ejaculatory ducts toward the urethra, passing first through the prostate gland, where milky prostatic fluid is added, forming the substance we call semen. The prostatic fluid helps the sperm swim faster, which is important for getting to the egg cell.
Finally, about a teaspoon of semen is ejected out, or ejaculated, through the far end of the urethra at the end of the penis. From the time the sperm leave the man’s body, they have between 12 and 48 hours to find and fertilize the egg cell, assuming an egg is available. Most of the sperm won't make it. Of the 300 million sperm ejaculated, only about 200 or so will survive to reach the egg cell and only one of those will succeed in fertilizing it.
Sperm production
Review Date: 3/31/2024
Reviewed By: Sovrin M. Shah, MD, Associate Professor, Department of Urology, The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Animations
- Breast engorgement
- Cell division
- Cesarean section
- Conception - general
- Conception - pregnancy
- Conception of identical twins
- C-section
- Early labor
- Egg cell production
- Egg production
- Endometriosis
- Fetal ear development
- Formation of twins
- Human face formation
- Infant formulas
- Kids - How big is the baby?
- Kids - How does the baby co...
- Kids - Is it a girl or boy?
- Kids - Umbilical cord
- Kids - Where do babies come...
- Newborn jaundice
- NICU consultants and suppor...
- Ovulation
- Placenta delivery
- Placenta formation
- Preeclampsia
- Pregnancy
- Pregnancy care
- Sperm production
- Sperm release pathway
- Storing breast milk
- The role of amniotic fluid
- Twin-to-twin transfusion sy...
- Ultrasound
- Vaginal delivery
Illustrations
- 24-week fetus
- Abnormal discharge from the...
- Abnormal menstrual periods
- Absence of menstruation (am...
- Amniocentesis
- Amniocentesis
- Amniotic fluid
- Amniotic fluid
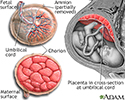
- Anatomy of a normal placenta
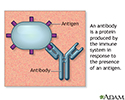
- Antibodies
- Baby burping position
- Bananas and nausea
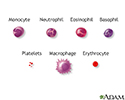
- Blood cells
- Blood test
- Breast infection
- Breastfeeding
- Bulging fontanelles
- Candida - fluorescent stain
- Caput succedaneum
- Cesarean section
- Cesarean section
- Cesarean section
- Childbirth
- Chorionic villus sampling
- Congenital hip dislocation
- Congenital toxoplasmosis
- Crying - excessive (0 to 6 ...
- Delivery presentations
- Developmental milestones
- Early weeks of pregnancy
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Emergency Childbirth
- Emergency Childbirth
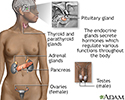
- Endocrine glands
- Endometriosis
- Endometritis
- Erythroblastosis fetalis - ...
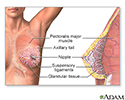
- Female breast
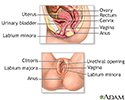
- Female reproductive anatomy
- Female reproductive anatomy
- Female reproductive anatomy...
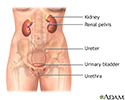
- Female urinary tract
- Fetal blood testing
- Fetal head molding
- Fetus at 10 weeks
- Fetus at 12 weeks
- Fetus at 16 weeks
- Fetus at 26 to 30 weeks
- Fetus at 3.5 weeks
- Fetus at 30 to 32 weeks
- Fetus at 7.5 weeks
- Fetus at 8.5 weeks
- First trimester of pregnancy
- Folic acid
- Folic acid benefits
- Folic acid source
- Follicle development
- Fontanelles
- Foreskin
- Gestational ages
- Gestational diabetes
- Gonadotropins
- Head circumference
- Heat rash
- Height/weight chart
- Hormonal effects in newborns
- Humidifiers and health
- Hysterectomy
- Infant blood sample
- Infant care following delivery
- Infant diaphragmatic hernia
- Infant heat rash
- Infant intestines
- Infant jaundice
- Infantile reflexes
- Influenza vaccines
- Intraductal papilloma
- Intrauterine transfusion
- Jaundiced infant
- Large fontanelles
- Large fontanelles (lateral view)
- Macrosomia
- Male reproductive anatomy
- Male reproductive anatomy
- Male urinary tract
- Mammary gland
- Meconium
- Morning sickness
- Moro reflex
- Newborn head molding
- Newborn test
- Normal female breast anatomy
- Normal uterine anatomy (cut...
- Ovarian cyst
- Ovarian hypofunction
- Overproductive ovaries
- Pelvic adhesions
- Pelvic laparoscopy
- Placenta
- Placenta
- Placenta
- Placenta previa
- Polyhydramnios
- Preeclampsia
- Pregnancy test
- Primary amenorrhea
- Primary infertility
- Secondary amenorrhea
- Secondary infection
- Side sectional view of fema...
- Single palmar crease
- Skull of a newborn
- Slit-lamp exam
- Sperm
- Stein-Leventhal syndrome
- Sunken fontanelles (superio...
- Tobacco health risks
- Transvaginal ultrasound
- Ultrasound in pregnancy
- Ultrasound, color - normal ...
- Ultrasound, normal fetus - ...
- Ultrasound, normal fetus - ...
- Ultrasound, normal fetus - ...
- Ultrasound, normal fetus - face
- Ultrasound, normal fetus - ...
- Ultrasound, normal fetus - foot
- Ultrasound, normal fetus - ...
- Ultrasound, normal fetus - ...
- Ultrasound, normal fetus - ...
- Ultrasound, normal fetus - ...
- Ultrasound, normal placenta...
- Ultrasound, normal relaxed ...
- Umbilical cord healing
- Uterus
- Vaginal bleeding during pre...
- Well baby visits
- Yeast infections

 Bookmark
Bookmark