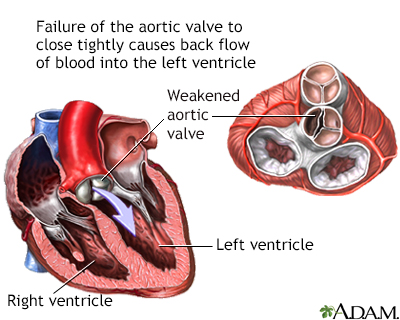
Aortic regurgitation
Aortic valve prolapse; Aortic insufficiency; Heart valve - aortic regurgitation; Valvular disease - aortic regurgitation; AI - aortic insufficiencyAortic regurgitation is a heart valve disease in which the aortic valve does not close tightly. This allows blood to flow from the aorta (the largest blood vessel) into the left ventricle (a chamber of the heart).
Causes
Any condition that prevents the aortic valve from closing completely can cause this problem. When the valve does not close all the way, some blood comes back each time the heart beats.
When a large amount of blood comes back, the heart must work harder to force out enough blood to meet the body's needs. The left lower chamber (left ventricle) of the heart widens (dilates) and the heart beats very strongly (bounding pulse). Over time, the heart becomes less able to supply enough blood to the body.
Bounding pulse
A bounding pulse is a strong throbbing felt over one of the arteries in the body. It is due to a forceful heartbeat.

In the past, rheumatic fever was the main cause of aortic regurgitation. The use of antibiotics to treat strep infections has made rheumatic fever less common. Therefore, aortic regurgitation is more commonly due to other causes. These include:
Rheumatic fever
Rheumatic fever is a disease that may develop after an infection with group A streptococcus bacteria (such as strep throat or scarlet fever). It can...
-
Ankylosing spondylitis
Ankylosing spondylitis
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a chronic form of arthritis. It mostly affects the bones and joints at the base of the spine where it connects with t...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Aortic dissection
Aortic dissection
Aortic dissection is a serious condition in which there is a tear in the wall of the major artery carrying blood out of the heart (aorta). As the te...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Congenital (present at birth) valve problems, such as bicuspid valve
-
Endocarditis (infection of the heart valves)
Endocarditis
Endocarditis is inflammation of the inside lining of the heart chambers and heart valves (endocardium). It is most often caused by a bacterial or, r...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - High blood pressure
-
Marfan syndrome
Marfan syndrome
Marfan syndrome is a disorder of connective tissue. This is the tissue that strengthens the body's structures. Disorders of connective tissue affect...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Reiter syndrome (also known as reactive arthritis)
Reiter syndrome
Reactive arthritis is a type of arthritis that follows an infection. It may also cause inflammation of the eyes, skin and urinary and genital system...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Syphilis
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
- Trauma to the chest
Aortic insufficiency is most common in men between the ages of 30 and 60.
Symptoms
The condition often has no symptoms for many years. Symptoms may come on slowly or suddenly. They may include:
-
Bounding pulse
Bounding pulse
A bounding pulse is a strong throbbing felt over one of the arteries in the body. It is due to a forceful heartbeat.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Chest pain similar to angina (rare)
Chest pain
Chest pain is discomfort or pain that you feel anywhere along the front of your body between your neck and upper abdomen.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleAngina
Angina is a type of chest discomfort or pain due to poor blood flow through the blood vessels (coronary arteries) of the heart muscle (myocardium). ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Fainting
Fainting
Fainting is a brief loss of consciousness due to a drop in blood flow to the brain. The episode most often lasts less than a couple of minutes and y...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Fatigue
Fatigue
Fatigue is a feeling of weariness, tiredness, or lack of energy.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
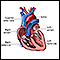
Palpitations (sensation of the heart beating)
Palpitations
Palpitations are feelings or sensations that your heart is pounding or racing. They can be felt in your chest, throat, or neck. You may:Have an unpl...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Shortness of breath with activity or when lying down
Shortness of breath
Breathing difficulty may involve:Difficult breathing Uncomfortable breathingFeeling like you are not getting enough air
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Waking up short of breath after falling asleep
- Swelling of the feet, legs, or abdomen
- Uneven, rapid, racing, pounding, or fluttering pulse
- Weakness that is more likely to occur with activity
Exams and Tests
Signs may include:
- Heart murmur that can be heard through a stethoscope
- Very forceful beating of the heart
- Bobbing of the head in time with the heartbeat
- Hard pulses in the arms and legs
- Low diastolic blood pressure
- Signs of fluid in the lungs
Aortic regurgitation may be seen on tests such as:
-
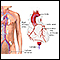
Aortic angiography
Aortic angiography
Aortic angiography is a procedure that uses a special dye and x-rays to see how blood flows through the aorta. The aorta is the large artery that ca...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Echocardiogram -- ultrasound examination of the heart
Echocardiogram
An echocardiogram is a test that uses sound waves to create pictures of the heart. The picture and information it produces is more detailed than a s...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Left heart catheterization
Left heart catheterization
Left heart catheterization is the passage of a thin flexible tube (catheter) into the left side of the heart. It is done to diagnose or treat certai...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
MRI or CT scan of the heart
MRI or CT scan of the heart
Heart magnetic resonance imaging is an imaging method that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the heart. It does not use ra...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Transthoracic echocardiogram (TTE) or transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE)
A chest x-ray may show swelling of the left lower heart chamber.
Chest x-ray
A chest x-ray is an x-ray of the chest, lungs, heart, large arteries, ribs, and diaphragm.

Lab tests cannot diagnose aortic insufficiency. However, they may help check for other causes of symptoms.
Treatment
You may not need treatment if you have no symptoms or only mild symptoms. However, you will need to see a health care provider for regular exams and echocardiograms.
Diuretics (water pills) or other types of medicines may be prescribed for symptoms of heart failure.
In the past, most people with heart valve problems were given antibiotics before dental work or an invasive procedure, such as colonoscopy. The antibiotics were given to prevent an infection of the damaged heart. However, antibiotics are now used much less often.
You may need to limit activity that requires more work from your heart. Talk to your provider.
Surgery to repair or replace the aortic valve corrects aortic regurgitation. The decision to have aortic valve replacement depends on your symptoms and the condition and function of your heart. There is increasing interest in a minimally invasive procedure in which a replacement valve is implanted via catheter. This is similar to a procedure traditionally done in people with aortic stenosis. This option may become more common in the future.
You may also need surgery to repair the aorta if it is enlarged.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Surgery can cure aortic insufficiency and relieve symptoms, unless you develop heart failure or other complications. People with angina or congestive heart failure due to aortic regurgitation do poorly without treatment.
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
- Abnormal heart rhythms
- Heart failure
-
Infection in the heart
Infection in the heart
Endocarditis is inflammation of the inside lining of the heart chambers and heart valves (endocardium). It is most often caused by a bacterial or, r...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if:
- You have symptoms of aortic regurgitation.
- You have aortic insufficiency and your symptoms worsen or new symptoms develop (especially chest pain, difficulty breathing, or swelling).
Difficulty breathing
Breathing difficulty may involve:Difficult breathing Uncomfortable breathingFeeling like you are not getting enough air
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleSwelling
Swelling is the enlargement of organs, skin, or other body parts. It is caused by a buildup of fluid in the tissues. The extra fluid can lead to a ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Prevention
Blood pressure control is very important if you are at risk for aortic regurgitation.
References
Bonow RO, Nishimura RA. Aortic Regurgitation. In: Libby P, Bonow RO, Mann DL, Tomaselli GF, Bhatt DL, Solomon SD, eds. Braunwald's Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 73.
Carabello BA, Kodali S. Valvular heart disease. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 60.
Leon MB, Mack MJ. Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement. In: Libby P, Bonow RO, Mann DL, Tomaselli GF, Bhatt DL, Solomon SD, eds. Braunwald's Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 74.
Writing Committee Members, Otto CM, Nishimura RA, Bonow RO, et al. 2020 ACC/AHA guideline for the management of patients with valvular heart disease: A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2021;162(2):e183-e353. PMID: 33972115 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33972115/.
-
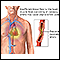
Aortic insufficiency - illustration
Aortic insufficiency is a heart valve disease where the aortic valve no longer functions adequately to control the flow of blood from the left ventricle into the aorta. Commonly, aortic insufficiency shows no symptoms for many years. Symptoms may then occur gradually or suddenly. Surgical repair or replacement of the aortic valve corrects aortic insufficiency.
Aortic insufficiency
illustration
-
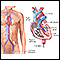
Aortic insufficiency - illustration
Aortic insufficiency is a heart valve disease where the aortic valve no longer functions adequately to control the flow of blood from the left ventricle into the aorta. Commonly, aortic insufficiency shows no symptoms for many years. Symptoms may then occur gradually or suddenly. Surgical repair or replacement of the aortic valve corrects aortic insufficiency.
Aortic insufficiency
illustration
Review Date: 2/27/2024
Reviewed By: Thomas S. Metkus, MD, Assistant Professor of Medicine and Surgery, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.