Restrictive cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy - restrictive; Infiltrative cardiomyopathy; Idiopathic myocardial fibrosisRestrictive cardiomyopathy refers to a set of changes in how the heart muscle functions. These changes cause the heart to fill poorly (more common) or squeeze poorly (less common). Sometimes, both problems are present.
Causes
In a case of restrictive cardiomyopathy, the heart muscle is of normal size or slightly enlarged. Most of the time, it also pumps normally. However, it does not relax normally during the time between heartbeats when the blood returns from the body (diastole).
Although the main problem is abnormal filling of the heart, the heart may not pump blood strongly when the disease progresses. The abnormal heart function can affect the lungs, liver, and other body systems. Restrictive cardiomyopathy may affect either or both of the lower heart chambers (ventricles). Restrictive cardiomyopathy is a rare condition. The most common causes are amyloidosis and scarring of the heart from an unknown cause. It also can occur after a heart transplant.
Other causes of restrictive cardiomyopathy include:
-
Cardiac amyloidosis
Cardiac amyloidosis
Cardiac amyloidosis is a disorder caused by deposits of an abnormal protein (amyloid) in the heart tissue. These deposits make it hard for the heart...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Carcinoid heart disease
Carcinoid heart disease
Carcinoid syndrome is a group of symptoms associated with carcinoid tumors. These are tumors most often of the small intestine, colon, appendix, pan...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Diseases of the heart lining (endocardium), such as endomyocardial fibrosis and Loeffler syndrome (rare)
- Iron overload (hemochromatosis)
-
Sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis is a disease in which inflammation occurs in the lymph nodes, lungs, liver, eyes, skin, and other tissues.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Scarring after radiation or chemotherapy
-
Scleroderma
Scleroderma
Scleroderma is a disease that involves the buildup of fibrous tissue in the skin and elsewhere in the body. It also damages the cells that line the ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Tumors of the heart
Symptoms
Symptoms of heart failure are most common. These symptoms often develop slowly over time. However, symptoms sometimes start very suddenly and are severe.
Heart failure
Heart failure is a condition in which the heart is no longer able to pump oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body efficiently. This causes symptom...

Common symptoms are:
- Cough
- Breathing problems that occur at night, with activity or when lying flat
- Fatigue and inability to exercise
- Loss of appetite
- Swelling of the abdomen
- Swelling of the feet and ankles
- Uneven or rapid pulse
Other symptoms may include:
- Chest pain
- Inability to concentrate
- Low urine output
- Need to urinate at night (in adults)
Exams and Tests
A physical exam may show:
- Enlarged (distended) or bulging neck veins
- Enlarged liver
- Lung crackles and abnormal or distant heart sounds in the chest heard through a stethoscope
Heart sounds
A heart murmur is a blowing, whooshing, or rasping sound heard during a heartbeat. The sound is caused by turbulent (rough) blood flow through the h...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Fluid backup into the hands and feet
- Signs of heart failure
Heart failure
Heart failure is a condition in which the heart is no longer able to pump oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body efficiently. This causes symptom...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Tests for restrictive cardiomyopathy include:
-
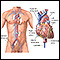
Cardiac catheterization and coronary angiography
Cardiac catheterization
Cardiac catheterization involves passing a thin flexible tube (catheter) into the right or left side of the heart. The catheter is most often insert...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
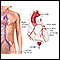
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleCoronary angiography
Coronary angiography is a procedure that uses a special dye (contrast material) and x-rays to see how blood flows through the arteries in your heart....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Chest CT scan
Chest CT scan
A chest CT (computed tomography) scan is an imaging method that uses x-rays to create cross-sectional pictures of the chest and upper abdomen....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
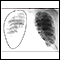
Chest x-ray
Chest x-ray
A chest x-ray is an x-ray of the chest, lungs, heart, large arteries, ribs, and diaphragm.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
Electrocardiogram
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a test that records the electrical activity of the heart.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Echocardiogram and Doppler study
Echocardiogram
An echocardiogram is a test that uses sound waves to create pictures of the heart. The picture and information it produces is more detailed than a s...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
MRI of the heart
MRI of the heart
Heart magnetic resonance imaging is an imaging method that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the heart. It does not use ra...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Nuclear heart scan (MUGA, RNV, PET)
-
Serum iron studies
Serum iron studies
A serum iron test measures how much iron is in your blood.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Serum and urine protein tests
Urine protein
The urine protein dipstick test measures the presence of all proteins, including albumin, in a urine sample. Albumin and protein can each also be mea...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Restrictive cardiomyopathy may appear similar to constrictive pericarditis. Cardiac catheterization may help confirm the diagnosis. Rarely, a biopsy of the heart may be required.
Constrictive pericarditis
Constrictive pericarditis is a process in which the sac-like covering of the heart (the pericardium) becomes thickened and scarred. Related conditio...
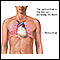
Biopsy of the heart
Myocardial biopsy is the removal of a small piece of heart muscle for examination.

Treatment
The condition causing the cardiomyopathy is treated when it can be found.
Few treatments are known to work well for restrictive cardiomyopathy. The main goal of treatment is to control symptoms and improve quality of life.
The following treatments may be used to control symptoms or prevent problems:
- Blood thinning medicines
- Chemotherapy (in some situations)
- Diuretics to remove fluid and help improve breathing
- Medicines to prevent or control abnormal heart rhythms
- Chemotherapeutic agents
- Medicines such as tafamidis that target abnormal proteins (amyloid fibrils)
- Liver transplantation
Additional treatments are also under investigation.
A heart transplant may be considered if the heart function is very poor and symptoms are severe.
Heart transplant
A heart transplant is surgery to remove a damaged or diseased heart and replace it with a healthy donor heart.

Outlook (Prognosis)
People with this condition often develop heart failure that gets worse. Problems with heart rhythm or "leaky" heart valves may also occur.
People with restrictive cardiomyopathy may be heart transplant candidates. The outlook depends on the cause of the condition, but it is usually poor. Survival after diagnosis may exceed 10 years.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your health care provider if you have symptoms of restrictive cardiomyopathy.
References
Elliott PM, Olivotto I. Diseases of the myocardium and endocardium. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 47.
Heidenreich PA, Bozkurt B, Aguilar D, et al. 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA guideline for the management of heartfailure: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2022;79(17):1757-1780. PMID: 35379504 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35379504/.
Hershberger RE. The dilated, restrictive, and infiltrative cardiomyopathies. In: Libby P, Bonow RO, Mann DL, Tomaselli GF, Bhatt DL, Solomon SD, eds. Braunwald's Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 52.
-
Cardiomyopathy overview
Animation
-
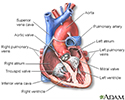
Heart - section through the middle - illustration
The interior of the heart is composed of valves, chambers, and associated vessels.
Heart - section through the middle
illustration
-
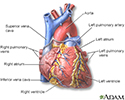
Heart - front view - illustration
The external structures of the heart include the ventricles, atria, arteries and veins. Arteries carry blood away from the heart while veins carry blood into the heart. The vessels colored blue indicate the transport of blood with relatively low content of oxygen and high content of carbon dioxide. The vessels colored red indicate the transport of blood with relatively high content of oxygen and low content of carbon dioxide.
Heart - front view
illustration
-
Heart - section through the middle - illustration
The interior of the heart is composed of valves, chambers, and associated vessels.
Heart - section through the middle
illustration
-
Heart - front view - illustration
The external structures of the heart include the ventricles, atria, arteries and veins. Arteries carry blood away from the heart while veins carry blood into the heart. The vessels colored blue indicate the transport of blood with relatively low content of oxygen and high content of carbon dioxide. The vessels colored red indicate the transport of blood with relatively high content of oxygen and low content of carbon dioxide.
Heart - front view
illustration
Review Date: 5/27/2024
Reviewed By: Michael A. Chen, MD, PhD, Associate Professor of Medicine, Division of Cardiology, Harborview Medical Center, University of Washington Medical School, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.