Cardiac tamponade
Tamponade; Pericardial tamponade; Pericarditis - tamponadeCardiac tamponade is pressure on the heart that occurs when blood or fluid builds up in the space between the heart muscle and the outer covering sac (pericardium) of the heart.
Causes
In this condition, blood or fluid collects in the sac surrounding the heart. This prevents the heart ventricles from expanding fully. The excess pressure from the fluid prevents the heart from working properly. As a result, the body does not get enough blood.
Cardiac tamponade can occur due to:
-
Dissecting aortic aneurysm (thoracic)
Dissecting aortic aneurysm
Aortic dissection is a serious condition in which there is a tear in the wall of the major artery carrying blood out of the heart (aorta). As the te...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - End-stage lung cancer
- Heart attack (acute MI)
Acute MI
Most heart attacks are caused by a blood clot that blocks one of the coronary arteries. The coronary arteries bring blood and oxygen to the heart. ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Heart surgery
-
Pericarditis caused by bacterial or viral infections
Pericarditis
Pericarditis is a condition in which the sac-like covering around the heart (pericardium) becomes inflamed.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Wounds to the heart
Other possible causes include:
- Heart tumors
-
Underactive thyroid gland
Underactive thyroid gland
Hypothyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone. This condition is often called underactive thyroid....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Kidney failure
Kidney failure
Acute kidney failure is the rapid (less than 2 days) loss of your kidneys' ability to remove waste and help balance fluids and electrolytes in your b...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Leukemia
- Placement of central lines
-
Radiation therapy to the chest
Radiation therapy to the chest
Radiation therapy uses high-powered radiation (such as x-rays or gamma rays), particles, or radioactive seeds to kill cancer cells.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Recent invasive heart procedures
-
Systemic lupus erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disease. In this disease, the immune system of the body mistakenly attacks healthy tissue. It c...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Dermatomyositis
- Heart failure
Cardiac tamponade due to disease occurs in about 2 out of 10,000 people.
Symptoms
Symptoms may include:
-
Anxiety, restlessness
Anxiety
Stress is a feeling of emotional or physical tension. It can come from any event or thought that makes you feel frustrated, angry, or nervous. Stres...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Breathing problems
- Sharp chest pain that is felt in the neck, shoulder, back, or abdomen
Chest pain
Chest pain is discomfort or pain that you feel anywhere along the front of your body between your neck and upper abdomen.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Chest pain that gets worse with deep breathing or coughing
- Problems breathing
- Discomfort, sometimes relieved by sitting upright or leaning forward
-
Fainting, lightheadedness
Fainting
Fainting is a brief loss of consciousness due to a drop in blood flow to the brain. The episode most often lasts less than a couple of minutes and y...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Pale, gray, or blue skin
- Palpitations
- Rapid breathing
- Swelling of the legs or abdomen
- Jaundice
Other symptoms that may occur with this disorder:
- Dizziness
- Drowsiness
- Weak or absent pulse
Exams and Tests
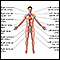
Echocardiogram is the test of choice to help make the diagnosis. This test may be done at the bedside in emergency cases.
Echocardiogram
An echocardiogram is a test that uses sound waves to create pictures of the heart. The picture and information it produces is more detailed than a s...
A physical exam may show:
- Blood pressure that falls when breathing deeply
- Rapid breathing
- Heart rate over 100 (normal is 60 to 100 beats per minute)
- Heart sounds are only faintly heard through a stethoscope
- Neck veins that may be bulging (distended) but the blood pressure is low
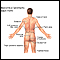
- Weak or absent peripheral pulses
Peripheral
Peripheral means "away from the center. " It refers to areas away from the center of the body or a body part. For example, the hands are peripheral ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Other tests may include:
-
Chest CT or MRI of chest
Chest CT
A chest CT (computed tomography) scan is an imaging method that uses x-rays to create cross-sectional pictures of the chest and upper abdomen....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleMRI of chest
A chest MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) scan is an imaging test that uses powerful magnetic fields and radio waves to create pictures of the chest (...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Chest x-ray
Chest x-ray
A chest x-ray is an x-ray of the chest, lungs, heart, large arteries, ribs, and diaphragm.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Coronary angiography
Coronary angiography
Coronary angiography is a procedure that uses a special dye (contrast material) and x-rays to see how blood flows through the arteries in your heart....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
ECG
ECG
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a test that records the electrical activity of the heart.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Right heart catheterization
Treatment
Cardiac tamponade is an emergency condition that needs to be treated in the hospital.
The fluid around the heart must be drained as quickly as possible. A procedure that uses a needle to remove fluid from the tissue that surrounds the heart will be done.
A procedure that uses a needle to remov...
Pericardiocentesis is a procedure that uses a needle to remove fluid from the pericardial sac. This is the tissue that surrounds the heart.
A surgical procedure to cut and remove part of the covering of the heart may also be done. This is known as surgical pericardiectomy or pericardial window.
Fluids are given to keep blood pressure normal until the fluid can be drained from around the heart. Medicines that increase blood pressure may also help keep the person alive until the fluid is drained.
Oxygen may be given to help reduce the workload on the heart by decreasing tissue demands for blood flow.
The cause of tamponade must be found and treated.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Death due to cardiac tamponade can occur quickly if the fluid or blood is not removed promptly from within the pericardium.
The outcome is often good if the condition is treated promptly. However, tamponade may come back.
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
-
Heart failure
Heart failure
Heart failure is a condition in which the heart is no longer able to pump oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body efficiently. This causes symptom...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Pulmonary edema
Pulmonary edema
Pulmonary edema is an abnormal buildup of fluid in the lungs. This buildup of fluid leads to shortness of breath.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Bleeding
-
Shock
Shock
Shock is a life-threatening condition that occurs when the body is not getting enough blood flow. Lack of blood flow means the cells and organs do n...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Death
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Go to the emergency room or call the local emergency number (such as 911) if symptoms develop. Cardiac tamponade is an emergency condition that needs immediate medical attention.
Prevention
Many cases can't be prevented. Knowing your personal risk factors may help you get early diagnosis and treatment.
References
Hoit BD, Oh JK. Pericardial diseases. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 62.
LeWinter MM, Cremer PC, Klein AL. Pericardial diseases. In: Libby P, Bonow RO, Mann DL, Tomaselli, GF, Bhatt DL, Solomon SD, eds. Braunwald's Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 86.
Mallemat HA, Tewelde SZ. Pericardiocentesis. In: Roberts JR, Custalow CB, Thomsen TW, eds. Roberts and Hedges' Clinical Procedures in Emergency Medicine and Acute Care. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 16.
-
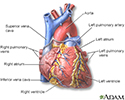
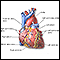
Heart - front view - illustration
The external structures of the heart include the ventricles, atria, arteries and veins. Arteries carry blood away from the heart while veins carry blood into the heart. The vessels colored blue indicate the transport of blood with relatively low content of oxygen and high content of carbon dioxide. The vessels colored red indicate the transport of blood with relatively high content of oxygen and low content of carbon dioxide.
Heart - front view
illustration
-
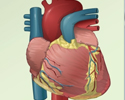
Pericardium - illustration
The pericardium is a thin double-layered sac which encloses the heart. Fluid is contained within the layers and lubricates the constantly rubbing surfaces.
Pericardium
illustration
-
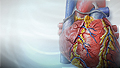
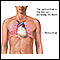
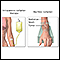
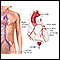
Cardiac tamponade - illustration
Cardiac tamponade is a condition involving compression of the heart caused by blood or fluid accumulation in the space between the myocardium (the muscle of the heart) and the pericardium (the outer covering sac of the heart). Blood or fluid collects within the pericardium. This prevents the ventricles from expanding fully, so they cannot adequately fill or pump blood. Cardiac tamponade is an emergency condition that requires hospitalization.
Cardiac tamponade
illustration
-
Heart - front view - illustration
The external structures of the heart include the ventricles, atria, arteries and veins. Arteries carry blood away from the heart while veins carry blood into the heart. The vessels colored blue indicate the transport of blood with relatively low content of oxygen and high content of carbon dioxide. The vessels colored red indicate the transport of blood with relatively high content of oxygen and low content of carbon dioxide.
Heart - front view
illustration
-
Pericardium - illustration
The pericardium is a thin double-layered sac which encloses the heart. Fluid is contained within the layers and lubricates the constantly rubbing surfaces.
Pericardium
illustration
-
Cardiac tamponade - illustration
Cardiac tamponade is a condition involving compression of the heart caused by blood or fluid accumulation in the space between the myocardium (the muscle of the heart) and the pericardium (the outer covering sac of the heart). Blood or fluid collects within the pericardium. This prevents the ventricles from expanding fully, so they cannot adequately fill or pump blood. Cardiac tamponade is an emergency condition that requires hospitalization.
Cardiac tamponade
illustration
Review Date: 5/13/2024
Reviewed By: Mary C. Mancini, MD, PhD, Cardiothoracic Surgeon, Shreveport, LA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.