Liver disease
The term "liver disease" applies to many conditions that stop the liver from working or prevent it from functioning well. Abdominal pain or swelling, yellowing of the skin or eyes (jaundice), or abnormal results of liver function tests may suggest you have liver disease.
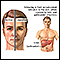
Jaundice
Jaundice is a yellow color of the skin, mucus membranes, or eyes. The yellow coloring comes from bilirubin, a byproduct of old red blood cells. Jau...
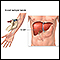
Liver function tests
Liver function tests are common tests that are used to see how well the liver is working. Tests include:AlbuminAlpha-1 antitrypsinAlkaline phosphata...
Related topics include:
- Alpha-1 anti-trypsin deficiency
-
Amebic liver abscess
Amebic liver abscess
Amebic liver abscess is a collection of pus in the liver in response to an intestinal parasite called Entamoeba histolytica.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Autoimmune hepatitis
Autoimmune hepatitis
Autoimmune hepatitis causes inflammation of the liver. It occurs when immune cells mistake the liver's normal cells for harmful invaders and attack ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Biliary atresia
Biliary atresia
Biliary atresia is a blockage in the tubes (ducts) that carry a liquid called bile from the liver to the gallbladder.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis is scarring of the liver and poor liver function. It is the last stage of chronic liver disease.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Coccidioidomycosis
Coccidioidomycosis
Valley fever is an infection that occurs when the spores of the fungus Coccidioides immitis or Coccidioides posadasii enter your body through the lun...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Delta virus (hepatitis D)
Delta virus (hepatitis D)
Hepatitis D is a viral infection caused by the hepatitis D virus (previously called the Delta agent). It causes symptoms only in people who also hav...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Drug-induced cholestasis
- Metabolic associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD)
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
-
Hemochromatosis
Hemochromatosis
Hemochromatosis is a condition in which there is too much iron in the body. It is also called iron overload.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A is inflammation (irritation and swelling) of the liver from the hepatitis A virus.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is irritation and swelling (inflammation) of the liver due to infection with the hepatitis B virus (HBV). Other types of viral hepatitis ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is a viral disease that leads to swelling (inflammation) of the liver. Other types of viral hepatitis include:Hepatitis AHepatitis BHepat...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Hepatocellular carcinoma
Hepatocellular carcinoma
Hepatocellular carcinoma is cancer that starts in the liver.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Liver disease due to alcohol
Liver disease due to alcohol
Alcoholic liver disease is damage to the liver and its function due to alcohol abuse.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Primary biliary cirrhosis
Primary biliary cirrhosis
The bile ducts are tubes that move bile from the liver to the small intestine. Bile is a substance that helps with digestion. All of the bile ducts...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Pyogenic liver abscess
Pyogenic liver abscess
Pyogenic liver abscess is a pus-filled pocket of fluid within the liver. Pyogenic means with pus.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Reye syndrome
Reye syndrome
Reye syndrome is characterized by sudden (acute) brain damage and liver function problems. This condition does not have a known cause. This syndrome...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Sclerosing cholangitis
Sclerosing cholangitis
Sclerosing cholangitis refers to swelling (inflammation), scarring, and destruction of the bile ducts inside and outside of the liver.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Wilson disease
Wilson disease
Wilson disease is an inherited disorder in which there is too much copper in the body's tissues. The excess copper damages the liver and nervous sys...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
References
Martin P. Approach to the patient with liver disease. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 132.
Williams MJ, Gordon-Walker TT. Hepatology. In: Penman ID, Ralston SH, Strachan MWJ, Hobson RP, eds. Davidson's Principles and Practice of Medicine. 24th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 24.
-
Fatty liver - CT scan - illustration
A CT scan of the upper abdomen showing a fatty liver (steatosis of the liver). Note the liver enlargement and dark color compared with the spleen (gray body in lower right).
Fatty liver - CT scan
illustration
-
Liver with disproportional fattening - CT scan - illustration
A CT scan of the upper abdomen showing disproportional steatosis (fattening) of the liver.
Liver with disproportional fattening - CT scan
illustration
-
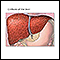
Cirrhosis of the liver - illustration
A chronic liver disease which causes damage to liver tissue, scarring of the liver (fibrosis; nodular regeneration), progressive decrease in liver function, excessive fluid in the abdomen (ascites), bleeding disorders (coagulopathy), increased pressure in the blood vessels (portal hypertension), and brain function disorders (hepatic encephalopathy). Excessive alcohol use is the leading cause of cirrhosis.
Cirrhosis of the liver
illustration
-
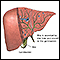
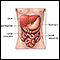
Liver - illustration
The liver serves a wide variety of body functions, including detoxifying blood and producing bile that aids in digestion.
Liver
illustration
-
Fatty liver - CT scan - illustration
A CT scan of the upper abdomen showing a fatty liver (steatosis of the liver). Note the liver enlargement and dark color compared with the spleen (gray body in lower right).
Fatty liver - CT scan
illustration
-
Liver with disproportional fattening - CT scan - illustration
A CT scan of the upper abdomen showing disproportional steatosis (fattening) of the liver.
Liver with disproportional fattening - CT scan
illustration
-
Cirrhosis of the liver - illustration
A chronic liver disease which causes damage to liver tissue, scarring of the liver (fibrosis; nodular regeneration), progressive decrease in liver function, excessive fluid in the abdomen (ascites), bleeding disorders (coagulopathy), increased pressure in the blood vessels (portal hypertension), and brain function disorders (hepatic encephalopathy). Excessive alcohol use is the leading cause of cirrhosis.
Cirrhosis of the liver
illustration
-
Liver - illustration
The liver serves a wide variety of body functions, including detoxifying blood and producing bile that aids in digestion.
Liver
illustration
Review Date: 5/14/2024
Reviewed By: Jenifer K. Lehrer, MD, Department of Gastroenterology, Aria - Jefferson Health Torresdale, Jefferson Digestive Diseases Network, Philadelphia, PA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.





