| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ectopic Pregnancy
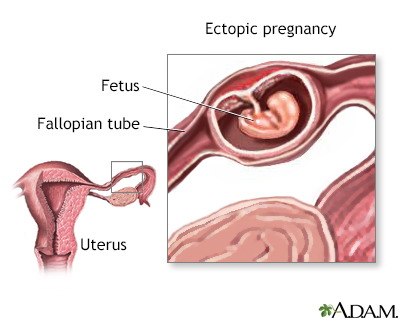
An ectopic pregnancy occurs when the fertilized egg implants in some part of the body other than the uterus. In 95% of all ectopic pregnancies, the egg is implanted in one of the fallopian tubes. In rare cases, these types of pregnancies occur in the ovaries, the abdomen, and in the lower portion of the uterus (cervix). Alternative names are abdominal, cervical, or tubal pregnancy.
If left untreated, an ectopic pregnancy can tear or rupture the fallopian tube, which is not designed to accommodate a growing embryo. An ectopic pregnancy can lead to severe, life-threatening internal bleeding.
Although all women are at risk, most ectopic pregnancies occur in women between the ages of 35 to 44. Ectopic pregnancy is also more prevalent in women whose fallopian tubes have been blocked or damaged due to endometriosis, scarring after tubal surgery, pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), or a previous ectopic pregnancy. Other risk factors include infertility, exposure to several STDs, smoking, and having an IUD in place during conception.
About 2 of every 100 pregnancies are ectopic. Thanks to new techniques for early diagnosis and medical care, they are usually treated by the eighth week of pregnancy, eliminating much of the risk to the mother. Unfortunately, though, since the fetus cannot survive outside of the uterus, the pregnancy cannot survive the treatment.
How Do I Know If I Might Have An Ectopic Pregnancy?
Immediate medical attention can often save the fallopian tube and improve your chances of remaining fertile in the future. If you are experiencing any or all of these symptoms, please call your health care provider:
- Significant cramping or tenderness, usually on one side of the lower abdomen.
- Brown vaginal spotting or light bleeding.
- Heavy bleeding if the tube ruptures.
- Nausea and vomiting (which might be difficult to distinguish from morning sickness).
- Dizziness or weakness. (If the tube ruptures, a weak pulse, clammy skin, and fainting are common.)
- Shoulder or neck pain (caused by the buildup of blood under the diaphragm when the tube ruptures).
If your health care provider suspects an ectopic pregnancy, she will perform a pelvic exam. Next, you will undergo some of the following tests:
- A series of highly sensitive pregnancy tests are administered to track the level of the hormone hCG in your blood. In a typical pregnancy, the level of this hormone doubles about every two days during the first 10 weeks. If the level of hCG falls or fails to rise as the pregnancy progresses, then it’s unlikely that you have a normal pregnancy, and it may either be an ectopic pregnancy or a miscarriage.
- Ultrasound exams are also used to determine whether your pregnancy is developing in the right place or if there is any fluid in the pelvis. With this technique, your health care provider can view your uterus and fallopian tubes to track the location of the developing fetus.
- Laparoscopic surgery is another option to try to locate a pregnancy that may be ectopic. In this procedure, the surgeon inserts a small camera through your belly button and looks at the tubes and ovaries to see if there is an ectopic pregnancy.
How Can I Treat It?
Treatment of an ectopic pregnancy usually consists of surgery called laparoscopy. In this procedure, a small incision is made in the lower abdomen, near or in the navel. Your surgeon then inserts a long, thin camera called a laparoscope into the pelvic region. This allows the surgeon to remove the embryo and repair or remove the affected fallopian tube.
Unless the fallopian tube has irreparable damage, it is usually possible to save it. This will improve your chances of a successful pregnancy in the future, though it may also be the site of a future ectopic pregnancy. A follow-up test of your hCG level is performed later to ensure that the entire ectopic pregnancy was removed.
The drug methotrexate is a medical alternative to surgery. An injection of the medication impairs cell growth and usually terminates the pregnancy. You’ll then need to come back for a series of blood tests to make sure the medicine has been effective. If the medicine isn’t working, you may need a second dose of medication. The tube may rupture even after treatment, and you’ll need to have surgery to remove the abnormal pregnancy.
How Can I Prevent It?
Ectopic pregnancies may be prevented by avoiding conditions that cause scarring or blocking to the fallopian tubes. This includes early diagnosis and adequate treatment of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), STDs, and the avoidance of smoking.
As always, it's important to talk to your health care provider before planning your pregnancy to ensure the best care possible.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: I've been having periodic cramping. Could I have an ectopic pregnancy without even knowing it?
A: Occasional cramping is most likely the result of ligaments stretching as your uterus grows, but an ectopic pregnancy can still cause occasional cramping. Cramping caused by an ectopic pregnancy is usually more constant and sharp, usually occurring in the lower abdomen only. But if the pain is persistent and worse than your normal period cramps, or if you’re unsure, contact your health care provider.
Q: Why have ectopic pregnancies become more common as of late?
A: No one is certain why ectopic pregnancies have become more common. Some medical professionals believe that an increase in pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is partially responsible.
Q: I've had an ectopic pregnancy before. What are my chances of having a successful pregnancy later?
A: Although the chances of having a successful pregnancy are lowered if you've already had an ectopic pregnancy, you still have a 60% chance of uterine implantation if your fallopian tube has not been removed. Even if one fallopian tube has been removed, your chances are as high as 40%. Women treated with methotrexate have about a 50% chance of a future normal pregnancy. Notably, women who keep their tube at the time of surgery have a higher risk of another ectopic pregnancy (about 15%) than those who have the tube removed (about 10%).
|
Review Date:
12/9/2012 Reviewed By: Irina Burd, MD, PhD, Maternal Fetal Medicine, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. |




