| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vaginal Bleeding During Pregnancy
Vaginal bleeding during pregnancy is any discharge of blood through the vagina from the time of conception to the end of pregnancy.
Between 20% and 30% of women experience some vaginal bleeding during their first 20 weeks of pregnancy. Up to 10% of women have vaginal bleeding in their third trimester. While it is often a normal part of the process of gestation, it may indicate complications. You should always report vaginal bleeding to your health care provider right away.
What Could It Be?
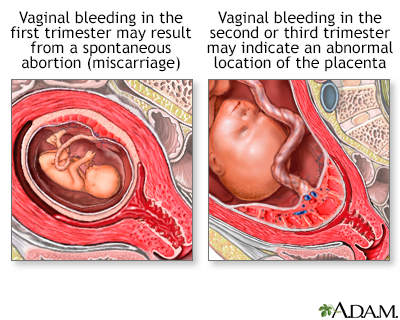
First-trimester bleeding isn’t always a problem. It may be caused by:
- Implantation of the fertilized egg in the uterus.
- Hormonal changes.
- Undetermined factors that cause no harm to the mother or baby.
More serious causes of first-trimester bleeding may include:
- Miscarriage. Almost all women who miscarry will have vaginal bleeding prior to the loss of the pregnancy.
- Ectopic pregnancy. When the fertilized egg develops outside of the uterus, usually in the fallopian tube, it may cause cramping and bleeding.
- Molar pregnancy. Also known as a hydatidiform mole or trophoblastic disease, molar pregnancy is a condition in which the pregnancy does not form properly.
Mid- or late-term bleeding may be caused by:
- Trauma to the sensitized cervix, such as sexual intercourse or an internal exam.
- Diseases of the vagina or cervix, including infections.
- Unknown causes that pose no threat to the mother or baby.
- Uterine fibroids or cervical polyps.
More serious causes of late-term bleeding may include:
- Placenta previa. The placenta has implanted in the lower portion of the uterus and covers the cervix and its opening.
- Placenta abruptio. The placenta becomes detached, either partially or fully, from the uterine wall.
- Late miscarriage.
- Preterm labor. Dilatation of the cervix associated with uterine contractions that occurs between 20 and 37 weeks of pregnancy is called preterm labor.
What Should I Do?
Immediately contact your health care provider any time you experience vaginal bleeding. You will be asked very specific questions during your visit. Try to be as precise as possible since the differences in bleeding with or without symptoms may signal different complications. If the bleeding is heavy or if you have bleeding with pain or cramping, and you can't reach your health care provider, go to the emergency room.
Questions your health care provider may ask include:
- How far along is the pregnancy?
- Has bleeding occurred before or during this pregnancy? Has it been constant since the beginning of the pregnancy?
- When did the bleeding begin? Is it intermittent or constant?
- How much bleeding is present?
- What is the color of the blood?
- Is there an odor to the blood?
- Is cramping present? Is there other abdominal pain, weakness, or increased fatigue?
- Is there fainting, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea? Is there a fever?
- Are there changes in urination or bowel movements?
- Has there been an injury, such as a fall?
- Have there been changes in physical activity?
- Has there been additional stress?
- When did you last have sexual intercourse? Did the bleeding occur during or after sexual intercourse?
- Does rest reduce or stop the bleeding?
Your health care provider will most likely perform a pelvic exam, with careful inspection of the cervix.
Other diagnostic tests may include:
- Blood tests
- Ultrasound
- Pap smear
- Cervical cultures or tests for infections
Frequently Asked Questions
Early-term bleeding is generally treated with bed rest. Your doctor may also advise you to take time off work, stay off your feet, and avoid sexual intercourse. While it seems logical that rest would help stabilize a pregnancy, there’s no scientific evidence to show that bed rest makes a difference. If the bleeding is severe, you may need to be hospitalized and given a blood transfusion.
Miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, molar pregnancy, complications of the placenta, and premature labor all require medical attention. Your health care provider will diagnose the problem and suggest treatment options.
Q: I am spotting just a bit, not even enough to cover my panty liner. Do I need to panic?
A: No. A little bit of spotting is common for women who have already had a normal viable pregnancy established by ultrasound. You should contact your health care provider the same day you notice the spotting. At an early visit, have your health care provider explain the difference between spotting and bleeding. (Spotting is periodic drops of blood. Bleeding is a light-to-heavy flow of blood.)
If you have spotting and haven’t yet had an ultrasound to show that your pregnancy is in your uterus, contact your health care provider right away. Spotting can be a sign of ectopic pregnancy. If an ectopic pregnancy isn’t treated, you can have life-threatening internal bleeding.
Q: What should I do if I'm bleeding heavily?
A: Contact your health care provider immediately. If you pass material that you think is tissue, place it in a clean jar or plastic bag and bring it to your health care provider for analysis.
Q: If I have vaginal bleeding, what are the chances that it is a serious complication?
A: Of the women who experience vaginal bleeding in the first trimester, half will have a miscarriage. But the odds of other problems are lower: ectopic pregnancy occurs in 16 out of 1,000 pregnancies; molar pregnancy occurs in one out of 1,500 to 2,000 births; placenta previa happens in one of 200 births; and placenta abruptio happens in one of 150 births.
Q: If my bleeding has stopped, do I still need to call my doctor?
A: Yes. Your doctor will need to diagnose the cause of the bleeding or at least rule out any concerning cause for the bleeding. Also, depending on your blood type, you might need an injection (Rhogam) to protect this pregnancy, and future pregnancies, from immune reactions from your body.
Q: I had some mild spotting during my first trimester. The doctor said it was nothing to worry about. Now I am in my third trimester and I am spotting again. Do I need to call the doctor this time?
A: Yes. Bleeding in the third trimester could signal a serious problem, whether or not it is accompanied by pain. Conditions such as placenta abruptio often do not develop until the end of the pregnancy; therefore, a health care provider needs to be consulted as soon as you notice the bleeding.
|
Review Date:
12/9/2012 Reviewed By: Irina Burd, MD, PhD, Maternal Fetal Medicine, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. |




