Pancreatic pseudocyst
Pancreatitis - pseudocystA pancreatic pseudocyst is a fluid-filled sac in the abdomen that arises from the pancreas. It may also contain tissue from the pancreas, enzymes, and blood.
Causes
The pancreas is an organ located behind the stomach. It produces chemicals (called enzymes) needed to digest food. It also produces the hormones insulin and glucagon.
Pancreatic pseudocysts most often develop after an episode of severe pancreatitis. Pancreatitis happens when your pancreas gets inflamed. There are many causes of this problem.
Pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis is sudden swelling and inflammation of the pancreas.

This problem may sometimes occur:
- In someone with long-term (chronic) swelling of the pancreas (pancreatitis), most often due to alcohol abuse
Swelling of the pancreas
Pancreatitis is swelling of the pancreas. Chronic pancreatitis is present when this problem does not heal or recurs and does not improve, gets worse...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - After trauma to the belly, more often in children
The pseudocyst happens when the ducts (tubes) in the pancreas are damaged and fluid with enzymes cannot drain.
Symptoms
Symptoms can occur within days to months after an attack of pancreatitis. They include:
-
Bloating of the abdomen
Bloating of the abdomen
Abdominal bloating is a condition in which the belly (abdomen) feels full and tight. Your belly may look swollen (distended).
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Constant pain or deep ache in the abdomen, which may also be felt in the back
- Nausea and vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Difficulty eating and digesting food
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will feel your abdomen for a pseudocyst. It will feel like a lump in the middle or left upper abdomen.
Tests that may help detect pancreatic pseudocyst include:
-
Abdominal CT scan
Abdominal CT scan
An abdominal CT scan is an imaging test that uses x-rays to create cross-sectional pictures of the belly area. CT stands for computed tomography....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Abdominal MRI
Abdominal MRI
An abdominal magnetic resonance imaging scan is an imaging test that uses powerful magnets and radio waves. The waves create pictures of the inside ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Abdominal ultrasound
Abdominal ultrasound
Abdominal ultrasound is a type of imaging test. It is used to look at organs in the abdomen, including the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, and kidneys...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)
Treatment
Treatment depends on the size of the pseudocyst and whether it is causing symptoms. Many pseudocysts go away on their own. Those that remain for more than 6 weeks and are larger than 5 centimeters (about 2 inches) in diameter may need treatment. However, size and duration do not always mean treatment is needed, especially in a person without any symptoms and whose pseudocyst is not getting bigger.
Possible treatments include:
- Drainage through the skin using a needle, most often guided by a CT scan.
-
Endoscopic-assisted drainage using an endoscope. In this, a tube containing a camera and a light is passed down into the stomach).
Endoscopic
An endoscope is a medical device with a light attached. It is used to look inside a body cavity or organ. The scope is inserted through a natural o...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Surgical drainage of the pseudocyst. A connection is made between the cyst and the stomach or small intestine. This may be done using a laparoscope.
Outlook (Prognosis)
The outcome is generally good with treatment. It is important to make sure that it is not a pancreatic cancer that starts in a cyst, which has a worse outcome.
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
- A pancreatic abscess can develop if the pseudocyst becomes infected.
Pancreatic abscess
A pancreatic abscess is an area filled with pus within the pancreas.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - The pseudocyst can break open (rupture). This can be a serious complication because shock and excess bleeding (hemorrhage) may develop.
Shock
Shock is a life-threatening condition that occurs when the body is not getting enough blood flow. Lack of blood flow means the cells and organs do n...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - The pseudocyst may press down on (compress) nearby organs.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
If you are known to have a pseudocyst, rupture of the pseudocyst is a medical emergency. Go to the emergency room or call 911 or the local emergency number if you develop symptoms of bleeding or shock, such as:
-
Fainting
Fainting
Fainting is a brief loss of consciousness due to a drop in blood flow to the brain. The episode most often lasts less than a couple of minutes and y...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Fever and chills
-
Rapid heartbeat
Rapid heartbeat
Palpitations are feelings or sensations that your heart is pounding or racing. They can be felt in your chest, throat, or neck. You may:Have an unpl...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Severe abdominal pain
Prevention
The way to prevent pancreatic pseudocysts is by preventing pancreatitis. If pancreatitis is caused by gallstones, the provider will perform surgery to remove the gallbladder (cholecystectomy).
Gallstones
Gallstones are hard deposits that form inside the gallbladder. These may be as small as a grain of sand or as large as a golf ball.

When pancreatitis occurs due to alcohol abuse, you must stop drinking alcohol to prevent future attacks.
When pancreatitis occurs due to high blood triglycerides, this condition should be treated.
References
Forsmark CE. Pancreatitis. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 130.
Javed AA, Lafaro KJ. Pancreas: Management of pancreatic pseudocyst. In: Cameron J, ed. Current Surgical Therapy. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:539-650.
Van Buren G, Fisher WE. Acute and chronic pancreatitis. In: Kellerman RD, Rakel DP, Heidelbaugh JJ, Lee EM, eds. Conn's Current Therapy 2024. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:175-182.
Vege SS. Acute pancreatitis. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease: Pathophysiology/Diagnosis/Management. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 58.
-
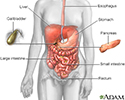
Digestive system - illustration
The esophagus, stomach, large and small intestine, aided by the liver, gallbladder and pancreas convert the nutritive components of food into energy and break down the non-nutritive components into waste to be excreted.
Digestive system
illustration
-
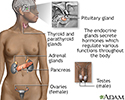
Endocrine glands - illustration
Endocrine glands release hormones (chemical messengers) into the bloodstream to be transported to various organs and tissues throughout the body. For instance, the pancreas secretes insulin, which allows the body to regulate levels of sugar in the blood. The thyroid gets instructions from the pituitary to secrete hormones which determine the rate of metabolism in the body (the more hormone in the bloodstream, the faster the chemical activity; the less hormone, the slower the activity).
Endocrine glands
illustration
-
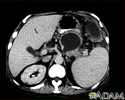
Pancreatic pseudocyst - CT scan - illustration
A CT scan of the upper abdomen showing a pseudocyst in the corpus, or tail, of the pancreas.
Pancreatic pseudocyst - CT scan
illustration
-
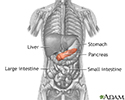
Pancreas - illustration
The pancreas is an elongated, tapered gland that is located behind the stomach and secretes digestive enzymes and the hormones insulin and glucagon.
Pancreas
illustration
-
Digestive system - illustration
The esophagus, stomach, large and small intestine, aided by the liver, gallbladder and pancreas convert the nutritive components of food into energy and break down the non-nutritive components into waste to be excreted.
Digestive system
illustration
-
Endocrine glands - illustration
Endocrine glands release hormones (chemical messengers) into the bloodstream to be transported to various organs and tissues throughout the body. For instance, the pancreas secretes insulin, which allows the body to regulate levels of sugar in the blood. The thyroid gets instructions from the pituitary to secrete hormones which determine the rate of metabolism in the body (the more hormone in the bloodstream, the faster the chemical activity; the less hormone, the slower the activity).
Endocrine glands
illustration
-
Pancreatic pseudocyst - CT scan - illustration
A CT scan of the upper abdomen showing a pseudocyst in the corpus, or tail, of the pancreas.
Pancreatic pseudocyst - CT scan
illustration
-
Pancreas - illustration
The pancreas is an elongated, tapered gland that is located behind the stomach and secretes digestive enzymes and the hormones insulin and glucagon.
Pancreas
illustration
Review Date: 12/31/2023
Reviewed By: Jenifer K. Lehrer, MD, Department of Gastroenterology, Aria - Jefferson Health Torresdale, Jefferson Digestive Diseases Network, Philadelphia, PA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.