Liver cancer - hepatocellular carcinoma
Primary liver cell carcinoma; Tumor - liver; Cancer - liver; HepatomaHepatocellular carcinoma is cancer that starts in the liver.
Causes
Hepatocellular carcinoma is the most common type of liver cancer. It occurs more often in men than women. It is most often diagnosed in people age 50 or older.
Hepatocellular carcinoma is not the same as metastatic liver cancer. Metastatic liver cancer starts in another organ (such as the breast or colon) and spreads to the liver.
Metastatic liver cancer
Liver metastases refer to cancer that has spread to the liver from somewhere else in the body. Liver metastases are not the same as cancer that start...
In most cases, the cause of hepatocellular liver cancer is long-term damage and scarring of the liver (cirrhosis). Cirrhosis may be caused by:
Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis is scarring of the liver and poor liver function. It is the last stage of chronic liver disease.
- Alcohol overuse
-
Autoimmune diseases of the liver
Autoimmune diseases
An autoimmune disorder occurs when the body's immune system attacks and destroys healthy body tissue by mistake. There are more than 80 autoimmune d...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Hepatitis B or hepatitis C virus infection
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is irritation and swelling (inflammation) of the liver due to infection with the hepatitis B virus (HBV). Other types of viral hepatitis ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleHepatitis C
Hepatitis C is a viral disease that leads to swelling (inflammation) of the liver. Other types of viral hepatitis include:Hepatitis AHepatitis BHepat...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Inflammation of the liver that is long-term (chronic hepatitis)
- Iron overload in the liver and body (hemochromatosis)
Hemochromatosis
Hemochromatosis is a condition in which there is too much iron in the body. It is also called iron overload.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis or MASH, which has become a more common cause of cirrhosis in western countries and is associated with obesity, diabetes and other metabolic disorders
People with hepatitis B or C are at high risk for liver cancer, even if they do not develop cirrhosis.
Symptoms
Symptoms of liver cancer may include any of the following:
-
Abdominal pain or tenderness, especially in the upper-right part
Abdominal pain
Abdominal pain is pain that you feel anywhere between your chest and groin. This is often referred to as the stomach region or belly.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Easy bruising or bleeding
- Enlarged abdomen due to fluid in the abdomen (ascites)
Ascites
Ascites is the build-up of fluid in the space between the lining of the abdomen and abdominal organs.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Yellow skin or eyes (jaundice)
Jaundice
Jaundice is a yellow color of the skin, mucus membranes, or eyes. The yellow coloring comes from bilirubin, a byproduct of old red blood cells. Jau...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Unexplained weight loss
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will perform a physical exam and ask about your symptoms. The physical exam may show an enlarged, tender liver or other signs of cirrhosis.
If your provider suspects liver cancer, tests that may be ordered include:
-
Abdominal CT scan
Abdominal CT scan
An abdominal CT scan is an imaging test that uses x-rays to create cross-sectional pictures of the belly area. CT stands for computed tomography....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Abdominal MRI scan
Abdominal MRI scan
An abdominal magnetic resonance imaging scan is an imaging test that uses powerful magnets and radio waves. The waves create pictures of the inside ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Abdominal ultrasound
Abdominal ultrasound
Abdominal ultrasound is a type of imaging test. It is used to look at organs in the abdomen, including the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, and kidneys...
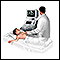 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
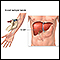
Liver biopsy
Liver biopsy
A liver biopsy is a test that takes a sample of tissue from the liver for examination.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Liver function tests
Liver function tests
Liver function tests are common tests that are used to see how well the liver is working. Tests include:AlbuminAlpha-1 antitrypsinAlkaline phosphata...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Serum alpha fetoprotein
Serum alpha fetoprotein
Alpha fetoprotein (AFP) is a protein produced by the liver and yolk sac of a developing baby during pregnancy. AFP levels go down soon after birth. ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Some people at risk for liver cancer may get regular blood tests and ultrasounds to see if tumors are developing.
Treatment
The treatment depends on how advanced the cancer is.
Surgery may be done if the tumor has not spread. Occasionally the tumor can be treated directly by a procedure known as embolization. This can be done by injecting radiation pellets or chemotherapy directly into the tumor via the blood vessels that feed the tumor. This can sometimes be done prior to surgery or as a procedure by itself.
Radiation treatments in the area of the cancer may also be helpful.
Radiation treatments
Radiation therapy uses high-powered radiation (such as x-rays or gamma rays), particles, or radioactive seeds to kill cancer cells.
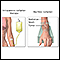
Ablation is another method that may be used. Ablate means to destroy. Types of ablation include using:
- Radio waves or microwaves
- Ethanol (an alcohol) or acetic acid (a chemical found in vinegar)
- Extreme cold (cryoablation)
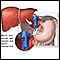
A liver transplant may be recommended.
Liver transplant
Liver transplant is surgery to replace a diseased liver with a healthy liver.
If the cancer can't be surgically removed or has spread outside the liver, there is usually no chance for long-term cure. Treatment instead focuses on improving and extending the person's life. Treatment in this case may use targeted therapy with medicines that can be taken as pills. Newer immunotherapy medicines may also be used and are now the most common forms of treatment for advanced liver cancer.
Targeted therapy
Targeted therapy uses medicines to stop cancer from growing and spreading. It does this with less harm to normal cells than other treatments. Stand...
Support Groups
You can ease the stress of illness by joining a cancer support group. Sharing with others who have common experiences and problems can help you not feel alone.
Cancer support group
The following organizations are good resources for information on cancer:American Cancer Society. Support and online communities. www. cancer. org/...
Outlook (Prognosis)
If the cancer can't be completely treated, the disease is usually fatal. But survival can vary, depending on how advanced the cancer is and how successful treatment is.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you develop ongoing abdominal pain, especially if you have a history of liver disease.
Liver disease
The term "liver disease" applies to many conditions that stop the liver from working or prevent it from functioning well. Abdominal pain or swelling...

Prevention
Preventive measures include:
- Preventing and treating viral hepatitis may help reduce your risk. Childhood vaccination against hepatitis B may reduce the risk for liver cancer in the future.
- Not drinking alcohol in excess.
- Screening for liver cancer in people with certain types of hemochromatosis (iron overload).
- Screening for liver cancer in people who have hepatitis B or C or cirrhosis.
- Controlling metabolic disorders such as obesity and diabetes.
References
Abou-Alfa GK, Jarnagin W, El Dika I, et al. Liver and bile duct cancer. In: Niederhuber JE, Armitage JO, Kastan MB, Doroshow JH, Tepper JE, eds. Abeloff's Clinical Oncology. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 77.
Di Bisceglie AM, Befeler AS. Hepatic tumors and cysts. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 96.
National Cancer Institute website. Primary liver cancer treatment (PDQ®)–health professional version. www.cancer.gov/types/liver/hp/adult-liver-treatment-pdq. Updated April 17, 2025. Accessed July 18, 2025.
National Comprehensive Cancer Network website. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: hepatocellular carcinoma. Version 1.2025. www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/hcc.pdf. Updated March 20, 2025. Accessed July 18, 2025.
-
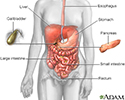
Digestive system - illustration
The esophagus, stomach, large and small intestine, aided by the liver, gallbladder and pancreas convert the nutritive components of food into energy and break down the non-nutritive components into waste to be excreted.
Digestive system
illustration
-
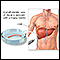
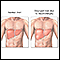
Liver biopsy - illustration
A liver biopsy is not a routine procedure, but is performed when it is necessary to determine the presence of liver disease and to look for malignancy, cysts, parasites, or other pathology. The actual procedure is only slightly uncomfortable. Most of the discomfort arises from being required to lie still for several hours afterwards to prevent bleeding from the biopsy site.
Liver biopsy
illustration
-
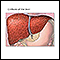
Hepatocellular cancer - CT scan - illustration
A CT scan of the upper abdomen showing an widespread (disseminated) carcinoma of the liver (hepato cellular carcinoma). The liver is the large organ on the left side of the picture. Note the moth-eaten appearance.
Hepatocellular cancer - CT scan
illustration
-
Digestive system - illustration
The esophagus, stomach, large and small intestine, aided by the liver, gallbladder and pancreas convert the nutritive components of food into energy and break down the non-nutritive components into waste to be excreted.
Digestive system
illustration
-
Liver biopsy - illustration
A liver biopsy is not a routine procedure, but is performed when it is necessary to determine the presence of liver disease and to look for malignancy, cysts, parasites, or other pathology. The actual procedure is only slightly uncomfortable. Most of the discomfort arises from being required to lie still for several hours afterwards to prevent bleeding from the biopsy site.
Liver biopsy
illustration
-
Hepatocellular cancer - CT scan - illustration
A CT scan of the upper abdomen showing an widespread (disseminated) carcinoma of the liver (hepato cellular carcinoma). The liver is the large organ on the left side of the picture. Note the moth-eaten appearance.
Hepatocellular cancer - CT scan
illustration
Review Date: 7/9/2025
Reviewed By: Warren Brenner, MD, Oncologist, Lynn Cancer Institute, Boca Raton, FL. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.