Primary biliary cholangitis
Primary biliary cirrhosis (the old name for the disease); PBCThe bile ducts are tubes that move bile from the liver to the small intestine. Bile is a substance that helps with digestion. All of the bile ducts together are called the biliary tract.
Bile
Bile is a fluid that is made and released by the liver and stored in the gallbladder. Bile helps with digestion. It breaks down fats into fatty acid...

When the bile ducts become swollen or inflamed, this blocks the flow of bile. These changes can lead to scarring of the liver called cirrhosis. This is called biliary cirrhosis. Advanced cirrhosis can lead to liver failure.
Causes
The cause of inflamed bile ducts in the liver is not known. However, primary biliary cholangitis is an autoimmune disorder. That means your body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue. The disease may be linked to autoimmune disorders such as:
Autoimmune disorders
An autoimmune disease occurs when the body's immune system attacks and destroys healthy body tissue by mistake. There are more than 80 autoimmune di...
-
Celiac disease
Celiac disease
Celiac disease is an autoimmune condition that damages the lining of the small intestine. This damage comes from a reaction to eating gluten. This ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Raynaud phenomenon
Raynaud phenomenon
Raynaud phenomenon is a condition in which cold temperatures or strong emotions cause blood vessel spasms. This blocks blood flow to the affected re...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Sicca syndrome (dry eyes or mouth)
- Thyroid disease
The disease most often affects middle-aged women.
Symptoms
More than one half of people have no symptoms at the time of diagnosis. Symptoms most often begin slowly. Early symptoms may include:
- Nausea and belly pain
- Fatigue and loss of energy
- Fatty deposits under the skin
- Fatty stools
- Itching (pruritus)
- Poor appetite and weight loss
As liver function worsens, symptoms may include:
- Fluid buildup in the legs (edema) and in the abdomen (ascites)
- Yellow color in the skin, mucous membranes, or eyes (jaundice)
- Redness on the palms of the hands
- In men, impotence, shrinking of the testicles, and breast swelling
- Easy bruising and abnormal bleeding, most often from swollen veins in the digestive tract
- Confusion or problems thinking
- Pale or clay-colored stools
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will do a physical exam.
The following tests can check to see if your liver is working properly:
- Albumin blood test
-
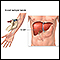
Liver function tests (serum alkaline phosphatase is most important)
Liver function tests
Liver function tests are common tests that are used to see how well the liver is working. Tests include:AlbuminAlpha-1 antitrypsinAlkaline phosphata...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Prothrombin time (PT)
Prothrombin time
Prothrombin time (PT) is a blood test that measures the time it takes for the liquid portion (plasma) of your blood to clot. It measures the functio...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Cholesterol and lipoprotein blood tests
Other tests that can help measure how severe liver disease may be include:
- Elevated immunoglobulin M level in the blood
-
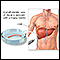
Liver biopsy
Liver biopsy
A liver biopsy is a test that takes a sample of tissue from the liver for examination.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Anti-mitochondrial antibodies (results are positive in about 95% of cases)
Anti-mitochondrial antibodies
Antimitochondrial antibodies (AMA) are substances (antibodies) that form against mitochondria. The mitochondria are an important part of cells. The...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Other antibody levels (especially if the anti-mitochondrial antibodies are negative)
- Special types of ultrasound or MRI that measure the amount of scar tissue (may be called elastography)
- Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP)
Treatment
The goal of treatment is to ease symptoms and prevent complications.
Cholestyramine (or colestipol) may reduce the itching. Ursodeoxycholic acid may improve removal of bile from the bloodstream. This may improve survival in some people. A newer drug called obeticholic acid (Ocaliva) is also available.
Vitamin replacement therapy restores vitamins A, K, E and D, which are lost in the fatty stools that may occur in people with primary biliary cholangitis. A calcium supplement or other bone medicines may be added to prevent or treat weak or soft bones.
Weak or soft bones
Osteoporosis is a disease in which bones become fragile and more likely to break (fracture).

Long-term monitoring and treatment of liver failure is needed.
Monitoring and treatment of liver failu...
Cirrhosis is scarring of the liver that often eventually causes poor liver function. It is the most advanced stage of chronic liver disease. You we...
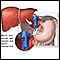
Liver transplant may be successful if it is done before liver failure occurs.
Liver transplant
Liver transplant is surgery to replace a diseased liver with a healthy liver.
Outlook (Prognosis)
The outcome can vary. If the condition is not treated, most people will die without a liver transplant. About one quarter of people who have had the disease for 10 years will have liver failure. Doctors can now use a statistical model to predict the best time to do the transplant. Other diseases, such as hypothyroidism and anemia, can also develop. DEXA scans for bone health are checked regularly.
Possible Complications
Progressive cirrhosis can lead to liver failure. Complications can include:
- Bleeding
- Damage to the brain (encephalopathy)
Encephalopathy
Loss of brain function occurs when the liver is unable to remove toxins from the blood. This is called hepatic encephalopathy (HE). This problem ma...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Fluid and electrolyte imbalance
Electrolyte
Electrolytes are minerals in your blood and other body fluids that carry an electric charge. Electrolytes affect how your body functions in many ways...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Kidney failure
-
Malabsorption
Malabsorption
Malabsorption involves problems with the body's ability to take in (absorb) nutrients from food.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Malnutrition
Malnutrition
Malnutrition is the condition that occurs when your body does not get enough nutrients.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Soft or weak bones (osteomalacia or osteoporosis)
- Ascites (fluid buildup in the abdominal cavity)
- Increased risk of liver cancer
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you have:
- Abdominal swelling
-
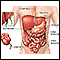
Blood in the stools
Blood in the stools
Black or tarry stools with a foul smell are a sign of a problem in the upper digestive tract. It most often indicates that there is bleeding in the ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Confusion
- Jaundice
- Itching of the skin that does not go away and is not related to other causes
-
Vomiting blood
Vomiting blood
Vomiting blood is regurgitating (throwing up) contents of the stomach that contains blood. Vomited blood may appear bright red, dark red, or look lik...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article
References
Eaton JE, Lindor KD. Primary biliary cholangitis. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 91.
Fogel EL, Sherman S. Diseases of the gallbladder and bile ducts. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 141.
Garcia-Tsao G. Cirrhosis and its sequelae. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 139.
Lamps LW. Liver: non-neoplastic diseases. In: Goldblum JR, Lamps LW, McKenney JK, Myers JL, eds. Rosai and Ackerman's Surgical Pathology. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 19.
-
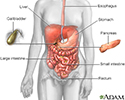
Digestive system - illustration
The esophagus, stomach, large and small intestine, aided by the liver, gallbladder and pancreas convert the nutritive components of food into energy and break down the non-nutritive components into waste to be excreted.
Digestive system
illustration
-
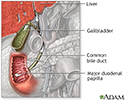
Bile pathway - illustration
The biliary system is comprised of the organs and duct system that create, transport, store and release bile into the duodenum for digestion. Includes the liver, gallbladder and bile ducts (named the cystic, hepatic, common, and pancreatic duct).
Bile pathway
illustration
-
Digestive system - illustration
The esophagus, stomach, large and small intestine, aided by the liver, gallbladder and pancreas convert the nutritive components of food into energy and break down the non-nutritive components into waste to be excreted.
Digestive system
illustration
-
Bile pathway - illustration
The biliary system is comprised of the organs and duct system that create, transport, store and release bile into the duodenum for digestion. Includes the liver, gallbladder and bile ducts (named the cystic, hepatic, common, and pancreatic duct).
Bile pathway
illustration
Review Date: 6/11/2024
Reviewed By: Jenifer K. Lehrer, MD, Department of Gastroenterology, Aria - Jefferson Health Torresdale, Jefferson Digestive Diseases Network, Philadelphia, PA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.