Cholangitis
Cholangitis is an infection of the bile ducts, the tubes that carry bile from the liver to the gallbladder and intestines. Bile is a liquid made by the liver that helps digest food.
Bile
Bile is a fluid that is made and released by the liver and stored in the gallbladder. Bile helps with digestion. It breaks down fats into fatty acid...

Causes
Cholangitis is most often caused by bacteria. This can occur when the duct is blocked by something, such as a gallstone or tumor. The infection causing this condition may also spread to the liver.
Risk factors include a previous history of gallstones, sclerosing cholangitis, HIV, narrowing of the common bile duct, and rarely, travel to countries where you might catch a worm or parasite infection.
Gallstones
Gallstones are hard deposits that form inside the gallbladder. These may be as small as a grain of sand or as large as a golf ball.

Symptoms
The following symptoms may occur:
-
Pain on the upper right side or upper middle part of the abdomen. It may also be felt in the back or below the right shoulder blade. The pain may come and go and feel sharp, cramp-like, or dull.
Pain
Abdominal pain is pain that you feel anywhere between your chest and groin. This is often referred to as the stomach region or belly.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Fever and chills.
- Dark urine and clay-colored or pale stools.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Yellowing of the skin (jaundice), which may come and go.
Exams and Tests
You may have the following tests to look for blockages:
-
Abdominal ultrasound
Abdominal ultrasound
Abdominal ultrasound is a type of imaging test. It is used to look at organs in the abdomen, including the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, and kidneys...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - CT scan
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)
- Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP)
-
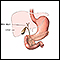
Percutaneous transhepatic cholangiogram (PTCA)
Percutaneous transhepatic cholangiogram
A percutaneous transhepatic cholangiogram (PTC) is an x-ray of the bile ducts. These are the tubes that carry bile from the liver to the gallbladder...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
You may also have the following blood tests:
-
Bilirubin level
Bilirubin
The bilirubin blood test measures the level of bilirubin in the blood. Bilirubin is a yellowish pigment found in bile, a fluid made by the liver. Bi...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Liver enzyme levels
-
Liver function tests
Liver function tests
Liver function tests are common tests that are used to see how well the liver is working. Tests include:AlbuminAlpha-1 antitrypsinAlkaline phosphata...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
White blood count (WBC)
White blood count
A WBC count is a blood test to measure the number of white blood cells (WBCs) in the blood. It is a part of a complete blood count (CBC). WBCs are a...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
Quick diagnosis and treatment are very important.
Antibiotics to cure infection are the first treatment done in most cases. ERCP or other surgical procedure is done when the person is stable. ERCP will drain the infection, which is usually needed along with antibiotics.
People who are very ill or are quickly getting worse may need surgery right away.
Outlook (Prognosis)
The outcome is very often good with treatment, but poor without it.
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
-
Sepsis
Sepsis
Sepsis is an illness in which the body has a severe, inflammatory response to bacteria or other germs.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your health care provider if you have symptoms of cholangitis.
Prevention
Treatment of gallstones, tumors, and infestations of parasites may reduce the risk for some people. A metal or plastic stent that is placed in the bile system may be needed to prevent the infection from returning.
Stent
A stent is a tiny tube placed into a hollow structure in your body. This structure can be an artery, a vein, or another structure, such as the tube ...
References
Fogel EL, Sherman S. Diseases of the gallbladder and bile ducts. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 141.
Sifri CD, Madoff LC. Infections of the liver and biliary system (liver abscess, cholangitis, cholecystitis). In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 75.
-
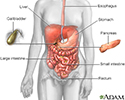
Digestive system - illustration
The esophagus, stomach, large and small intestine, aided by the liver, gallbladder and pancreas convert the nutritive components of food into energy and break down the non-nutritive components into waste to be excreted.
Digestive system
illustration
-
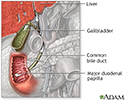
Bile pathway - illustration
The biliary system is comprised of the organs and duct system that create, transport, store and release bile into the duodenum for digestion. Includes the liver, gallbladder and bile ducts (named the cystic, hepatic, common, and pancreatic duct).
Bile pathway
illustration
-
Digestive system - illustration
The esophagus, stomach, large and small intestine, aided by the liver, gallbladder and pancreas convert the nutritive components of food into energy and break down the non-nutritive components into waste to be excreted.
Digestive system
illustration
-
Bile pathway - illustration
The biliary system is comprised of the organs and duct system that create, transport, store and release bile into the duodenum for digestion. Includes the liver, gallbladder and bile ducts (named the cystic, hepatic, common, and pancreatic duct).
Bile pathway
illustration
Review Date: 6/11/2024
Reviewed By: Jenifer K. Lehrer, MD, Department of Gastroenterology, Aria - Jefferson Health Torresdale, Jefferson Digestive Diseases Network, Philadelphia, PA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.