Cholangiocarcinoma
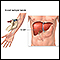
Bile duct cancerCholangiocarcinoma (CCA) is a rare cancerous (malignant) growth in one of the ducts that carries bile from the liver to the small intestine.
Bile
Bile is a fluid that is made and released by the liver and stored in the gallbladder. Bile helps with digestion. It breaks down fats into fatty acid...

Causes
The exact cause of CCA isn't known. However, many of these tumors are already quite advanced by the time they are found.
CCA may start anywhere along the bile ducts. These tumors block off the bile ducts.
Both men and women are affected. Most people are older than 65.
People with the following health problems may have a higher chance of developing CCA:
-
Bile duct (choledochal) cysts
Cysts
A cyst is a closed pocket or pouch of tissue. It can be filled with air, fluid, pus, or other material.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Chronic biliary and liver inflammation
Biliary
The biliary system creates, moves, stores, and releases bile into the duodenum. This helps the body digest food. It also assists in transporting wa...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - History of infection with parasitic worms, liver flukes
-
Primary sclerosing cholangitis
Sclerosing cholangitis
Sclerosing cholangitis refers to swelling (inflammation), scarring, and destruction of the bile ducts inside and outside of the liver.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Ulcerative colitis
Ulcerative colitis
Ulcerative colitis is a condition in which the lining of the large intestine (colon) and rectum become inflamed. It is a form of inflammatory bowel ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Symptoms
Symptoms of CCA may include any of the following:
-
Fever and chills
Fever
Fever is the temporary increase in the body's temperature in response to a disease or illness. A child has a fever when the temperature is at or abov...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Clay-colored stools and dark urine
-
Itching
Itching
Itching is a tingling or irritation of the skin that makes you want to scratch the area. Itching may occur all over the body or only in one location...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Loss of appetite
Loss of appetite
A decreased appetite is when your desire to eat is reduced. The medical term for a loss of appetite is anorexia.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Pain in the upper right abdomen that may radiate to the back
-
Weight loss
Weight loss
Unexplained weight loss is a decrease in body weight, when you did not try to lose the weight on your own. Many people gain and lose weight. Uninten...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Yellowing of the skin (jaundice)
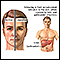
Jaundice
Jaundice is a yellow color of the skin, mucus membranes, or eyes. The yellow coloring comes from bilirubin, a byproduct of old red blood cells. Jau...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will perform a physical exam. Tests will be done to check for a tumor or blockage in the bile duct. These may include:
-
Abdominal CT scan
Abdominal CT scan
An abdominal CT scan is an imaging test that uses x-rays to create cross-sectional pictures of the belly area. CT stands for computed tomography....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
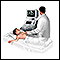
Abdominal ultrasound
Abdominal ultrasound
Abdominal ultrasound is a type of imaging test. It is used to look at organs in the abdomen, including the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, and kidneys...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Procedure that uses a viewing scope to look at the bile ducts (endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography or ERCP), during which tissue may be taken and looked at under a microscope
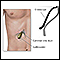
ERCP
ERCP is short for endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. It is a procedure that looks at the bile and pancreatic ducts. It is done through...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleTissue may be taken
A biliary tract biopsy is the removal of small amounts of cells and fluids from the duodenum, bile ducts, pancreas, or pancreatic duct. The sample i...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Blood tests that may be done include:
-
Liver function tests (especially alkaline phosphatase or bilirubin levels)
Liver function tests
Liver function tests are common tests that are used to see how well the liver is working. Tests include:AlbuminAlpha-1 antitrypsinAlkaline phosphata...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleBilirubin
The bilirubin blood test measures the level of bilirubin in the blood. Bilirubin is a yellowish pigment found in bile, a fluid made by the liver. Bi...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Complete blood count (CBC)
Complete blood count
A complete blood count (CBC) test measures the following:The number of white blood cells (WBC count)The number of red blood cells (RBC count)The numb...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
The goal is to treat the cancer and the blockage it causes. When possible, surgery to remove the tumor is the treatment of choice and may result in a cure. Often the cancer has already spread locally or to another area of the body by the time it is diagnosed. As a result, surgery to cure the cancer is not possible.
Chemotherapy or radiation may be given after surgery to decrease the risk of the cancer returning.
Chemotherapy
The term chemotherapy is used to describe cancer-killing drugs. Chemotherapy may be used to:Cure the cancerShrink the cancerPrevent the cancer from ...
Radiation
Radiation therapy uses high-powered radiation (such as x-rays or gamma rays), particles, or radioactive seeds to kill cancer cells.
In select cases, a liver transplant can be tried.
Endoscopic therapy with stent placement can temporarily relieve blockages in the biliary ducts. This may also relieve jaundice when the tumor cannot be removed.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Completely removing the tumor allows some people to survive with the possibility of complete cure.
The survival time varies greatly from several months to several years. Outlook depends on:
- The location of CCA
- The cell type of CCA
- The stage of the tumor
- The person's age and general health
- Whether surgery is an option
- The person's response to treatment
If the tumor cannot be completely removed, a cure is generally not possible. With treatment, about one half of affected people live a year, and about one half live longer, but rarely beyond 5 years. You and your family may want to start thinking about end-of-life planning, such as:
-
Palliative care
Palliative care
Polycythemia means there are too many red blood cells (RBCs) in an infant's blood.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Hospice care
-
Advance care directives
Advance care directives
Membranous nephropathy is a kidney disorder that leads to changes and inflammation of the structures inside the kidney that help filter wastes and fl...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Health care agents
Possible Complications
Complications of CCA include:
- Infection
- Liver failure
- Spread (metastasis) of tumor to other organs
Metastasis
Metastasis is the movement or spreading of cancer cells from one organ or tissue to another. Cancer cells usually spread through the blood or the ly...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you have jaundice or other symptoms of cholangiocarcinoma.
References
Gibson RN, Sutherland TR. The biliary system. In: Adam A, Dixon AK, Gillard JH, Schaefer-Prokop CM, eds. Grainger & Allison's Diagnostic Radiology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 24.
Koea JB. Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. In: Jarnagin WR, ed. Blumgart's Surgery of the Liver, Biliary Tract and Pancreas. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 50.
National Cancer Institute website. Bile duct cancer (cholangiocarcinoma) treatment (PDQ) -- health professional version. www.cancer.gov/types/liver/hp/bile-duct-treatment-pdq. Updated March 28, 2024. Accessed December 2, 2024.
Rizvi SH, Gores GJ. Tumors of the bile ducts, gallbladder, and ampulla. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 69.
-
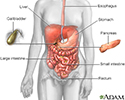
Digestive system - illustration
The esophagus, stomach, large and small intestine, aided by the liver, gallbladder and pancreas convert the nutritive components of food into energy and break down the non-nutritive components into waste to be excreted.
Digestive system
illustration
-
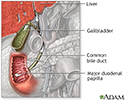
Bile pathway - illustration
The biliary system is comprised of the organs and duct system that create, transport, store and release bile into the duodenum for digestion. Includes the liver, gallbladder and bile ducts (named the cystic, hepatic, common, and pancreatic duct).
Bile pathway
illustration
-
Digestive system - illustration
The esophagus, stomach, large and small intestine, aided by the liver, gallbladder and pancreas convert the nutritive components of food into energy and break down the non-nutritive components into waste to be excreted.
Digestive system
illustration
-
Bile pathway - illustration
The biliary system is comprised of the organs and duct system that create, transport, store and release bile into the duodenum for digestion. Includes the liver, gallbladder and bile ducts (named the cystic, hepatic, common, and pancreatic duct).
Bile pathway
illustration
Review Date: 6/17/2024
Reviewed By: Todd Gersten, MD, Hematology/Oncology, Florida Cancer Specialists & Research Institute, Wellington, FL. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.