Diabetes eye exams
Diabetic retinopathy - eye exams; Diabetes - eye exams; Glaucoma - diabetic eye exam; Macular edema - diabetic eye examDiabetes can harm your eyes. It can damage the small blood vessels in your retina, the back wall of your eyeball. This condition is called diabetic retinopathy.
Diabetes
Diabetes is a long-term (chronic) disease in which the body cannot regulate the amount of sugar in the blood.
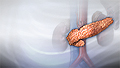
Retina
The retina is the light-sensitive layer of tissue at the back of the eyeball. Images that come through the eye's lens are focused on the retina. Th...
Diabetic retinopathy
Diabetes can harm the eyes. It can damage the small blood vessels in the retina, the back part of your eye. This condition is called diabetic retin...

Diabetes also increases your risk of glaucoma, cataracts, and other eye problems.
Glaucoma
Glaucoma is a group of eye conditions that can damage the optic nerve. This nerve sends the images you see to your brain. Most often, optic nerve da...

You may not notice that your eyes are damaged until the problem is very bad. Your eye doctor (optometrist or ophthalmologist) can catch problems early if you get regular eye exams. This is very important. The early stages of diabetic retinopathy don't cause changes in vision and you won't have symptoms. Only an eye exam can detect the problem, so that steps can be taken to prevent the eye damage from getting worse.
You Need Regular Eye Exams
Even if the health care provider who takes care of your diabetes checks your eyes, you need an eye exam every 1 to 2 years by an eye doctor who takes care of people with diabetes. An eye doctor has equipment that can check the back of your eye much better than your regular provider can.
If you have eye problems because of diabetes, you will probably see your eye doctor more often. You may need special treatment to prevent your eye problems from getting worse.
You may see two different types of eye doctors:
- An optometrist is a doctor of optometry. Optometrists provide regular eye and vision care and monitor diabetes-related eye conditions.
- An ophthalmologist is a medical doctor who is an eye specialist. Along with regular eye and vision care, an ophthalmologist treats more involved eye conditions that may require medicines or surgery.
What is a Dilated Retinal Exam?
The doctor will check your vision using a chart of random letters of different sizes. This is called the Snellen chart.
You will then be given eye drops to widen (dilate) the pupils of your eyes so that the doctor can better see the back of the eye. You may feel stinging when the drops are first placed. You may have a metallic taste in your mouth.
To see the back of your eye, the doctor looks through a special magnifying glass using a bright light. The doctor can then see areas that may be damaged by diabetes:
- Blood vessels in the front or middle parts of the eye
- The back of the eye
- The optic nerve area
Another device called a slit lamp is used to see the clear surface of the eye (cornea).
The doctor may take photos of the back of your eye to get a more detailed exam. This exam is called a digital retinal scan (or imaging). A special camera is used to take photos of your retina without dilating your eyes. The doctor then views the photos and lets you know if you need more tests or treatment.
After Your eye Exam
If you had drops to dilate your eyes, your vision will be blurred for about 6 hours. It will be harder to focus on things that are near. You should have someone drive you home.
Also, sunlight can damage your eye more easily when your pupils are dilated. Wear dark glasses or shade your eyes until the effects of the drops wear off.
References
American Academy of Ophthalmology website. Diabetic retinopathy PPP 2019. www.aao.org/preferred-practice-pattern/diabetic-retinopathy-ppp. Updated October 2019. Accessed July 30, 2024.
American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 12. Retinopathy, neuropathy, and foot care: standards of medical care in diabetes-2024. Diabetes Care. 2024;47(Suppl 1):S231-S243. PMID: 38078577 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38078577/.
Brownlee M, Aiello LP, Sun JK, et al. Complications of diabetes mellitus. In: Melmed S, Auchus, RJ, Goldfine AB, Koenig RJ, Kopp PA, eds. Williams Textbook of Endocrinology. 15th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 38.
Skugor M. Diabetes mellitus. In: Sadda SVR, Saraff D, Freund KB, et al, eds. Ryan's Retina. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 48.
-
Diabetic retinopathy - illustration
Diabetes causes an excessive amount of glucose to remain in the blood stream which may cause damage to the blood vessels. Within the eye the damaged vessels may leak blood and fluid into the surrounding tissues and cause vision problems.
Diabetic retinopathy
illustration
-
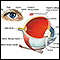
External and internal eye anatomy - illustration
The cornea allows light to enter the eye. As light passes through the eye the iris changes shape by expanding and letting more light through or constricting and letting less light through to change pupil size. The lens then changes shape to allow the accurate focusing of light on the retina. Light excites photoreceptors that eventually, through a chemical process, transmit nerve signals through the optic nerve to the brain. The brain processes these nerve impulses into sight.
External and internal eye anatomy
illustration
-
Diabetic retinopathy - illustration
Diabetes causes an excessive amount of glucose to remain in the blood stream which may cause damage to the blood vessels. Within the eye the damaged vessels may leak blood and fluid into the surrounding tissues and cause vision problems.
Diabetic retinopathy
illustration
-
External and internal eye anatomy - illustration
The cornea allows light to enter the eye. As light passes through the eye the iris changes shape by expanding and letting more light through or constricting and letting less light through to change pupil size. The lens then changes shape to allow the accurate focusing of light on the retina. Light excites photoreceptors that eventually, through a chemical process, transmit nerve signals through the optic nerve to the brain. The brain processes these nerve impulses into sight.
External and internal eye anatomy
illustration
Review Date: 7/21/2024
Reviewed By: Sandeep K. Dhaliwal, MD, board-certified in Diabetes, Endocrinology, and Metabolism, Springfield, VA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.



