Urethritis
Urethral syndrome; NGU; Non-gonococcal urethritisUrethritis is inflammation (swelling and irritation) of the urethra. The urethra is the tube that carries urine from the body.
Causes
Both bacteria and viruses may cause urethritis. Some of the bacteria that cause this condition include E coli, chlamydia, and gonorrhea. These bacteria also cause urinary tract infections (UTIs) and some sexually transmitted diseases. Viral causes are herpes simplex virus and cytomegalovirus.
Chlamydia
Chlamydia is an infection caused by the bacteria Chlamydia trachomatis. It is most often spread through sexual contact.
Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea is a common sexually transmitted infection (STI).
Urinary tract infections
A urinary tract infection, or UTI, is an infection of the urinary tract. The infection can occur at different points in the urinary tract, including...
Herpes simplex virus
Genital herpes is a sexually transmitted infection. It is caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV). This article focuses on HSV type 2 infection....
Other causes include:
- Injury
- Sensitivity to the chemicals used in spermicides, contraceptive jellies, or foams
Sometimes the cause is unknown.
Risks for urethritis include:
- Being a female
- Being male, ages 20 to 35
- Having many sexual partners
- High-risk sexual behavior (such as men having penetrating anal sex without a condom)
- History of sexually transmitted diseases
Symptoms
In men:
-
Blood in the urine or semen
Blood in the urine or semen
Blood in the semen is called hematospermia. It may be in amounts too small to be seen except with a microscope, or it may be visible in the ejaculat...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Burning pain while urinating (dysuria)
Dysuria
Painful urination is any pain, discomfort, or burning sensation when passing urine.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Discharge from penis
- Fever (rare)
-
Frequent or urgent urination
Frequent or urgent urination
Frequent urination means needing to urinate more often than usual. Urgent urination is a sudden, strong need to urinate. This causes a discomfort i...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Itching, tenderness, or swelling in penis
- Enlarged lymph nodes in the groin area
- Pain with intercourse or ejaculation
In women:
- Abdominal pain
- Burning pain while urinating
- Fever and chills
- Frequent or urgent urination
- Pelvic pain
- Pain with intercourse
- Vaginal discharge
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will examine you. In men, the exam will include the abdomen, bladder area, penis, and scrotum. The physical exam may show:
- Discharge from the penis
- Tender and enlarged lymph nodes in the groin area
- Tender and swollen penis
A digital rectal exam will also be performed.
Digital rectal exam
A digital rectal exam is an exam of the lower rectum. Your health care provider uses a gloved, lubricated finger to check for any abnormal findings....
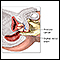
Women will have abdominal and pelvic exams. The provider will check for:
- Discharge from the urethra
- Tenderness of the lower abdomen
- Tenderness of the urethra
The following tests may be done:
-
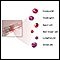
Complete blood count (CBC)
Complete blood count
A complete blood count (CBC) test measures the following:The number of white blood cells (WBC count)The number of red blood cells (RBC count)The numb...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
C-reactive protein test
C-reactive protein test
C-reactive protein (CRP) is produced by the liver. The level of CRP rises when there is inflammation in the body. It is one of a group of proteins,...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Cystoscopy (examination of the urethra and bladder with a camera)
- Pelvic ultrasound (women only)
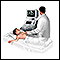
Ultrasound
Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to make images of organs and structures inside the body.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Pregnancy test (women only)
-
Urinalysis and urine cultures
Urinalysis
Urinalysis is the physical, chemical, and microscopic examination of urine. It involves a number of tests to detect and measure various compounds th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Tests for gonorrhea, chlamydia, and other sexually transmitted illnesses (STI)
Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea is a common sexually transmitted infection (STI).
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleChlamydia
Chlamydia is an infection caused by the bacteria Chlamydia trachomatis. It is most often spread through sexual contact.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Urethral swab
Treatment
The goals of treatment are to:
- Get rid of the cause of infection
- Improve symptoms
- Prevent the spread of infection
If you have a bacterial infection, you will be given antibiotics.
You may take both pain relievers for general body pain and products for localized urinary tract pain, plus antibiotics.
People with urethritis who are being treated should avoid sex, or use condoms during sex. Your sexual partner must also be treated if the condition is caused by an infection.
Urethritis caused by trauma or chemical irritants is treated by avoiding the source of injury or irritation.
Urethritis that does not clear up after antibiotic treatment and lasts for at least 6 weeks is called chronic urethritis. Different antibiotics may be used to treat this problem.
Outlook (Prognosis)
With the correct diagnosis and treatment, urethritis most often clears up without further problems.
However, urethritis can lead to long-term damage to the urethra and scar tissue called a urethral stricture. It can also cause damage to other urinary organs in both men and women. In women, the infection could lead to fertility problems if it spreads to the pelvis.
Urethral stricture
Urethral stricture is an abnormal narrowing of the urethra. The urethra is the tube that carries urine out of the body from the bladder.

Possible Complications
Men with urethritis are at risk for the following:
- Bladder infection (cystitis)
Cystitis
A urinary tract infection, or UTI, is an infection of the urinary tract. The infection can occur at different points in the urinary tract, including...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
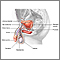
Epididymitis
Epididymitis
Epididymitis is swelling (inflammation) of the tube that connects the testicle with the vas deferens. The tube is called the epididymis.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Infection in the testicles (orchitis)
Orchitis
Orchitis is swelling (inflammation) of one or both of the testicles.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Prostate infection (prostatitis)
After a severe infection, the urethra may become scarred and then narrowed.
Women with urethritis are at risk for the following:
- Bladder infection (cystitis)
-
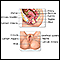
Cervicitis
Cervicitis
Cervicitis is swelling or inflamed tissue of the end of the uterus (cervix).
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID -- an infection of the uterus lining, fallopian tubes, or ovaries)
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you have symptoms of urethritis.
Prevention
Things you can do to help avoid urethritis include:
- Keep the area around the opening of the urethra clean.
- Follow safer sex practices. Have one sexual partner only (monogamy) and use condoms.
References
Babu TM, Urban MA, Augenbraun MH. Urethritis. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 107.
Swygard H, Cohen MS. Approach to the patient with a sexually transmitted infection. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 264.
-
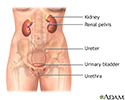
Female urinary tract - illustration
The female and male urinary tracts are relatively the same except for the length of the urethra.
Female urinary tract
illustration
-
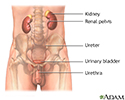
Male urinary tract - illustration
The male and female urinary tracts are relatively the same except for the length of the urethra.
Male urinary tract
illustration
-
Female urinary tract - illustration
The female and male urinary tracts are relatively the same except for the length of the urethra.
Female urinary tract
illustration
-
Male urinary tract - illustration
The male and female urinary tracts are relatively the same except for the length of the urethra.
Male urinary tract
illustration
Review Date: 9/2/2024
Reviewed By: Kelly L. Stratton, MD, FACS, Associate Professor, Department of Urology, University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City, OK. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.