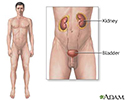
Analgesic nephropathy
Phenacetin nephritis; Nephropathy - analgesic; Nephropathy - NSAIDAnalgesic nephropathy involves damage to one or both kidneys caused by overexposure to mixtures of medicines, especially over-the-counter pain medicines (analgesics).
Causes
Analgesic nephropathy involves damage within the internal structures of the kidney. It is caused by long-term use of analgesics (pain medicines), especially over-the-counter (OTC) medicines that contain phenacetin or acetaminophen, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as aspirin, ibuprofen, or naproxen.
This condition frequently occurs as a result of self-medicating, often for some type of chronic pain such as headache or arthritis.
Risk factors include:
- Use of OTC analgesics containing more than one active ingredient
- Taking 6 or more pills a day for 3 years
- Chronic headaches, painful menstrual periods, backache, or musculoskeletal pain
- Emotional or behavioral changes
- History of dependent behaviors including smoking, alcohol use, and excessive use of tranquilizers
Symptoms
There may be no symptoms in the beginning. Over time, as the kidneys are injured by the medicine, symptoms of kidney disease will develop, including:
Kidney disease
Chronic kidney disease is the slow loss of kidney function over time. The main job of the kidneys is to remove wastes and excess water from the body...

- Fatigue, weakness
-
Increased urinary frequency or urgency
Increased urinary frequency or urgency
Frequent urination means needing to urinate more often than usual. Urgent urination is a sudden, strong need to urinate. This causes a discomfort i...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Blood in the urine
-
Flank pain or back pain
Flank pain
Flank pain is pain in one side of the body between the upper belly area (abdomen) and the back.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Decreased urine output
Decreased urine output
Decreased urine output means that you produce less urine than normal. Most adults make at least 500 milliliters of urine in 24 hours (a little over ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Decreased alertness, including drowsiness, confusion, and lethargy
Decreased alertness
Decreased alertness is a state of reduced awareness and is often a serious condition. A coma is the most severe state of decreased alertness in which...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Decreased sensation, numbness (especially in the legs)
- Nausea, vomiting
- Easy bruising or bleeding
- Swelling (edema) throughout the body
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will examine you and ask about your symptoms. During the exam, your provider may find:
- Your blood pressure is high.
- When listening with a stethoscope, your heart and lungs have abnormal sounds.
- You have swelling, especially in the lower legs.
- Your skin shows premature aging.
Tests that may be done include:
-
Complete blood count
Complete blood count
A complete blood count (CBC) test measures the following:The number of white blood cells (WBC count)The number of red blood cells (RBC count)The numb...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - CT scan of kidney
-
Intravenous pyelogram (IVP)
Intravenous pyelogram
An intravenous pyelogram (IVP) is a special x-ray exam of the kidneys, bladder, and ureters (the tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladd...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Toxicology screen
Toxicology screen
A toxicology screen refers to various tests that determine the type and approximate amount of legal and illegal drugs a person has taken by measuring...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Urinalysis
Urinalysis
Urinalysis is the physical, chemical, and microscopic examination of urine. It involves a number of tests to detect and measure various compounds th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Kidney ultrasound
Treatment
The primary goals of treatment are to prevent further damage of the kidneys and to treat kidney failure. Your provider may tell you to stop taking all suspect painkillers, particularly OTC medicines.
To treat kidney failure, your provider may suggest diet changes and fluid restriction. Eventually, dialysis or a kidney transplant may be needed.
Dialysis
Dialysis treats end-stage kidney disease also called kidney failure. It removes waste from your blood when your kidneys can no longer do their job. ...

Kidney transplant
A kidney transplant is surgery to place a healthy kidney into a person with kidney failure.

Counseling may help you develop alternative methods of controlling chronic pain.
Outlook (Prognosis)
The damage to the kidney may be acute and temporary, or chronic and long term.
Possible Complications
Complications that may result from analgesic nephropathy include:
-
Acute kidney failure
Acute kidney failure
Acute kidney failure is the rapid (less than 2 days) loss of your kidneys' ability to remove waste and help balance fluids and electrolytes in your b...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Chronic kidney failure
Chronic kidney failure
Chronic kidney disease is the slow loss of kidney function over time. The main job of the kidneys is to remove wastes and excess water from the body...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Kidney disorder in which the spaces between the kidney tubules become inflamed
(interstitial nephritis)
Interstitial nephritis
Interstitial nephritis is a kidney disorder in which the spaces between the kidney tubules become swollen (inflamed). This can cause problems with t...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Tissue death in areas where the openings of the collecting ducts enter the kidney and where urine flows into the ureters
(renal papillary necrosis)
Renal papillary necrosis
Renal papillary necrosis is a disorder of the kidneys in which all or part of the renal papillae die. The renal papillae are the areas where the ope...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Urinary tract infections that are ongoing or keep coming back
- High blood pressure
-
Cancer of the kidney or ureter
Cancer
Cancer is the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the body. Cancerous cells are also called malignant cells.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you have any of the following:
- Symptoms of analgesic nephropathy, especially if you have been using painkillers for a long time
- Blood or solid material in your urine
- Amount of your urine has decreased
Prevention
Follow your provider's instructions when using medicines, including OTCs. Do not take more than the recommended dose without asking your provider.
References
Aronson JK. Paracetamol (acetaminophen) and combinations. In: Aronson JK, eds. Meyler's Side Effects of Drugs. 16th ed. Waltham, MA: Elsevier; 2016:474-493.
Parazella MA, Rosner MH. Tubulointerstitial diseases. In: Yu ASL, Chertow GM, Luyckx VA, Marsden PA, Skorecki K, Taal MW, eds. Brenner and Rector's The Kidney. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 35.
Segal MS, Yu X. Herbal and over-the-counter medicines and the kidney. In: Johnson RJ,, Floege J, Tonelli M, eds. Comprehensive Clinical Nephrology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 79.
Review Date: 8/28/2023
Reviewed By: Walead Latif, MD, Nephrologist and Clinical Associate Professor, Rutgers Medical School, Newark, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.