Acute kidney failure
Kidney failure; Renal failure; Renal failure - acute; ARF; Kidney injury - acuteAcute kidney failure is the rapid (less than 2 days) loss of your kidneys' ability to remove waste and help balance fluids and electrolytes in your body.
Electrolytes
Electrolytes are minerals in your blood and other body fluids that carry an electric charge. Electrolytes affect how your body functions in many ways...
Causes
There are many possible causes of kidney damage. They include:
-
Acute tubular necrosis (ATN; damage to the tubule cells of the kidneys)
Acute tubular necrosis
Acute tubular necrosis (ATN) is a kidney disorder involving damage to the tubule cells of the kidneys, which can lead to acute kidney failure. The t...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Autoimmune kidney disease
- Blood clot in the blood vessels to the kidneys
- Decreased blood flow from cholesterol (cholesterol emboli)
- Decreased blood flow due to very low blood pressure, which can result from burns, dehydration, hemorrhage, injury, septic shock, serious illness, or surgery
Burns
Burns commonly occur by direct or indirect contact with heat, electric current, radiation, or chemical agents. Burns can lead to cell death, which c...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleDehydration
Dehydration occurs when your body does not have as much water and fluids as it needs. Dehydration can be mild, moderate, or severe, based on how much...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleSeptic shock
Septic shock is a serious condition that occurs when a body-wide infection leads to dangerously low blood pressure.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Disorders that cause clotting within the kidney blood vessels
- Infections that directly injure the kidney, such as acute pyelonephritis or septicemia
Pyelonephritis
A urinary tract infection, or UTI, is an infection of the urinary tract. The infection can occur at different points in the urinary tract, including...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleSepticemia
Septicemia is an infection in the bloodstream that is caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi. Also called sepsis, septicemia is a serious, life-threa...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Pregnancy complications, including placental abruption or placenta previa
Placental abruption
The placenta is the organ that supplies nutrients and oxygen to the baby during pregnancy. Placental abruption occurs when the placenta detaches fro...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Urinary tract blockage
Urinary tract blockage
Obstructive uropathy is a condition in which the flow of urine is blocked. This causes the urine to back up and injure one or both kidneys.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Illicit drugs such as cocaine and heroin
- Medicines including non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), certain antibiotics and blood pressure medicines, intravenous contrast (dye), some cancer and HIV medicines
Symptoms
Symptoms of acute kidney failure may include any of the following:
- Blood in the stools
- Blood in the urine
-
Breath odor and metallic taste in the mouth
Breath odor
Breath odor is the scent of the air you breathe out of your mouth. Unpleasant breath odor is commonly called bad breath.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Bruising easily
-
Changes in mental status or mood
Changes in mental status
Confusion is the inability to think as clearly or quickly as you normally do. You may feel disoriented and have difficulty paying attention, remembe...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Decreased appetite
-
Decreased sensation, especially in the hands or feet
Decreased sensation
Numbness and tingling are abnormal sensations that can occur anywhere in your body, but they are often felt in your fingers, hands, feet, arms, or le...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Fatigue or slow sluggish movements
Fatigue
Fatigue is a feeling of weariness, tiredness, or lack of energy.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Flank pain (between the ribs and hips)
Flank pain
Flank pain is pain in one side of the body between the upper belly area (abdomen) and the back.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Hand tremor
Hand tremor
A tremor is a type of shaking movement. A tremor is most often noticed in the hands and arms. It may affect any body part, including the head, tong...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Heart murmur
Heart murmur
A heart murmur is a blowing, whooshing, or rasping sound heard during a heartbeat. The sound is caused by turbulent (rough) blood flow through the h...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - High blood pressure
- Nausea or vomiting, may last for days
- Nosebleeds
- Persistent hiccups
- Prolonged bleeding
-
Seizures
Seizures
A seizure is the physical changes in behavior that occurs during an episode of specific types of abnormal electrical activity in the brain. The term ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Shortness of breath
-
Swelling due to the body keeping in fluid (may be seen in the legs, ankles, and feet)
Swelling
Swelling is the enlargement of organs, skin, or other body parts. It is caused by a buildup of fluid in the tissues. The extra fluid can lead to a ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Urination changes, such as little or no urine, excessive urination at night, or urination that stops completely
Excessive urination at night
Normally, the amount of urine your body produces decreases at night. This allows most people to sleep 6 to 8 hours without having to urinate. Some p...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will examine you.
Tests to check how well your kidneys are working include:
-
BUN (blood urea nitrogen)
BUN
BUN stands for blood urea nitrogen. Urea nitrogen is what forms when protein breaks down. A test can be done to measure the amount of urea nitrogen ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Creatinine clearance
Creatinine clearance
The creatinine clearance test helps provide information about how well the kidneys are working. The test compares the creatinine level in urine with...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Serum creatinine
Serum creatinine
The creatinine blood test measures the level of creatinine in the blood. This test is done to see how well your kidneys are working. Creatinine in t...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Serum potassium and electrolyte levels
Serum potassium
This test measures the amount of potassium in the fluid portion (serum) of the blood. Potassium (K+) helps nerves and muscles communicate. It also ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Urinalysis
Urinalysis
Urinalysis is the physical, chemical, and microscopic examination of urine. It involves a number of tests to detect and measure various compounds th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Other blood tests may be done to find the underlying cause of kidney failure.
A kidney or abdominal ultrasound is the preferred test for diagnosing a blockage in the urinary tract. X-ray, CT scan, or MRI of the abdomen can also tell if there is a blockage.
X-ray
X-rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation, just like visible light. An x-ray machine sends individual x-ray waves through the body. The images...

CT scan
A computed tomography (CT) scan is an imaging method that uses x-rays to create pictures of cross-sections of the body. Related tests include:Abdomin...

MRI of the abdomen
An abdominal magnetic resonance imaging scan is an imaging test that uses powerful magnets and radio waves. The waves create pictures of the inside ...

Treatment
Once the cause is found, the goal of treatment is to help your kidneys work again and prevent fluid and waste from building up in your body while they heal. Usually, you will have to stay overnight in the hospital for treatment.
The amount of liquid you drink will be limited to the amount of urine you can produce. You will be told what you may and may not eat to reduce the buildup of toxins that the kidneys would normally remove. Your diet may need to be high in carbohydrates and low in protein, salt, and potassium.
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are one of the main nutrients in our diet. They help provide energy for our body. There are three main types of carbohydrates found i...

Protein
Proteins are the building blocks of life. Every cell in the human body contains protein. The basic structure of protein is a chain of amino acids. ...

You may need antibiotics to treat or prevent infection. Water pills (diuretics) may be used to help remove fluid from your body.
Medicines will be given through a vein to help control your blood potassium level.
You may need dialysis. This is a treatment that does what healthy kidneys normally do -- rid the body of harmful wastes, extra salt, and water. Dialysis can save your life if your potassium levels are dangerously high. Dialysis will also be used if:
Dialysis
Dialysis treats end-stage kidney disease also called kidney failure. It removes waste from your blood when your kidneys can no longer do their job. ...

- Your mental status changes
-
You develop pericarditis
Pericarditis
Pericarditis is a condition in which the sac-like covering around the heart (pericardium) becomes inflamed.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - You retain too much fluid
- You cannot remove nitrogen waste products from your body
Dialysis will most often be short term. In some cases, the kidney damage is so great that dialysis is needed permanently.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if your urine output slows or stops or you have other symptoms of acute kidney failure.
Prevention
To prevent acute kidney failure:
- Health problems such as high blood pressure or diabetes should be well controlled.
- Avoid drugs and medicines that can cause kidney injury.
References
Agarwal A, Barasch J. Acute kidney injury. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 106.
Oh MS, Briefel G, Pincus MR. Evaluation of renal function, water, electrolytes, and acid-base balance. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 24th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 15.
Weisbord SD, Palevsky PM. Prevention and management of acute kidney injury. In: Yu ASL, Chertow GM, Luyckx VA, Marsden PA, Skorecki K, Taal MW, eds. Brenner and Rector's The Kidney. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 29.
-
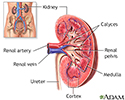
Kidney anatomy - illustration
The kidneys are responsible for removing wastes from the body, regulating electrolyte balance and blood pressure, and the stimulation of red blood cell production.
Kidney anatomy
illustration
Review Date: 5/6/2024
Reviewed By: Walead Latif, MD, Nephrologist and Clinical Associate Professor, Rutgers Medical School, Newark, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.