Poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis (GN)
Glomerulonephritis - poststreptococcal; Postinfectious glomerulonephritisPoststreptococcal glomerulonephritis (GN) is a kidney disorder that occurs after infection with certain strains of streptococcus bacteria.
Causes
Poststreptococcal GN is a form of glomerulonephritis. It is caused by an infection with a type of streptococcus bacteria. The infection does not occur in the kidneys, but in a different part of the body, such as the skin or throat. The disorder may develop 1 to 2 weeks after an untreated throat infection, or 3 to 4 weeks after a skin infection.
Glomerulonephritis
Glomerulonephritis is a type of kidney disease in which the part of your kidneys that helps filter waste and fluids from the blood is damaged....

It may occur in people of any age, but it most often occurs in children ages 6 through 10. Although skin and throat infections are common in children, poststreptococcal GN is rarely a complication of these infections. Poststreptococcal GN causes the tiny blood vessels in the filtering units of the kidneys (glomeruli) to become inflamed. This makes the kidneys less able to filter the blood to create urine.
The condition is not common today because infections that can lead to the disorder are treated with antibiotics.
Risk factors include:
-
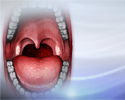
Strep throat
Strep throat
Strep throat is a disease that causes a sore throat (pharyngitis). It is an infection with a bacteria called group A streptococcus.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Streptococcal skin infections (such as impetigo)
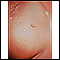
Impetigo
Impetigo is a common infection of the outermost layer of the skin.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Symptoms
Symptoms may include any of the following:
-
Decreased urine output
Decreased urine output
Decreased urine output means that you produce less urine than normal. Most adults make at least 500 milliliters of urine in 24 hours (a little over ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Rust-colored urine
- Swelling (edema), general swelling, swelling of the abdomen, swelling of the face or eyes, swelling of the feet, ankles, hands
- Visible blood in the urine
- Joint pain
- Joint stiffness or swelling
Exams and Tests
A physical examination shows swelling (edema), especially in the face. Abnormal sounds may be heard when listening to the heart and lungs with a stethoscope. Blood pressure is often high.
Other tests that may be done include:
-
Anti-DNase B
Anti-DNase B
Anti-DNase B is a blood test to look for antibodies to a substance (protein) produced by group A Streptococcus. This is the bacteria that cause stre...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Serum ASO (and streptolysin O)
Serum ASO
Antistreptolysin O (ASO) titer is a blood test to measure antibodies against streptolysin O, a substance produced by group A streptococcus bacteria. ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Serum complement levels
Serum complement levels
Complement is a blood test that measures the activity of certain proteins in the liquid portion of your blood. The complement system is a group of ne...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Urinalysis
Urinalysis
Urinalysis is the physical, chemical, and microscopic examination of urine. It involves a number of tests to detect and measure various compounds th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Kidney biopsy (usually not needed)
Kidney biopsy
A kidney biopsy is the removal of a small piece of kidney tissue for examination.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
There is no specific treatment for this disorder. Treatment is focused on relieving symptoms.
- Antibiotics, such as penicillin, will likely be used to destroy any streptococcal bacteria that remain in the body.
- Blood pressure medicines and diuretic drugs may be needed to control swelling and high blood pressure.
- Corticosteroids and other anti-inflammatory medicines are generally not effective.
You may need to limit salt in your diet to control swelling and high blood pressure.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Poststreptococcal GN usually goes away by itself after several weeks to months.
In small number of adults, it may get worse and lead to long-term (chronic) kidney failure. Sometimes, it can progress to end-stage kidney disease, which requires dialysis and a kidney transplant.
End-stage kidney disease
End-stage kidney disease (ESKD) is the last stage of long-term (chronic) kidney disease. This is when your kidneys can no longer support your body's...

Dialysis
Facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy is a condition that causes muscle weakness and loss of muscle tissue that gets worse over time.
Kidney transplant
A kidney transplant is surgery to place a healthy kidney into a person with kidney failure.

Possible Complications
Health problems that may result from this disorder include:
-
Acute renal failure (rapid loss of kidneys' ability to remove waste and help balance fluids and electrolytes in the body)
Acute renal failure
Acute kidney failure is the rapid (less than 2 days) loss of your kidneys' ability to remove waste and help balance fluids and electrolytes in your b...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Chronic glomerulonephritis
- Chronic kidney disease
-
Heart failure or pulmonary edema (fluid buildup in the lungs)
Heart failure
Heart failure is a condition in which the heart is no longer able to pump oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body efficiently. This causes symptom...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticlePulmonary edema
Pulmonary edema is an abnormal buildup of fluid in the lungs. This buildup of fluid leads to shortness of breath.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
End-stage renal disease
End-stage renal disease
End-stage kidney disease (ESKD) is the last stage of long-term (chronic) kidney disease. This is when your kidneys can no longer support your body's...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Hyperkalemia (abnormally high potassium level in the blood)
Hyperkalemia
High potassium level is a problem in which the amount of potassium in the blood is higher than normal. The medical name of this condition is hyperka...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - High blood pressure (hypertension)
-
Nephrotic syndrome (group of symptoms that include protein in the urine, low blood protein levels in the blood, high cholesterol levels, high triglyceride levels, and swelling)
Nephrotic syndrome
Nephrotic syndrome is a group of symptoms and abnormal test results that include protein in the urine, low blood protein levels in the blood, high ch...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your health care provider if:
- You have symptoms of poststreptococcal GN
- You have poststreptococcal GN, and you have decreased urine output or other new symptoms
Prevention
Treating known streptococcal infections may help prevent poststreptococcal GN. Also, practicing good hygiene such as washing hands often prevents the spread of the infection.
References
Flores FX. Isolated glomerular diseases associated with recurrent gross hematuria. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 537.
Radhakrishnan J, Stokes MB. Glomerular disorders and nephrotic syndromes. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 107.
Saha MK, Pendergraft WF, Jennette JC, Falk RJ. Primary glomerular disease. In: Yu ASL, Chertow GM, Luyckx VA, Marsden PA, Skorecki K, Taal MW, eds. Brenner and Rector's The Kidney. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 31.
Stevens DL, Bryant AE, Hagman MM. Nonpneumococcal streptococcal infections and rheumatic fever. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 269.
-
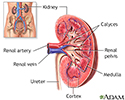
Kidney anatomy - illustration
The kidneys are responsible for removing wastes from the body, regulating electrolyte balance and blood pressure, and the stimulation of red blood cell production.
Kidney anatomy
illustration
-
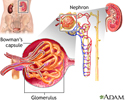
Glomerulus and nephron - illustration
The kidneys remove excess fluid and waste from your body. Blood is filtered in the kidneys through nephrons. Each nephron contains a network of small blood vessels, called glomerulus, which are enclosed in a sac called Bowman's capsule. The filtered waste product (urine) flows through tiny tubes and is then passed from the kidneys to the bladder through bigger tubes called ureters.
Glomerulus and nephron
illustration
-
Kidney anatomy - illustration
The kidneys are responsible for removing wastes from the body, regulating electrolyte balance and blood pressure, and the stimulation of red blood cell production.
Kidney anatomy
illustration
-
Glomerulus and nephron - illustration
The kidneys remove excess fluid and waste from your body. Blood is filtered in the kidneys through nephrons. Each nephron contains a network of small blood vessels, called glomerulus, which are enclosed in a sac called Bowman's capsule. The filtered waste product (urine) flows through tiny tubes and is then passed from the kidneys to the bladder through bigger tubes called ureters.
Glomerulus and nephron
illustration
Review Date: 8/28/2023
Reviewed By: Walead Latif, MD, Nephrologist and Clinical Associate Professor, Rutgers Medical School, Newark, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.