Renal pelvis or ureter cancer
Transitional cell cancer of the renal pelvis or ureter; Kidney cancer - renal pelvis; Ureter cancer; Urothelial carcinomaCancer of the renal pelvis or ureter is cancer that forms in the renal pelvis (center of the kidney) or ureter (tube that carries urine from the kidney to the bladder).
Causes
Cancer can grow in the urine collection system (renal pelvis and ureter), but it is uncommon. Renal pelvis and ureter cancers affect men more often than women. These cancers are more common in people older than 65.
The exact causes of this cancer are not known. Long-term (chronic) irritation of the kidney from harmful substances removed in the urine may be a factor. This irritation may be caused by:
- Kidney damage from medicines, especially ones for pain (analgesic nephropathy)
Analgesic nephropathy
Analgesic nephropathy involves damage to one or both kidneys caused by overexposure to mixtures of medicines, especially over-the-counter pain medici...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Exposure to certain dyes and chemicals used to manufacture leather goods, textiles, plastics, and rubber
- Smoking
People who have had bladder cancer are also at risk.
Symptoms
Symptoms may include any of the following:
- Constant back pain
-
Blood in the urine
Blood in the urine
Blood in your urine is called hematuria. The amount may be very small and only detected with urine tests or under a microscope. In other cases, the...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Burning, pain, or discomfort with urination
Discomfort with urination
Painful urination is any pain, discomfort, or burning sensation when passing urine.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Fatigue
Fatigue
Fatigue is a feeling of weariness, tiredness, or lack of energy.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Flank pain
Flank pain
Flank pain is pain in one side of the body between the upper belly area (abdomen) and the back.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Unexplained weight loss
Weight loss
Unexplained weight loss is a decrease in body weight, when you did not try to lose the weight on your own. Many people gain and lose weight. Uninten...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Loss of appetite
- Anemia
-
Urinary frequency or urgency
Urinary frequency or urgency
Frequent urination means needing to urinate more often than usual. Urgent urination is a sudden, strong need to urinate. This causes a discomfort i...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will perform a physical exam, and examine your belly area (abdomen). In rare cases, this may reveal an enlarged kidney.
If tests are done:
- Urinalysis may show blood in the urine.
- A complete blood count (CBC) may show anemia.
CBC
A complete blood count (CBC) test measures the following:The number of white blood cells (WBC count)The number of red blood cells (RBC count)The numb...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleAnemia
Anemia is a condition in which the body does not have enough healthy red blood cells. Red blood cells provide oxygen to body tissues. Different type...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Urine cytology (microscopic examination of cells) may reveal cancer cells.
Urine cytology
A cytology exam of urine is a test used to detect cancer and other diseases of the urinary tract.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Other tests that may be ordered include:
-
Abdominal CT scan
Abdominal CT scan
An abdominal CT scan is an imaging test that uses x-rays to create cross-sectional pictures of the belly area. CT stands for computed tomography....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Chest x-ray
- Cystoscopy with ureteroscopy
-
Intravenous pyelogram (IVP)
Intravenous pyelogram
An intravenous pyelogram (IVP) is a special x-ray exam of the kidneys, bladder, and ureters (the tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladd...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Kidney ultrasound
Kidney ultrasound
Abdominal ultrasound is a type of imaging test. It is used to look at organs in the abdomen, including the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, and kidneys...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
MRI of the abdomen
MRI of the abdomen
An abdominal magnetic resonance imaging scan is an imaging test that uses powerful magnets and radio waves. The waves create pictures of the inside ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Renal scan
Renal scan
A renal scan is a nuclear medicine exam in which a small amount of radioactive material (radioisotope) is used to measure the function of the kidneys...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - PET scan
These tests may reveal a tumor or show that the cancer has spread from the kidneys.
Treatment
The goal of treatment is to eliminate the cancer.
The following procedures may be used to treat the condition:
- Nephroureterectomy -- This involves removal of the entire kidney, ureter, and the bladder cuff (tissue that connects ureter to the bladder)
- Nephrectomy -- Surgery to remove all or part of the kidney is often done. This may include removing part of the bladder and tissues around it, or the lymph nodes.
- Ureter resection -- Surgery to remove part of the ureter that contains cancer, and some healthy tissue around it. This may be used in case of superficial tumors present in the lower part of the ureter near the bladder. This may help to preserve the kidney.
-
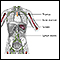
Chemotherapy -- This is used when the cancer has spread outside of the kidney or ureter. Because these tumors are similar to a form of bladder cancer, they are treated with a similar type of chemotherapy.
Chemotherapy
The term chemotherapy is used to describe cancer-killing drugs. Chemotherapy may be used to:Cure the cancerShrink the cancerPrevent the cancer from ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Immunotherapy -- This is used when the cancer has spread outside of the kidney or ureter. Because these tumors are similar to a form of bladder cancer, they are treated with a similar type of immunotherapy.
Support Groups
You can ease the stress of illness by joining a cancer support group. Sharing with others who have common experiences and problems can help you not feel alone.
Support group
The following organizations are good resources for information on cancer:American Cancer Society. Support and online communities. www. cancer. org/...
Outlook (Prognosis)
Outcome varies, depending on the location of the tumor and whether the cancer has spread. Cancer that is only in the kidney or ureter may be cured with surgery.
Cancer that has spread to other organs is usually not curable.
Possible Complications
Complications from this cancer may include:
-
Kidney failure
Kidney failure
Acute kidney failure is the rapid (less than 2 days) loss of your kidneys' ability to remove waste and help balance fluids and electrolytes in your b...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Local spread of the tumor with increasing pain
- Spread of the cancer to lung, liver, and bone
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you have any of the symptoms listed above.
Prevention
Measures that may help prevent this cancer include:
- Follow your provider's advice regarding medicines, including over-the-counter pain medicine.
- Stop smoking.
- Wear protective equipment if you are likely to be exposed to substances that are toxic to the kidneys.
References
Bajorin DF. Tumors of the kidney, bladder, ureters, and renal pelvis. In: Goldman L, Cooney K, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 182.
National Cancer Institute website. Transitional cell cancer of the renal pelvis and ureter treatment (pdq) -- health professional version. www.cancer.gov/types/kidney/hp/transitional-cell-treatment-pdq. Updated January 5, 2024. Accessed June 18, 2024.
Wong WW, Daniels TB, Peterson JL, Tyson MD, Tan WW. Kidney and ureteral carcinoma. In: Tepper JE, Foote RL, Michalski JM, eds. Gunderson & Tepper's Clinical Radiation Oncology. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 64.
-
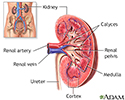
Kidney anatomy - illustration
The kidneys are responsible for removing wastes from the body, regulating electrolyte balance and blood pressure, and the stimulation of red blood cell production.
Kidney anatomy
illustration
Review Date: 6/17/2024
Reviewed By: Todd Gersten, MD, Hematology/Oncology, Florida Cancer Specialists & Research Institute, Wellington, FL. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.