Non-Hodgkin lymphoma
Lymphoma - non-Hodgkin; Lymphocytic lymphoma; Histiocytic lymphoma; Lymphoblastic lymphoma; Cancer - non-Hodgkin lymphoma; NHL; Non-Hodgkin's lymphomaNon-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) is cancer of the lymph tissue. Lymph tissue is found in the lymph nodes, spleen, and other organs of the immune system.
White blood cells, called lymphocytes, are found in lymph tissue. They help prevent infections. Most lymphomas start in a type of white blood cell called the B lymphocyte, or B cell.
Causes
For most people, the cause of NHL is unknown. But lymphomas may develop in people with weakened immune systems, including people who have had an organ transplant or people with HIV infection or Epstein-Barr virus infection.
NHL most often affects adults. Men develop NHL more often than women. Children can also develop some forms of NHL.
There are many types of NHL. One classification (grouping) is by how fast the cancer spreads. The cancer may be low grade (slow growing), intermediate grade, or high grade (fast growing).
NHL is further grouped by how the cancer cells look under the microscope, what type of white blood cell it originates from, what special tests show about it, and whether there are certain DNA changes (gene variants) in the tumor cells themselves.
Symptoms
Symptoms depend on what area of the body is affected by the cancer and how fast the cancer is growing.
Symptoms may include:
- Night sweats
- Fatigue
- Fever and chills that come and go
- Itching
-
Swollen lymph nodes in the neck, underarms, groin, or other areas
Swollen lymph nodes
Lymph nodes are present throughout your body. They are an important part of your immune system. Lymph nodes help your body recognize and fight germ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Weight loss
- Coughing or shortness of breath if the cancer affects the thymus gland or lymph nodes in the chest, putting pressure on the windpipe (trachea) or its branches
- Abdominal pain or swelling, leading to loss of appetite, constipation, nausea, and vomiting
- Headache, concentration problems, personality changes, or seizures if the cancer affects the brain
Seizures
A seizure is the physical changes in behavior that occurs during an episode of specific types of abnormal electrical activity in the brain. The term ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will perform a physical exam and check body areas with lymph nodes to feel if they are swollen.
The disease is usually diagnosed after a biopsy of suspected abnormal tissue, usually a lymph node biopsy.
Lymph node biopsy
A lymph node biopsy is the removal of lymph node tissue for examination under a microscope. The lymph nodes are small glands that make white blood ce...

Other tests that may be done include:
- Blood test to check protein levels, liver function, kidney function, and uric acid level
-
Complete blood count (CBC) and white blood cell differential to check for anemia and low white blood cell count
Complete blood count
A complete blood count (CBC) test measures the following:The number of white blood cells (WBC count)The number of red blood cells (RBC count)The numb...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleWhite blood cell differential
The blood differential test measures the percentage of each type of white blood cell (WBC) that you have in your blood. It also reveals if there are...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
CT scans of the chest, abdomen and pelvis
CT scans
A computed tomography (CT) scan is an imaging method that uses x-rays to create pictures of cross-sections of the body. Related tests include:Abdomin...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Bone marrow biopsy
Bone marrow biopsy
A bone marrow biopsy is the removal of marrow from inside one of your bones. Bone marrow is the soft tissue inside bones that helps form blood cells...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
PET scan
PET scan
A positron emission tomography (PET) scan is a type of imaging test. It uses a radioactive substance called a tracer to look for disease in the body...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article
If tests show you have NHL, more tests may be done to see how far it has spread. This is called staging. Staging helps guide future treatment and follow-up.
Staging
Cancer staging is a way to describe how much cancer is in your body and where it is located. Staging helps determine where the original tumor is, ho...
Treatment
Treatment depends on:
- The specific type of NHL
- The stage when you are first diagnosed
- Your age and overall health
- Symptoms, including weight loss, fever, and night sweats
You may receive chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or both. Or you may not need immediate treatment. Your provider can tell you more about your specific treatment.
Chemotherapy
The term chemotherapy is used to describe cancer-killing drugs. Chemotherapy may be used to:Cure the cancerShrink the cancerPrevent the cancer from ...
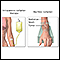
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-powered radiation (such as x-rays or gamma rays), particles, or radioactive seeds to kill cancer cells.
Radioimmunotherapy may be used in some cases. This involves linking a radioactive substance to an antibody that targets the cancerous cells and injecting the substance into the body.
A type of chemotherapy called targeted therapy may be tried. It uses a medicine to focus on specific targets (molecules) in or on cancer cells. Using these targets, the medicine disables the cancer cells so they cannot spread.
Targeted therapy
Targeted therapy uses medicines to stop cancer from growing and spreading. It does this with less harm to normal cells than other treatments. Stand...
High-dose chemotherapy may be given when NHL recurs or fails to respond to the first treatment administered. This is followed by an autologous stem cell transplant (using your own stem cells) to rescue (rebuild) the bone marrow after the high-dose chemotherapy. Stem cells from donors can also be used. With certain types of NHL, these treatment steps are used at first remission to try and achieve a cure. CAR-T cell therapy (a form of immunotherapy) can be used if lymphoma comes back or does not respond to other treatments.
Stem cell transplant
A bone marrow transplant is a procedure to replace damaged or diseased bone marrow with healthy bone marrow stem cells. Bone marrow is the soft, fatt...

Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy is a type of cancer treatment that relies on the body's infection-fighting system (immune system). It uses substances made by the body...
Blood transfusions or platelet transfusions may be required if blood counts are low.
You and your provider may need to manage other concerns during your lymphoma treatment, including:
-
Having chemotherapy at home
Having chemotherapy at home
You or your child will be going home from the hospital soon. Your health care provider has prescribed medicines or other treatments that you or your...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Managing your pets during chemotherapy
Managing your pets
If you have a weak immune system, having a pet can put you at risk for serious illness from diseases that can spread from animals to humans. Learn w...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Bleeding problems
Bleeding problems
Your bone marrow makes cells called platelets. These cells keep you from bleeding too much by helping your blood clot. Chemotherapy, radiation, and...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Dry mouth
Dry mouth
Some cancer treatments and medicines can cause dry mouth. Take good care of your mouth during your cancer treatment. Follow the measures outlined b...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Eating enough calories
Eating enough calories
If you are sick or undergoing cancer treatment, you may not feel like eating. But it is important to get enough protein and calories so you do not l...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article
Support Groups
You can ease the stress of illness by joining a cancer support group. Sharing with others who have common experiences and problems can help you not feel alone.
Cancer support group
The following organizations are good resources for information on cancer:American Cancer Society. Support and online communities. www. cancer. org/...
Outlook (Prognosis)
Low-grade NHL often cannot be cured by chemotherapy alone. Low-grade NHL progresses slowly and may take many years before the disease gets worse or even requires treatment. The need for treatment is usually determined by the type of lymphoma, symptoms, and how fast the disease is progressing.
Chemotherapy may cure many types of high-grade lymphomas. If the cancer does not respond to chemotherapy, the disease can cause rapid death.
Possible Complications
NHL itself and its treatments can lead to health problems. These include:
-
Autoimmune hemolytic anemia, a condition in which red blood cells are destroyed by the immune system
Autoimmune hemolytic anemia
Anemia is a condition in which the body does not have enough healthy red blood cells. Red blood cells provide oxygen to the body's tissues. Red bloo...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Infection
- Side effects of chemotherapy medicines
Keep following up with a provider who knows about monitoring and preventing these complications.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you develop symptoms of this disorder.
If you have NHL, contact your provider if you experience persistent fever or other signs of infection.
References
Abramson JS. Non-Hodgkin lymphomas. In: Niederhuber JE, Armitage JO, Kastan MB, Doroshow JH, Tepper JE, eds. Abeloff's Clinical Oncology. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 103.
National Cancer Institute website. Childhood non-Hodgkin lymphoma treatment (PDQ) - health professional version. www.cancer.gov/types/lymphoma/hp/child-nhl-treatment-pdq. Updated April 17, 2025. Accessed April 22, 2025.
National Cancer Institute website. Indolent B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma treatment (PDQ) - health professional version. www.cancer.gov/types/lymphoma/hp/indolent-b-cell-lymphoma-treatment-pdq. Updated March 21, 2025. Accessed April 22, 2025.
Vose JM, Armitage JO. Non-Hodgkin lymphomas. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 171.
-
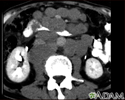
Lymphoma, malignant - CT scan - illustration
This abdominal CT scan shows tumor masses (malignant lymphomas) in the area behind the peritoneal cavity (retroperitoneal space).
Lymphoma, malignant - CT scan
illustration
-
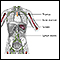
Immune system structures - illustration
The immune system protects the body from potentially harmful substances. The inflammatory response (inflammation) is part of innate immunity. It occurs when tissues are injured by bacteria, trauma, toxins, heat or any other cause.
Immune system structures
illustration
-
Lymphatic system - illustration
The lymphatic system filters fluid from around cells. It is an important part of the immune system. When people refer to swollen glands in the neck, they are usually referring to swollen lymph nodes. Common areas where lymph nodes can be easily felt, especially if they are enlarged, are the groin, armpits (axilla), above the clavicle (supraclavicular), in the neck (cervical), and the back of the head just above hairline (occipital).
Lymphatic system
illustration
-
Lymphoma, malignant - CT scan - illustration
This abdominal CT scan shows tumor masses (malignant lymphomas) in the area behind the peritoneal cavity (retroperitoneal space).
Lymphoma, malignant - CT scan
illustration
-
Immune system structures - illustration
The immune system protects the body from potentially harmful substances. The inflammatory response (inflammation) is part of innate immunity. It occurs when tissues are injured by bacteria, trauma, toxins, heat or any other cause.
Immune system structures
illustration
-
Lymphatic system - illustration
The lymphatic system filters fluid from around cells. It is an important part of the immune system. When people refer to swollen glands in the neck, they are usually referring to swollen lymph nodes. Common areas where lymph nodes can be easily felt, especially if they are enlarged, are the groin, armpits (axilla), above the clavicle (supraclavicular), in the neck (cervical), and the back of the head just above hairline (occipital).
Lymphatic system
illustration
Review Date: 2/3/2025
Reviewed By: Warren Brenner, MD, Oncologist, Lynn Cancer Institute, Boca Raton, FL. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.