Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia
Waldenström macroglobulinemia; Macroglobulinemia - primary; Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma; Monoclonal macroglobulinemia; Waldenström macroglobulinemiaWaldenström macroglobulinemia (WM) is a cancer of the B lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell). WM is associated with the overproduction of proteins called IgM antibodies.
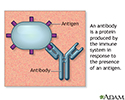
Antibodies
An antibody is a protein produced by the body's immune system when it detects harmful substances, called antigens. Examples of antigens include micr...
Causes
WM is a result of a condition called lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma. This is a cancer of the white blood cells, in which the B immune cells start dividing rapidly. The exact cause of too much production of the IgM antibody is unknown. Hepatitis C may increase the risk of WM. Gene mutations are often found in the malignant B cells.
Cancer
Cancer is the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the body. Cancerous cells are also called malignant cells.
Production of excess IgM antibodies can cause several types of problems:
- Hyperviscosity, which causes the blood to become too thick. This can make it harder for blood to flow through small blood vessels.
- Neuropathy, or nerve damage, when the IgM antibody damages nerve tissue.
-
Anemia, when the IgM antibody binds to red blood cells and damages them.
Anemia
Anemia is a condition in which the body does not have enough healthy red blood cells. Red blood cells provide oxygen to body tissues. Different type...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Kidney disease, when the IgM antibody deposits in kidney tissue.
-
Cryoglobulinemia and vasculitis (inflammation of the blood vessels) when the IgM antibody forms immune complexes with cold exposure.
Cryoglobulinemia
Cryoglobulinemia is the presence of abnormal proteins in the blood. These proteins thicken in cold temperatures.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
WM is very rare. Most people with this condition are over 65 years of age.
Symptoms
Symptoms of WM may include any of the following:
-
Bleeding of the gums and nosebleeds
Bleeding of the gums
Bleeding gums can be a sign that you have or may develop gum disease. Ongoing gum bleeding may be due to plaque buildup on the teeth. It can also b...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Blurred or decreased vision
Blurred or decreased vision
There are many types of eye problems and vision disturbances, such as: Halos Blurred vision (the loss of sharpness of vision and the inability to see...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Bluish skin in the fingers after cold exposure
Bluish skin
A bluish color to the skin or mucous membrane is usually due to a lack of oxygen in the blood. The medical term is cyanosis.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Dizziness or confusion
Dizziness
Dizziness is a term that is often used to describe 2 different symptoms: lightheadedness and vertigo. Lightheadedness is a feeling that you might fai...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleConfusion
Confusion is the inability to think as clearly or quickly as you normally do. You may feel disoriented and have difficulty paying attention, remembe...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Easy bruising of the skin
- Fatigue
- Diarrhea
-
Numbness, tingling, or burning pain in the hands, feet, fingers, toes, ears, or nose
Numbness
Numbness and tingling are abnormal sensations that can occur anywhere in your body, but they are often felt in your fingers, hands, feet, arms, or le...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Rash
Rash
Rashes involve changes in the color, feeling or texture of your skin.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
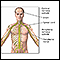
Swollen glands
Swollen glands
Lymph nodes are present throughout your body. They are an important part of your immune system. Lymph nodes help your body recognize and fight germ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Unintentional weight loss
Unintentional weight loss
Unexplained weight loss is a decrease in body weight, when you did not try to lose the weight on your own. Many people gain and lose weight. Uninten...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Vision loss in one eye
Exams and Tests
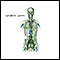
A physical exam may reveal a swollen spleen, liver, and lymph nodes. An eye exam may show enlarged veins in the retina or retinal bleeding (hemorrhages).
Swollen spleen
Splenomegaly is a larger-than-normal spleen. The spleen is an organ in the upper left part of the belly.
A complete blood count (CBC) may show a low number of red blood cells or platelets. Blood chemistry may show evidence of kidney disease.
Complete blood count
A complete blood count (CBC) test measures the following:The number of white blood cells (WBC count)The number of red blood cells (RBC count)The numb...
Blood chemistry
A comprehensive metabolic panel is a group of blood tests. They provide an overall picture of your body's chemical balance and metabolism. Metaboli...

A blood test called serum protein electrophoresis shows an increased level of the IgM antibody. Levels are often higher than 3000 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL), or 30 grams per liter (g/L). An immunofixation test will be done to show if the IgM antibody is derived from a single cell type (clonal).
Serum protein electrophoresis
This lab test measures the types of protein in the fluid (serum) part of a blood sample. This fluid is called serum.

A serum viscosity test can tell if the blood has become thick. Symptoms usually occur when the blood is four times thicker than normal.
A bone marrow biopsy will show increased numbers of abnormal cells that look like both lymphocytes and plasma cells.
Bone marrow biopsy
A bone marrow biopsy is the removal of marrow from inside one of your bones. Bone marrow is the soft tissue inside bones that helps form blood cells...

Additional tests that may be done include:
-
24-hour urine protein
24-hour urine protein
A 24-hour urine protein measures the amount of protein released in urine over a 24-hour period.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Total protein
Total protein
The total protein test measures the total amount of two classes of proteins found in the fluid portion of your blood. These are albumin and globulin...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Immunofixation in urine
Immunofixation in urine
Urine immunofixation is a test to look for abnormal proteins in urine.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
T (thymus derived) lymphocyte count
T (thymus derived) lymphocyte count
A T-cell count measures the number of T cells in the blood. T cells are a type of white blood cell that help your immune system fight infection and ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Bone x-rays
x-rays
X-rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation, just like visible light. An x-ray machine sends individual x-ray waves through the body. The images...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
Some people with WM who have increased IgM antibodies do not have symptoms. This condition is known as smoldering WM. No treatment is needed other than careful follow-up.
In people with symptoms, treatment aims at decreasing the symptoms and the risk of developing organ damage. There is no current standard treatment. Your health care provider may suggest that you participate in a clinical trial.
Plasmapheresis removes IgM antibodies from the blood. It also controls the symptoms caused by blood thickening.
Medicines may include corticosteroids, a combination of chemotherapy medicines and the monoclonal antibody to B cells, rituximab.
Autologous stem cell transplant may be recommended for some people with otherwise good health.
Autologous stem cell transplant
A bone marrow transplant is a procedure to replace damaged or diseased bone marrow with healthy bone marrow stem cells. Bone marrow is the soft, fatt...

People who have a low number of red or white blood cells or platelets may need transfusions or antibiotics.
Outlook (Prognosis)
The average survival is about 5 years. Some people live more than 10 years.
In some people, the disorder may produce few symptoms and progress slowly.
Possible Complications
Complications of WM may include:
- Changes in mental function, possibly leading to coma
Coma
Decreased alertness is a state of reduced awareness and is often a serious condition. A coma is the most severe state of decreased alertness in which...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Heart failure
Heart failure
Heart failure is a condition in which the heart is no longer able to pump oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body efficiently. This causes symptom...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Gastrointestinal bleeding or malabsorption
-
Vision problems
Vision problems
There are many types of eye problems and vision disturbances, such as: Halos Blurred vision (the loss of sharpness of vision and the inability to see...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Hives
Hives
Hives are raised, usually itchy, red bumps (welts) on the surface of the skin. They can be an allergic reaction to food or medicine. They can also ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if symptoms of WM develop.
References
Castillo JJ, Treon SP. Waldenström macroglobulinemia/lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma. In: Hoffman R, Benz EJ, Silberstein LE, et al, eds. Hematology: Basic Principles and Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 92.
Kapoor P, Ansell SM, Fonseca R, et al. Diagnosis and management of Waldenström macroglobulinemia: Mayo stratification of macroglobulinemia and risk-adapted therapy (mSMART) guidelines 2016. JAMA Oncol. 2017;3(9):1257-1265. PMID: 28056114 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28056114/.
Rajkumar SV. Plasma cell disorders. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 173.
-
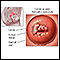
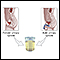
Waldenstroms - illustration
Lymphocytoid appearing plasma cell nucleus similar to a lymphocyte and cytoplasm similar to a plasma cell.
Waldenstroms
illustration
-
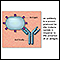
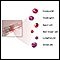
Antibodies - illustration
Antigens are large molecules (usually proteins) on the surface of cells, viruses, fungi, bacteria, and some non-living substances such as toxins, chemicals, drugs, and foreign particles. The immune system recognizes antigens and produces antibodies that destroy substances containing antigens.
Antibodies
illustration
-
Waldenstroms - illustration
Lymphocytoid appearing plasma cell nucleus similar to a lymphocyte and cytoplasm similar to a plasma cell.
Waldenstroms
illustration
-
Antibodies - illustration
Antigens are large molecules (usually proteins) on the surface of cells, viruses, fungi, bacteria, and some non-living substances such as toxins, chemicals, drugs, and foreign particles. The immune system recognizes antigens and produces antibodies that destroy substances containing antigens.
Antibodies
illustration
Review Date: 5/9/2024
Reviewed By: Neil J. Gonter, MD, Assistant Professor of Medicine, Columbia University, NY and private practice specializing in Rheumatology at Rheumatology Associates of North Jersey, Teaneck, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.