Brucellosis
Cyprus fever; Undulant fever; Gibraltar fever; Malta fever; Mediterranean feverBrucellosis is a bacterial infection that occurs from contact with animals carrying brucella bacteria.
Causes
Brucella can infect cattle, goats, camels, dogs, and pigs. The bacteria can spread to humans by:
- Coming in contact with infected meat or the placenta of infected animals
- Eating unpasteurized cheese
- Drinking unpasteurized milk
Brucellosis is rare in the United States. About 100 to 200 cases occur each year. Most cases are caused by the Brucella melitensis bacteria.
People working in jobs where they often come in contact with animals or meat are at higher risk. This includes slaughterhouse workers, farmers, and veterinarians.
Brucella is found in many countries worldwide including:
- Egypt
- Iraq
- Iran
- Jordan
- Saudi Arabia
- Chad
- Greece
- Mexico
Symptoms
Acute brucellosis may begin with mild flu-like symptoms, or symptoms such as:
Acute
Acute means sudden. Acute symptoms appear, change, or worsen rapidly. It is the opposite of chronic.
Flu-like
The flu (influenza) is a viral respiratory illness that causes fever, chills, runny nose, body aches, and cough. It spreads easily from person to pe...
- Abdominal pain
- Back pain
- Fever and chills
- Excessive sweating
- Fatigue
- Headache
- Joint and muscle pain
- Loss of appetite
- Swollen glands
- Weakness
- Weight loss
High fever spikes often occur every afternoon. The name undulant fever is often used to describe this disease because the fever rises and falls in waves.
The illness may be chronic and last for years.
Chronic
Chronic refers to something that continues over an extended period of time. A chronic condition is usually long-lasting and does not easily or quick...

Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will examine you and ask about your symptoms. You'll also be asked if you've been in contact with animals or possibly eaten dairy products that were not pasteurized.
Tests that may be done include:
-
Blood test for brucellosis
Blood test for brucellosis
Serology for brucellosis is a blood test to look for the presence of antibodies against Brucella. These are the bacteria that cause the disease bruc...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Blood culture
Blood culture
A blood culture is a laboratory test to check for bacteria or other germs in a blood sample.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Bone marrow culture
Bone marrow culture
Bone marrow culture is an examination of the soft, fatty tissue found inside certain bones. The bone marrow tissue produces blood cells. This test ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Urine culture
Urine culture
A urine culture is a lab test to check for bacteria or other germs in a urine sample. It can be used to check for a urinary tract infection in adults...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
CSF (spinal fluid) culture
CSF (spinal fluid) culture
A cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) culture is a lab test to look for bacteria, fungi, and viruses in the fluid that moves in the space around the spinal cor...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Biopsy and culture of specimen from affected organ
Treatment
Antibiotics are used to treat the infection and prevent it from coming back. These include:
- Doxycycline
- Streptomycin
- Gentamicin
- Rifampin
Often, you need to take antibiotics for 6 weeks. If there are complications from brucellosis, you will likely need to take the medicines for a longer period.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Symptoms may come and go for years. Also, the illness can come back after a long period of not having symptoms.
Possible Complications
Health problems that may result from brucellosis include:
- Bone and joint infection and damage
-
Encephalitis (swelling or inflammation of the brain)
Encephalitis
Encephalitis is irritation and swelling (inflammation) of the brain, most often due to infections.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Infective endocarditis (inflammation of the inside lining of the heart chambers and heart valves)
Infective endocarditis
Endocarditis is inflammation of the inside lining of the heart chambers and heart valves (endocardium). It is most often caused by a bacterial or, r...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Meningitis (infection of the membranes covering the brain and spinal cord)
Meningitis
Meningitis is an infection of the membranes covering the brain and spinal cord. This covering is called the meninges.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider for an appointment if:
- You develop symptoms of brucellosis
- Your symptoms get worse or do not improve with treatment
- You develop new symptoms after treatment for brucellosis
Prevention
Drinking and eating only pasteurized dairy products, such as milk and cheeses, is the most important way to reduce the risk for brucellosis. People who handle meat should wear protective eyewear and clothing and protect skin breaks from infection.
Skin breaks
A cut is a break or opening in the skin. It is also called a laceration. A cut may be deep, smooth, or jagged. It may be near the surface of the s...

Detecting infected animals controls the infection at its source. Vaccination is available for cattle, but not humans.
References
Gotuzzo E, Ryan ET. Brucellosis. In: Ryan ET, Hill DR, Solomon T, Aronson NE, Endy TP, eds. Hunter's Tropical Medicine and Emerging Infectious Diseases. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 75.
Gul HC, Erdem H. Brucellosis (Brucella species). In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 226.
-
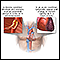
Brucellosis - illustration
Brucellosis is a disease that starts with flu-like symptoms. Complications may include arthritis, heart disease and brain damage.
Brucellosis
illustration
-
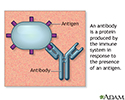
Antibodies - illustration
Antigens are large molecules (usually proteins) on the surface of cells, viruses, fungi, bacteria, and some non-living substances such as toxins, chemicals, drugs, and foreign particles. The immune system recognizes antigens and produces antibodies that destroy substances containing antigens.
Antibodies
illustration
-
Brucellosis - illustration
Brucellosis is a disease that starts with flu-like symptoms. Complications may include arthritis, heart disease and brain damage.
Brucellosis
illustration
-
Antibodies - illustration
Antigens are large molecules (usually proteins) on the surface of cells, viruses, fungi, bacteria, and some non-living substances such as toxins, chemicals, drugs, and foreign particles. The immune system recognizes antigens and produces antibodies that destroy substances containing antigens.
Antibodies
illustration
Review Date: 8/26/2023
Reviewed By: Jatin M. Vyas, MD, PhD, Roy and Diana Vagelos Professor in Medicine, Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons, Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Medicine, New York, NY. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.