H influenzae meningitis
H influenzae meningitis; H. flu meningitis; Haemophilus influenzae type b meningitisMeningitis is an infection of the membranes covering the brain and spinal cord. This covering is called the meninges.
Meningitis
Meningitis is an infection of the membranes covering the brain and spinal cord. This covering is called the meninges.

Bacteria are one type of germ that can cause meningitis. Haemophilus influenzae type b is one kind of bacteria that causes meningitis.
Causes
H influenzae meningitis is caused by Haemophilus influenzae type b bacteria. This illness is not the same as the flu (influenza), which is caused by a virus.
Influenza
The flu (influenza) is a viral respiratory illness that causes fever, chills, runny nose, body aches, and cough. It spreads easily from person to pe...
Before the Hib vaccine, H influenzae was the leading cause of bacterial meningitis in children under age 5. Since the vaccine became available in the United States, this type of meningitis occurs much less often in children in the United States.
H influenzae meningitis may occur after an upper respiratory infection. The infection usually spreads from the lungs and airways to the blood, then to the brain area.
Risk factors include:
- Attending day care
-
Cancer
Cancer
Cancer is the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the body. Cancerous cells are also called malignant cells.
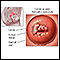 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Ear infection (otitis media) with H influenzae infection
Otitis media
Suspected ear infections are one of the most common reasons parents take their children to their health care provider. The most common type of ear i...
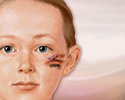 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Family member with an H influenzae infection
- Native American race
- Pregnancy
- Older age
- Sinus infection (sinusitis)
Sinusitis
Sinusitis is present when the tissue lining the sinuses become swollen or inflamed. It occurs as the result of an inflammatory reaction or an infect...
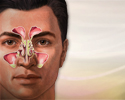 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Sore throat (pharyngitis)
Pharyngitis
Pharyngitis, or sore throat, is discomfort, pain, or scratchiness in the throat. It often makes it painful to swallow.
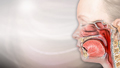 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Upper respiratory infection
- Weakened immune system
Symptoms
Symptoms usually come on quickly, and may include:
-
Fever and chills
Fever
Fever is the temporary increase in the body's temperature in response to a disease or illness. A child has a fever when the temperature is at or abov...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleChills
Chills refers to feeling cold after being in a cold environment. The word can also refer to an episode of shivering along with paleness and feeling ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Mental status changes
Mental status changes
Confusion is the inability to think as clearly or quickly as you normally do. You may feel disoriented and have difficulty paying attention, remembe...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Nausea and vomiting
Nausea and vomiting
Nausea is feeling an urge to vomit. It is often called "being sick to your stomach. "Vomiting or throwing-up forces the contents of the stomach up t...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Sensitivity to light (photophobia)
- Severe headache
Headache
A headache is pain or discomfort in the head, scalp, or neck. Serious causes of headaches are rare. Most people with headaches can feel much better...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Stiff neck (meningismus)
Other symptoms that can occur include:
-
Agitation
Agitation
Agitation is an unpleasant state of extreme arousal. An agitated person may feel stirred up, excited, tense, confused, or irritable.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Bulging fontanelles in infants
Bulging fontanelles
A bulging fontanelle is an outward curving of an infant's soft spot (fontanelle).
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Decreased consciousness
- Poor feeding and irritability in children
-
Rapid breathing
Rapid breathing
A normal breathing rate for an adult at rest is 12 to 20 breaths per minute. For an infant, a normal rate is 30 to 60 breaths per minute. Tachypnea ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Unusual posture, with the head and neck arched backwards (opisthotonos)
Opisthotonos
Opisthotonos is a condition in which a person holds their body in an abnormal position. The person is usually rigid and arches their back, with thei...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will perform a physical exam. Questions will focus on symptoms and possible exposure to someone who might have the same symptoms, such as a stiff neck and fever.
If your provider thinks meningitis is possible, a lumbar puncture (spinal tap) is done to take a sample of spinal fluid for testing.
Spinal tap
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) collection is a test to look at the fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. CSF acts as a cushion, protecting the b...

Other tests that may be done include:
-
Blood culture
Blood culture
A blood culture is a laboratory test to check for bacteria or other germs in a blood sample.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Chest x-ray
Chest x-ray
A chest x-ray is an x-ray of the chest, lungs, heart, large arteries, ribs, and diaphragm.
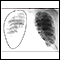 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
CT scan of the head
CT scan of the head
A head computed tomography (CT) scan uses many x-rays to create pictures of the head, including the skull, brain, eye sockets, and sinuses.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Complete blood count (CBC)
Complete blood count
A complete blood count (CBC) test measures the following:The number of white blood cells (WBC count)The number of red blood cells (RBC count)The numb...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Gram stain or other special stains, and culture of the spinal fluid
Gram stain
A Gram stain is a test used to identify bacteria. It is one of the most common ways to quickly diagnose bacterial infection in the body.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleCulture of the spinal fluid
A cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) culture is a lab test to look for bacteria, fungi, and viruses in the fluid that moves in the space around the spinal cor...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
Antibiotics will be given as soon as possible. Ceftriaxone is one of the most commonly used antibiotics. Ampicillin may sometimes be used.
Corticosteroids may be used to fight inflammation.
Unvaccinated people who are in close contact with someone who has H influenzae meningitis should be given antibiotics to prevent infection. Such people include:
- Household members
- Roommates in dormitories
- Those who come into close contact with an infected person
Outlook (Prognosis)
Meningitis is a dangerous infection and it can be deadly. The sooner it is treated, the better the chance for recovery. Young children and adults over age 50 have the highest risk for death.
Possible Complications
Long-term complications may include:
- Brain damage
- Buildup of fluid between the skull and brain (subdural effusion)
Subdural effusion
A subdural effusion is a collection of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) trapped between the surface of the brain and the outer lining of the brain (the dura...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Buildup of fluid inside the skull that leads to brain swelling (hydrocephalus)
Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is a buildup of fluid inside the skull that leads to the brain pushing against the skull. Hydrocephalus means "water on the brain. "...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Hearing loss
Hearing loss
Hearing loss is being partly or totally unable to hear sound in one or both ears.
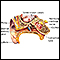 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Seizures
Seizures
A seizure is the physical changes in behavior that occurs during an episode of specific types of abnormal electrical activity in the brain. The term ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call 911 or the local emergency number or go to an emergency room if you suspect meningitis in a young child who has the following symptoms:
- Feeding problems
- High-pitched cry
- Irritability
- Persistent, unexplained fever
Meningitis can quickly become a life-threatening illness.
Prevention
Infants and young children can be protected with the Hib vaccine.
Hib vaccine
All content below is taken in its entirety from the CDC Hib (Haemophilus Influenzae Type b) Vaccine Information Statement (VIS): www. cdc. gov/vaccin...
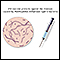
Close contacts in the same household, school, or day care center should be watched for early signs of the disease as soon as the first person is diagnosed. All unvaccinated family members and close contacts of this person should begin antibiotic treatment as soon as possible to prevent the spread of the infection. Ask your provider about antibiotics during the first visit.
Always use good hygiene habits, such as washing hands before and after changing a diaper, and after using the bathroom.
References
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. Meningitis. About bacterial meningitis. www.cdc.gov/meningitis/about/bacterial-meningitis.html. Updated January 9, 2024. Accessed September 10, 2024.
Hasbun R, Van de Beek D, Brouwer MC, Tunkel AR. Acute meningitis. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 87.
Nath A. Meningitis: bacterial, viral, and other. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 381.
-
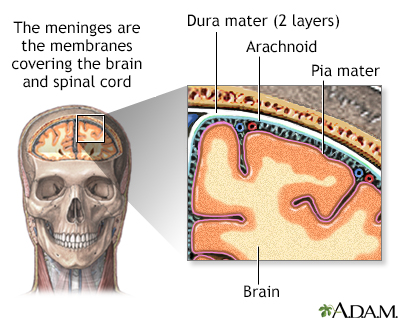
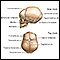
Meninges of the brain - illustration
The organs of the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) are covered by connective tissue layers collectively called the meninges. Consisting of the pia mater (closest to the CNS structures), the arachnoid and the dura mater (farthest from the CNS), the meninges also support blood vessels and contain cerebrospinal fluid. These are the structures involved in meningitis, an inflammation of the meninges, which, if severe, may become encephalitis, an inflammation of the brain.
Meninges of the brain
illustration
-
Meninges of the spine - illustration
The organs of the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) are covered by 3 connective tissue layers collectively called the meninges. Consisting of the pia mater (closest to the CNS structures), the arachnoid and the dura mater (farthest from the CNS), the meninges also support blood vessels and contain cerebrospinal fluid. These are the structures involved in meningitis, an inflammation of the meninges, which, if severe, may become encephalitis, an inflammation of the brain.
Meninges of the spine
illustration
-
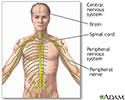
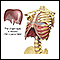
Central nervous system and peripheral nervous system - illustration
The central nervous system is made up of the brain and the spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system includes nerves outside the brain and spinal cord.
Central nervous system and peripheral nervous system
illustration
-
CSF cell count - illustration
CSF (cerebrospinal fluid) is a clear fluid that circulates in the space surrounding the spinal cord and brain. A CSF cell count is a test to measure the number of red and white blood cells that are in CSF.
CSF cell count
illustration
-
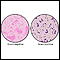
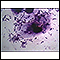
Haemophilus influenzae organism - illustration
This is a Gram stain of spinal fluid from a person with meningitis. The rod-like organisms seen in the fluid are Haemophilus influenzae, one of the most common causes of childhood meningitis (prior to the widespread use of the H influenzae vaccine). The large red-colored objects are cells in the spinal fluid. A vaccine to prevent infection by Haemophilus influenzae (type B) is available as one of the routine childhood immunizations (Hib), typically given at 2, 4, and 12 months.
Haemophilus influenzae organism
illustration
-
Haemophilus influenza organism - illustration
This picture shows the organism Haemophilus influenza. Infections caused by Haemophilus influenza usually occur in children under 6 years old and are extremely serious. Haemophilus (type B) is responsible for meningitis, periorbital cellulitis, buccal cellulitis and epiglottitis, septic arthritis, osteomyelitis, pericarditis, and bacteremia. The small organisms live within cells (intracellular) as shown in this picture. (Image courtesy of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.)
Haemophilus influenza organism
illustration
-
Meninges of the brain - illustration
The organs of the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) are covered by connective tissue layers collectively called the meninges. Consisting of the pia mater (closest to the CNS structures), the arachnoid and the dura mater (farthest from the CNS), the meninges also support blood vessels and contain cerebrospinal fluid. These are the structures involved in meningitis, an inflammation of the meninges, which, if severe, may become encephalitis, an inflammation of the brain.
Meninges of the brain
illustration
-
Meninges of the spine - illustration
The organs of the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) are covered by 3 connective tissue layers collectively called the meninges. Consisting of the pia mater (closest to the CNS structures), the arachnoid and the dura mater (farthest from the CNS), the meninges also support blood vessels and contain cerebrospinal fluid. These are the structures involved in meningitis, an inflammation of the meninges, which, if severe, may become encephalitis, an inflammation of the brain.
Meninges of the spine
illustration
-
Central nervous system and peripheral nervous system - illustration
The central nervous system is made up of the brain and the spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system includes nerves outside the brain and spinal cord.
Central nervous system and peripheral nervous system
illustration
-
CSF cell count - illustration
CSF (cerebrospinal fluid) is a clear fluid that circulates in the space surrounding the spinal cord and brain. A CSF cell count is a test to measure the number of red and white blood cells that are in CSF.
CSF cell count
illustration
-
Haemophilus influenzae organism - illustration
This is a Gram stain of spinal fluid from a person with meningitis. The rod-like organisms seen in the fluid are Haemophilus influenzae, one of the most common causes of childhood meningitis (prior to the widespread use of the H influenzae vaccine). The large red-colored objects are cells in the spinal fluid. A vaccine to prevent infection by Haemophilus influenzae (type B) is available as one of the routine childhood immunizations (Hib), typically given at 2, 4, and 12 months.
Haemophilus influenzae organism
illustration
-
Haemophilus influenza organism - illustration
This picture shows the organism Haemophilus influenza. Infections caused by Haemophilus influenza usually occur in children under 6 years old and are extremely serious. Haemophilus (type B) is responsible for meningitis, periorbital cellulitis, buccal cellulitis and epiglottitis, septic arthritis, osteomyelitis, pericarditis, and bacteremia. The small organisms live within cells (intracellular) as shown in this picture. (Image courtesy of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.)
Haemophilus influenza organism
illustration
Review Date: 8/29/2024
Reviewed By: Jatin M. Vyas, MD, PhD, Roy and Diana Vagelos Professor in Medicine, Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons, Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Medicine, New York, NY. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.