Meningitis - cryptococcal
Cryptococcal meningitisCryptococcal meningitis is a fungal infection of the tissues covering the brain and spinal cord. These tissues are called meninges.
Meningitis
Meningitis is an infection of the membranes covering the brain and spinal cord. This covering is called the meninges.

Causes
In most cases, cryptococcal meningitis is caused by the fungus Cryptococcus neoformans. This fungus is found in soil around the world. Cryptococcus gattii can also cause meningitis, but this form can cause disease in people with a normal immune system as well.
This type of meningitis is not spread from person to person. Usually, it spreads through the bloodstream to the brain from another place in the body that has the initial infection.
Cryptococcus neoformans meningitis most often affects people with a weakened immune system, including people with:
-
AIDS
AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is the virus that causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). When a person becomes infected with HIV, the ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
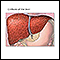
Cirrhosis (a type of liver disease)
Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis is scarring of the liver and poor liver function. It is the last stage of chronic liver disease.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Diabetes
Diabetes
Diabetes is a long-term (chronic) disease in which the body cannot regulate the amount of sugar in the blood.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Leukemia
Leukemia
Leukemia is a type of blood cancer that begins in the bone marrow. Bone marrow is the soft tissue in the center of the bones, where blood cells are ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Lymphoma
Lymphoma
Hodgkin lymphoma is a cancer of lymph tissue. Lymph tissue is found in the lymph nodes, spleen, liver, bone marrow, and other sites.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis is a disease in which inflammation occurs in the lymph nodes, lungs, liver, eyes, skin, and other tissues.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - An organ transplant
Cryptococcus neoformans meningitis is rare in people who have a normal immune system and no long-term health problems.
Symptoms
This form of meningitis starts slowly, over a few days to a few weeks. Symptoms may include:
- Fever
-
Hallucinations
Hallucinations
Hallucinations involve sensing things such as visions, sounds, or smells that seem real but are not. These things are created by the mind.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Headache
-
Mental status change (confusion)
Mental status change
Confusion is the inability to think as clearly or quickly as you normally do. You may feel disoriented and have difficulty paying attention, remembe...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Nausea and vomiting
-
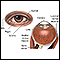
Sensitivity to light
Sensitivity to light
Photophobia is eye discomfort in bright light.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Stiff neck
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will examine you and ask about your symptoms.
A lumbar puncture (spinal tap) is used to diagnose meningitis. In this test, a sample of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is removed from the space around your spine and tested.
Spinal tap
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) collection is a test to look at the fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. CSF acts as a cushion, protecting the b...

Other tests that may be done include:
-
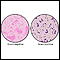
Blood culture
Blood culture
A blood culture is a laboratory test to check for bacteria or other germs in a blood sample.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
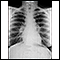
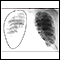
Chest x-ray
Chest x-ray
A chest x-ray is an x-ray of the chest, lungs, heart, large arteries, ribs, and diaphragm.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Cryptococcal antigen in CSF or blood
- CSF examination for cell count, glucose, and protein
-
CT scan of the head
CT scan of the head
A head computed tomography (CT) scan uses many x-rays to create pictures of the head, including the skull, brain, eye sockets, and sinuses.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Gram stain, other special stains, and culture of CSF
Gram stain
A Gram stain is a test used to identify bacteria. It is one of the most common ways to quickly diagnose bacterial infection in the body.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleCulture of CSF
A cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) culture is a lab test to look for bacteria, fungi, and viruses in the fluid that moves in the space around the spinal cor...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
Antifungal medicines are used to treat this form of meningitis. Intravenous (IV, through a vein) therapy with amphotericin B is the most common treatment. It is often combined with an oral antifungal medicine called 5-flucytosine.
Intravenous
Intravenous means "within a vein. " Most often it refers to giving medicines or fluids through a needle or tube inserted into a vein. This allows th...
Another oral medicine, fluconazole, may also be effective in high doses. If needed, it will be prescribed later in the disease course.
Outlook (Prognosis)
People who recover from cryptococcal meningitis need long-term medicine to prevent the infection from coming back. People with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS, will also need long-term treatment to improve their immune system.
HIV/AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is the virus that causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). When a person becomes infected with HIV, the ...

Possible Complications
These complications may occur from this infection:
- Brain damage
-
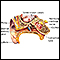
Hearing or vision loss
Hearing
Hearing loss is being partly or totally unable to hear sound in one or both ears.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
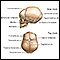
Hydrocephalus (excessive CSF in the brain)
Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is a buildup of fluid inside the skull that leads to the brain pushing against the skull. Hydrocephalus means "water on the brain. "...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Seizures
Seizures
A seizure is the physical changes in behavior that occurs during an episode of specific types of abnormal electrical activity in the brain. The term ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Death
Amphotericin B can have side effects such as:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fever and chills
- Joint and muscles aches
- Kidney damage
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call 911 or the local emergency number if you develop any of the serious symptoms listed above. Meningitis can quickly become a life-threatening illness.
Call the local emergency number or go to an emergency room if you suspect meningitis in a young child who has these symptoms:
- Feeding difficulties
- High-pitched cry
- Irritability
- Persistent, unexplained fever
References
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. Meningitis. About fugal meningitis. www.cdc.gov/meningitis/about/fungal-meningitis.html. Updated January 7, 2025. Accessed March 13, 2025.
Chen SC-A. Cryptococcosis. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 309.
Perfect JR. Cryptococcosis (Cryptococcus neoformans and Cryptococcus gattii). In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 262.
-
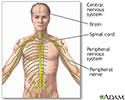
Central nervous system and peripheral nervous system - illustration
The central nervous system is made up of the brain and the spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system includes nerves outside the brain and spinal cord.
Central nervous system and peripheral nervous system
illustration
Review Date: 11/10/2024
Reviewed By: Jatin M. Vyas, MD, PhD, Roy and Diana Vagelos Professor in Medicine, Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons, Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Medicine, New York, NY. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.