Peritonitis - spontaneous bacterial
Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP); Ascites - peritonitis; Cirrhosis - peritonitisThe peritoneum is the thin tissue that lines the inner wall of the abdomen and covers most of the organs in the abdomen. Peritonitis is present when this tissue becomes inflamed or infected.
Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP) is present when this tissue becomes infected and there is no clear cause.
Causes
SBP is most often caused by infection in fluid that collects in the peritoneal cavity (ascites). The fluid buildup often occurs in people with advanced liver or kidney disease.
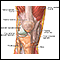
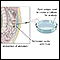
Ascites
Ascites is the build-up of fluid in the space between the lining of the abdomen and abdominal organs.

Risk factors for liver disease include:
- Very heavy alcohol use
- Chronic hepatitis B or hepatitis C
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is irritation and swelling (inflammation) of the liver due to infection with the hepatitis B virus (HBV). Other types of viral hepatitis ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleHepatitis C
Hepatitis C is a viral disease that leads to swelling (inflammation) of the liver. Other types of viral hepatitis include:Hepatitis AHepatitis BHepat...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Other diseases that lead to cirrhosis
SBP also occurs in people who are on peritoneal dialysis for kidney failure.
Peritonitis may have other causes in which case it is called secondary peritonitis. These include infection from other organs or leakage of enzymes or other toxins into the abdomen.
Peritonitis may have other causes
The peritoneum is the thin tissue that lines the inner wall of the abdomen and covers most of the organs in the abdomen. Peritonitis is present when...

Symptoms
Symptoms include:
-
Abdominal pain and bloating
Abdominal pain
Abdominal pain is pain that you feel anywhere between your chest and groin. This is often referred to as the stomach region or belly.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Abdominal tenderness
Tenderness
Abdominal point tenderness is the localized pain you feel when pressure is placed over a certain part of the belly area (abdomen).
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Fever
Fever
Fever is the temporary increase in the body's temperature in response to a disease or illness. A child has a fever when the temperature is at or abov...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Low urine output
Low urine output
Decreased urine output means that you produce less urine than normal. Most adults make at least 500 milliliters of urine in 24 hours (a little over ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Other symptoms include:
-
Chills
Chills
Chills refers to feeling cold after being in a cold environment. The word can also refer to an episode of shivering along with paleness and feeling ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Joint pain
-
Nausea and vomiting
Nausea and vomiting
Nausea is feeling an urge to vomit. It is often called "being sick to your stomach. "Vomiting or throwing-up forces the contents of the stomach up t...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Exams and Tests
Tests will be done to check for infection and other causes of abdominal pain:
-
Blood culture
Blood culture
A blood culture is a laboratory test to check for bacteria or other germs in a blood sample.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - White blood cell count in a sample of peritoneal fluid
- Chemical examination of peritoneal fluid
-
Culture of peritoneal fluid
Culture of peritoneal fluid
Peritoneal fluid culture is a laboratory test performed on a sample of peritoneal fluid. It is done to detect bacteria or fungi that cause infection...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - CT scan or ultrasound of the abdomen
Treatment
Treatment depends on the cause of the SBP.
SBP
Peritonitis is an inflammation (irritation) of the peritoneum. This is the thin tissue that lines the inner wall of the abdomen and covers most of t...

-
Surgery may be needed if SBP is caused by a foreign object, such as a catheter used in peritoneal dialysis.
Peritoneal dialysis
Dialysis treats end-stage kidney failure. It removes harmful substances from the blood when the kidneys cannot. This article focuses on peritoneal d...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Antibiotics to control infection.
-
Fluids given through the veins.
Fluids given through the veins
Intravenous means "within a vein. " Most often it refers to giving medicines or fluids through a needle or tube inserted into a vein. This allows th...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article
You will need to stay in the hospital so health care providers can rule out other causes such as a ruptured appendix and diverticulitis.
Diverticulitis
Diverticula are small, bulging sacs or pouches that form on the inner wall of the intestine. Diverticulitis occurs when these pouches become inflame...

Outlook (Prognosis)
In most cases, the infection can be treated. However, kidney or liver disease may limit recovery.
Liver disease
The term "liver disease" applies to many conditions that stop the liver from working or prevent it from functioning well. Abdominal pain or swelling...

Possible Complications
Complications may include:
-
Loss of brain function occurs when the liver is unable to remove toxins from the blood.
Loss of brain function
Loss of brain function occurs when the liver is unable to remove toxins from the blood. This is called hepatic encephalopathy (HE). This problem ma...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Kidney problem caused by liver failure.
Kidney problem caused by liver failure
Hepatorenal syndrome is a condition in which there is progressive kidney failure that occurs in a person with cirrhosis of the liver. It is a seriou...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Sepsis.
Sepsis
Sepsis is an illness in which the body has a severe, inflammatory response to bacteria or other germs.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you have symptoms of peritonitis. This can be a medical emergency situation.
Prevention
Steps should be taken to prevent infection in people with peritoneal catheters.
Long-term antibiotics may be used:
- To prevent peritonitis from coming back in people with liver failure
- To prevent peritonitis in people who have acute gastrointestinal bleeding due to other conditions
References
Garcia-Tsao G. Cirrhosis and its sequelae. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 139.
Kuemmerle JF. Inflammatory and anatomic diseases of the intestine, peritoneum, mesentery, and omentum. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 128.
Sola E, Gines P. Ascites and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 93.
Review Date: 6/11/2024
Reviewed By: Jenifer K. Lehrer, MD, Department of Gastroenterology, Aria - Jefferson Health Torresdale, Jefferson Digestive Diseases Network, Philadelphia, PA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.