Meningitis - tuberculous
Tubercular meningitis; TB meningitisTuberculous meningitis is an infection of the tissues covering the brain and spinal cord (meninges).
Causes
Tuberculous meningitis is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This is the bacterium that causes tuberculosis (TB). The bacteria spread to the brain and spine from another place in the body, usually the lung.
Tuberculous meningitis is very rare in the United States. Most cases are in people who traveled to the United States from other countries where TB is common.
People who have the following have a higher chance of developing tuberculous meningitis:
-
HIV/AIDS
HIV/AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is the virus that causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). When a person becomes infected with HIV, the ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Drink alcohol in excess
Drink alcohol in excess
Alcohol use disorder is when your drinking causes serious problems in your life, yet you keep drinking. You may also need more and more alcohol to f...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
TB of the lung
TB of the lung
Pulmonary tuberculosis (TB) is a contagious bacterial infection that involves the lungs. It may spread to other organs.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Weakened immune system
Symptoms
The symptoms often start slowly, and may include:
- Fever and chills
-
Mental status changes
Mental status changes
Confusion is the inability to think as clearly or quickly as you normally do. You may feel disoriented and have difficulty paying attention, remembe...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Nausea and vomiting
- Sensitivity to light (photophobia)
- Severe headache
- Stiff neck (meningismus)
Other symptoms that can occur with this disease may include:
- Agitation
-
Bulging fontanelles (soft spots) in babies
Bulging fontanelles
A bulging fontanelle is an outward curving of an infant's soft spot (fontanelle).
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Decreased consciousness
Decreased consciousness
Decreased alertness is a state of reduced awareness and is often a serious condition. A coma is the most severe state of decreased alertness in which...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Poor feeding or irritability in children
- Unusual posture, with the head and neck arched backward (opisthotonos). This is usually found in infants (less than 3 months old)
Opisthotonos
Opisthotonos is a condition in which a person holds their body in an abnormal position. The person is usually rigid and arches their back, with thei...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will examine you. This will usually show that you have the following:
- Fast heart rate
- Fever
- Mental status changes
- Stiff neck
A lumbar puncture (spinal tap) is an important test in diagnosing meningitis. It is done to collect a sample of cerebrospinal fluid for examination. More than one sample may be needed to make the diagnosis.
Spinal tap
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) collection is a test to look at the fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. CSF acts as a cushion, protecting the b...

Other tests that may be done include:
-
Biopsy of the brain or meninges (rare)
Biopsy
A biopsy is the removal of a small piece of tissue for lab examination.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Blood culture
Blood culture
A blood culture is a laboratory test to check for bacteria or other germs in a blood sample.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
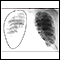
Chest x-ray
Chest x-ray
A chest x-ray is an x-ray of the chest, lungs, heart, large arteries, ribs, and diaphragm.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) examination for cell count, glucose, and protein
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) examination
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis is a group of lab tests that measure chemicals in the cerebrospinal fluid. CSF is a clear fluid that surrounds an...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
CT scan of the head
CT scan of the head
A head computed tomography (CT) scan uses many x-rays to create pictures of the head, including the skull, brain, eye sockets, and sinuses.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Gram stain, other special stains, and culture of CSF
Gram stain
A Gram stain is a test used to identify bacteria. It is one of the most common ways to quickly diagnose bacterial infection in the body.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleCulture of CSF
A cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) culture is a lab test to look for bacteria, fungi, and viruses in the fluid that moves in the space around the spinal cor...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) of CSF
- Skin test for TB (PPD)
PPD
The PPD skin test is a method used to diagnose silent (latent) tuberculosis (TB) infection. PPD stands for purified protein derivative.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Other tests to look for TB
Treatment
You will be given several medicines to fight the TB bacteria. Sometimes, treatment is started even if your provider thinks you have the disease, but testing has not confirmed it yet.
Treatment usually lasts for at least 12 months. Medicines called corticosteroids may also be used.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Tuberculous meningitis is life threatening if untreated. Long-term follow-up is needed to detect recurring infections.
Possible Complications
Untreated, the disease can cause any of the following:
- Brain damage
- Build-up of fluid between the skull and brain (subdural effusion)
Subdural effusion
A subdural effusion is a collection of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) trapped between the surface of the brain and the outer lining of the brain (the dura...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Hearing loss
-
Hydrocephalus (build-up of fluid inside the skull that leads to brain swelling)
Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is a buildup of fluid inside the skull that leads to the brain pushing against the skull. Hydrocephalus means "water on the brain. "...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Seizures
Seizures
A seizure is the physical changes in behavior that occurs during an episode of specific types of abnormal electrical activity in the brain. The term ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Death
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call 911 or the local emergency number or go to an emergency room if you suspect meningitis in a young child who has the following symptoms:
- Feeding problems
- High-pitched cry
- Irritability
- Persistent unexplained fever
Call the local emergency number if you develop any of the serious symptoms listed above. Meningitis can quickly become a life-threatening illness.
Prevention
Treating people who have signs of a non-active (dormant) TB infection can prevent its spread. A PPD test and other TB tests can be done to tell if you have this type of infection.
Some countries with a high incidence of TB give people a vaccine called BCG to prevent TB. But, the effectiveness of this vaccine is limited, and it is not usually used in the United States. The BCG vaccine may help prevent severe forms of TB, such as meningitis, in very young children who live in areas where the disease is common.
References
Bailey TC, Philips JA. Tuberculosis. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 299.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. Tuberculosis (TB). www.cdc.gov/tb/index.html. Updated January 17, 2025. Accessed March 13, 2025.
Cruz AT, Starke JR. Tuberculosis. In: Cherry JD, Kaplan SL, Harrison GJ, Steinbach WJ, Hotez PJ, Williams JV, eds. Feigin and Cherry's Textbook of Pediatric Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 96.
Fitzgerald DW, Sterling TR, Haas DW. Mycobacterium tuberculosis. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 249.
-
Meninges of the brain - illustration
The organs of the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) are covered by connective tissue layers collectively called the meninges. Consisting of the pia mater (closest to the CNS structures), the arachnoid and the dura mater (farthest from the CNS), the meninges also support blood vessels and contain cerebrospinal fluid. These are the structures involved in meningitis, an inflammation of the meninges, which, if severe, may become encephalitis, an inflammation of the brain.
Meninges of the brain
illustration
-
Meninges of the spine - illustration
The organs of the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) are covered by 3 connective tissue layers collectively called the meninges. Consisting of the pia mater (closest to the CNS structures), the arachnoid and the dura mater (farthest from the CNS), the meninges also support blood vessels and contain cerebrospinal fluid. These are the structures involved in meningitis, an inflammation of the meninges, which, if severe, may become encephalitis, an inflammation of the brain.
Meninges of the spine
illustration
-
Bacteria - illustration
Bacterial infections can lead to the formation of pus, or to the spread of the bacteria in the blood.
Bacteria
illustration
-
Meninges of the brain - illustration
The organs of the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) are covered by connective tissue layers collectively called the meninges. Consisting of the pia mater (closest to the CNS structures), the arachnoid and the dura mater (farthest from the CNS), the meninges also support blood vessels and contain cerebrospinal fluid. These are the structures involved in meningitis, an inflammation of the meninges, which, if severe, may become encephalitis, an inflammation of the brain.
Meninges of the brain
illustration
-
Meninges of the spine - illustration
The organs of the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) are covered by 3 connective tissue layers collectively called the meninges. Consisting of the pia mater (closest to the CNS structures), the arachnoid and the dura mater (farthest from the CNS), the meninges also support blood vessels and contain cerebrospinal fluid. These are the structures involved in meningitis, an inflammation of the meninges, which, if severe, may become encephalitis, an inflammation of the brain.
Meninges of the spine
illustration
-
Bacteria - illustration
Bacterial infections can lead to the formation of pus, or to the spread of the bacteria in the blood.
Bacteria
illustration
Review Date: 11/10/2024
Reviewed By: Jatin M. Vyas, MD, PhD, Roy and Diana Vagelos Professor in Medicine, Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons, Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Medicine, New York, NY. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.