Chlamydia infections in women
Cervicitis - chlamydia; STI - chlamydia; STD - chlamydia; Sexually transmitted - chlamydia; PID - chlamydia; Pelvic inflammatory disease - chlamydiaChlamydia is an infection that can be passed from one person to another through sexual contact. This type of infection is known as sexually transmitted infection (STI).
Causes
Chlamydia is caused by the bacteria Chlamydia trachomatis. Both males and females may have this infection. However, they may not have symptoms. As a result, you may become infected or pass the infection to your partner without knowing it.
You are more likely to become infected with chlamydia if you:
- Have sex without wearing a male or female condom
- Have more than one sexual partner
- Use drugs or alcohol and then have sex
- Have been infected with chlamydia before
Symptoms
Many women do not have symptoms. But some have:
- Burning when they urinate
- Pain in the lower part of the belly, possibly with fever
- Painful intercourse
-
Vaginal discharge or bleeding after intercourse
Vaginal discharge
Vaginal discharge refers to secretions from the vagina. The discharge may be:Thick, pasty, or thinClear, cloudy, bloody, white, yellow, or greenOdor...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Rectal pain
Exam and Tests
If you have symptoms of a chlamydia infection, your health care provider will collect a sample for culture or a test called nucleic acid amplification.
In the past, testing required a pelvic exam by a health care provider. Today, very accurate tests can be done on urine samples. Vaginal swabs, which a woman collects herself, can also be tested. Results take 1 to 2 days to come back. Your provider may also check you for other types of STIs. The most common STIs are:
-
Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea is a common sexually transmitted infection (STI).
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
HIV/AIDS
HIV/AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is the virus that causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). When a person becomes infected with HIV, the ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Syphilis
Syphilis
Syphilis is a bacterial infection that is most often spread through sexual contact.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Hepatitis
Hepatitis
Hepatitis is swelling and inflammation of the liver.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Herpes
Herpes
Herpes viral culture of a lesion is a laboratory test to check if a skin sore is infected with the herpes virus.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Even if you have no symptoms, you may need a chlamydia test if you:
- Are 24 years old or younger and are sexually active (get tested every year)
- Have a new sexual partner, more than one partner or a partner with an STI
Treatment
Chlamydia can be treated with an antibiotic. Some of these are safe to take if you are pregnant. Common side effects include:
-
Nausea
Nausea
Nausea is feeling an urge to vomit. It is often called "being sick to your stomach. "Vomiting or throwing-up forces the contents of the stomach up t...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Upset stomach
- Diarrhea
Both you and your partner need to take the antibiotics.
- Finish all of them, even if you feel better and still have some left.
- All of your sexual partners should be treated. Have them take the medicines even if they do not have symptoms. This will prevent you from passing the STIs back and forth.
You and your partner are asked to abstain from sexual intercourse during the time of treatment.
Gonorrhea often occurs with chlamydia. Therefore, treatment for gonorrhea is often given at the same time.
Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea is a common sexually transmitted infection (STI).
Safer sex practices are needed to prevent becoming infected with chlamydia or spreading it to others.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Antibiotic treatment almost always works. You and your partner should take the medicines as directed.
If chlamydia spreads into your uterus and fallopian tubes, it can cause scarring. Scarring can make it harder for you to get pregnant. You can help prevent this by:
- Finishing your antibiotics when you are treated.
- Making sure your sexual partners also take antibiotics. You may ask your provider for a prescription for your partner without your partner being seen by the provider.
- Talking to your provider about being tested for chlamydia and seeing your provider if you have symptoms.
- Wearing condoms and practicing safer sex.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if:
- You have symptoms of chlamydia.
- You are worried that you might have chlamydia.
References
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. Sexually transmitted infections treatment guidelines, 2021. Chlamydial infections in adolescents and adults. www.cdc.gov/std/treatment-guidelines/chlamydia.htm. Updated July 22, 2021. Accessed April 22, 2024.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. Getting tested for STIs. www.cdc.gov/sti/testing/. Updated April 9, 2024. Accessed July 24, 2024.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. Sexually transmitted infections treatment guidelines, 2021. Chlamydial infections in adolescents and adults. www.cdc.gov/std/treatment-guidelines/chlamydia.htm. Updated July 22, 2021. Accessed April 22, 2024.
Reno HEL, Geisler WM. Diseases caused by chlamydiae. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 294.
US Preventive Services Task Force, Davidson KW, Barry MJ, et al. Screening for chlamydia and gonorrhea: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. JAMA. 2021;326(10):949-956. PMID: 34519796 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34519796/.
-
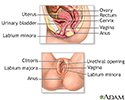
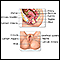
Female reproductive anatomy - illustration
Internal structures of the female reproductive anatomy include the uterus, ovaries, and cervix. External structures include the labium minora and majora, the vagina and the clitoris.
Female reproductive anatomy
illustration
-
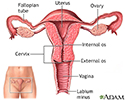
Uterus - illustration
The uterus is a hollow muscular organ located in the female pelvis between the bladder and rectum. The ovaries produce the eggs that travel through the fallopian tubes. Once the egg has left the ovary it can be fertilized and implant itself in the lining of the uterus. The main function of the uterus is to nourish the developing fetus prior to birth.
Uterus
illustration
-
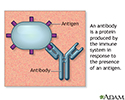
Antibodies - illustration
Antigens are large molecules (usually proteins) on the surface of cells, viruses, fungi, bacteria, and some non-living substances such as toxins, chemicals, drugs, and foreign particles. The immune system recognizes antigens and produces antibodies that destroy substances containing antigens.
Antibodies
illustration
-
Female reproductive anatomy - illustration
Internal structures of the female reproductive anatomy include the uterus, ovaries, and cervix. External structures include the labium minora and majora, the vagina and the clitoris.
Female reproductive anatomy
illustration
-
Uterus - illustration
The uterus is a hollow muscular organ located in the female pelvis between the bladder and rectum. The ovaries produce the eggs that travel through the fallopian tubes. Once the egg has left the ovary it can be fertilized and implant itself in the lining of the uterus. The main function of the uterus is to nourish the developing fetus prior to birth.
Uterus
illustration
-
Antibodies - illustration
Antigens are large molecules (usually proteins) on the surface of cells, viruses, fungi, bacteria, and some non-living substances such as toxins, chemicals, drugs, and foreign particles. The immune system recognizes antigens and produces antibodies that destroy substances containing antigens.
Antibodies
illustration
Review Date: 4/16/2024
Reviewed By: John D. Jacobson, MD, Professor Emeritus, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Loma Linda University School of Medicine, Loma Linda, CA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.