Primary lymphoma of the brain
Brain lymphoma; Cerebral lymphoma; Primary lymphoma of the central nervous system; PCNSL; Lymphoma - B-cell lymphoma, brainPrimary lymphoma of the brain is cancer of white blood cells that starts in the brain.
Causes
The cause of primary brain lymphoma is not known.
People with a weakened immune system are at high risk for primary lymphoma of the brain. Common causes of a weakened immune system include HIV/AIDS and having had an organ transplant (especially heart transplant).
Primary lymphoma of the brain may be linked to Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), especially in people with HIV/AIDS. EBV is the virus that causes mononucleosis.
Epstein-Barr virus
Epstein-Barr virus antibody test is a blood test to detect antibodies to the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), which is a cause of the infectious disease mon...

HIV/AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is the virus that causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). When a person becomes infected with HIV, the ...

Mononucleosis
Mononucleosis, or mono, is a viral infection that causes fever, sore throat, and swollen lymph glands, most often in the neck.

Primary brain lymphoma is more common in people ages 45 to 70. The rate of primary brain lymphoma is rising. Almost 1,500 new patients are diagnosed with primary brain lymphoma every year in the United States.
Symptoms
Symptoms of primary brain lymphoma may include any of the following:
- Changes in speech or vision
- Confusion or hallucinations
Hallucinations
Hallucinations involve sensing things such as visions, sounds, or smells that seem real but are not. These things are created by the mind.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Seizures
Seizures
A seizure is the physical changes in behavior that occurs during an episode of specific types of abnormal electrical activity in the brain. The term ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Headaches, nausea, or vomiting
Headaches
A headache is pain or discomfort in the head, scalp, or neck. Serious causes of headaches are rare. Most people with headaches can feel much better...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Leaning to one side when walking
- Weakness in hands or loss of coordination
-
Numbness to hot, cold, and pain
Numbness
Numbness and tingling are abnormal sensations that can occur anywhere in your body, but they are often felt in your fingers, hands, feet, arms, or le...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Personality changes
- Weight loss
Exams and Tests
The following tests may be done to help diagnose a primary lymphoma of the brain:
-
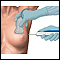
Biopsy of the brain tumor
Biopsy
A biopsy is the removal of a small piece of tissue for lab examination.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Head CT scan, PET scan or MRI
Head CT scan
A head computed tomography (CT) scan uses many x-rays to create pictures of the head, including the skull, brain, eye sockets, and sinuses.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleMRI
A head MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is an imaging test that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the brain and surrounding...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Spinal tap (lumbar puncture)
Spinal tap
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) collection is a test to look at the fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. CSF acts as a cushion, protecting the b...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
The main treatment is with chemotherapy and certain monoclonal antibodies, which are a type of lab-made protein to treat many diseases, including cancer.
Chemotherapy
The term chemotherapy is used to describe cancer-killing drugs. Chemotherapy may be used to:Cure the cancerShrink the cancerPrevent the cancer from ...
Younger people may receive high-dose chemotherapy, possibly followed by an autologous stem cell transplant.
Autologous stem cell transplant
A bone marrow transplant is a procedure to replace damaged or diseased bone marrow with healthy bone marrow stem cells. Bone marrow is the soft, fatt...

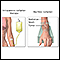
Radiation therapy of the whole brain may be done after chemotherapy, but is often avoided due to potential neurologic complications.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-powered radiation (such as x-rays or gamma rays), particles, or radioactive seeds to kill cancer cells.
Boosting the immune system, such as in those with HIV/AIDS or a history of organ transplant, may also be tried.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Without treatment, people with primary brain lymphoma survive for less than 6 months. When treated with chemotherapy, half of the patients will be in remission 10 years after being diagnosed. Survival may improve with autologous stem cell transplant.
Possible Complications
Possible complications include:
- Chemotherapy side effects, including low blood counts
- Radiation side effects, including confusion, headaches, nervous system (neurologic) problems, and tissue death
- Return (recurrence) of the lymphoma
References
National Cancer Institute website. Primary CNS lymphoma treatment (PDQ) - health professional version. www.cancer.gov/types/lymphoma/hp/primary-cns-lymphoma-treatment-pdq. Updated December 2, 2022. Accessed May 13, 2024.
National Comprehensive Cancer Network website. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology (NCCN guidelines): central nervous system cancers. Version 1.2023. www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/cns.pdf. Updated May 31, 2024. Accessed June 18, 2024.
Roque A, Hochberg FH, Baehring JM. Primary nervous system tumors in adults. In: Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC, Pomeroy SL, Newman NJ, eds. Bradley and Daroff's Neurology in Clinical Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 74.
-
Brain - illustration
The major areas of the brain have one or more specific functions.
Brain
illustration
-
MRI of the brain - illustration
An MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) of the brain creates a detailed image of the complex structures in the brain. An MRI can give a three-dimensional depiction of the brain, making location of problems such as tumors or aneuryms more precise.
MRI of the brain
illustration
-
Brain - illustration
The major areas of the brain have one or more specific functions.
Brain
illustration
-
MRI of the brain - illustration
An MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) of the brain creates a detailed image of the complex structures in the brain. An MRI can give a three-dimensional depiction of the brain, making location of problems such as tumors or aneuryms more precise.
MRI of the brain
illustration
Review Date: 3/31/2024
Reviewed By: Todd Gersten, MD, Hematology/Oncology, Florida Cancer Specialists & Research Institute, Wellington, FL. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.



