Drug-induced tremor
Tremor - drug-induced; Shaking - drug tremorDrug-induced tremor is involuntary shaking due to the use of medicines. Involuntary means you shake without trying to do so and can't stop when you try. The shaking occurs when you move or try to hold your arms, hands, or head in a certain position. It is not associated with other symptoms.
Causes
Drug-induced tremor is a nervous system and muscle response to certain medicines. Medicines that can cause tremors include the following:
- Cancer medicines such as thalidomide and cytarabine
- Seizure medicines such as divalproex sodium (Depakote)
- Asthma medicines such as theophylline and albuterol
- Immune suppressing medicines such as cyclosporine and tacrolimus
- Mood stabilizers such as lithium carbonate
-
Stimulants such as caffeine and amphetamines
Stimulants
Stimulants are chemicals (usually drugs or medicines that increase your heart rate, breathing rate, and brain function. Some stimulants affect only ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleCaffeine
Caffeine is a substance that is found in certain plants. It can also be man-made and added to foods. It is a central nervous system stimulant and a...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Antidepressant medicines such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and tricyclics
- Heart medicines such as amiodarone, procainamide, and others
- Certain antibiotics
- Steroids
- Certain antivirals, such as acyclovir and vidarabine
- Alcohol
- Nicotine
- Certain high blood pressure medicines
- Epinephrine and norepinephrine
- Too much thyroid medicine (levothyroxine)
- Tetrabenazine, a medicine to treat excessive movement disorder
Symptoms
Your tremor may affect your hands, arms, head, or eyelids. In rare cases, your lower body is affected. Your tremor may not affect both sides of the body equally.
The shaking is usually fast, about 4 to 12 movements per second.
Your tremor may be:
- Episodic (occurring in bursts, sometimes about an hour after taking the medicine)
- Intermittent (comes and goes with activity, but not always)
- Sporadic (happens on occasion)
Your tremor can:
- Occur either with movement or at rest
- Disappear during sleep
- Get worse with voluntary movement and emotional stress
Other symptoms may include:
- Head nodding
- Shaking or quivering sound to the voice
- Problems with writing, drawing, drinking from a cup, or using tools if the tremor affects the hands
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider can make the diagnosis by performing a physical exam and asking about your medical and personal history. You will also be asked about the medicines you take.
Tests may be done to check for other reasons for your tremor. A tremor that occurs when the muscles are relaxed or that affects the legs or coordination may be a sign of another condition, such as Parkinson disease. The speed of the tremor can be an important way to determine its cause.
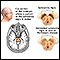
Parkinson disease
Parkinson disease results from certain brain cells dying. These cells help control movement and coordination. The disease leads to shaking (tremors...
Other causes of tremors may include:
- Essential tremor
-
Alcohol withdrawal
Alcohol withdrawal
Alcohol withdrawal refers to symptoms that may occur when a person who has been drinking too much alcohol on a regular basis suddenly stops drinking ...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Cigarette smoking
-
Overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism)
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland makes too much thyroid hormone. The condition is often called overactive thyroid.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Parkinson disease
-
Adrenal gland tumor (pheochromocytoma)
Pheochromocytoma
Pheochromocytoma is a rare tumor of adrenal gland tissue that typically arises from the adrenal gland. It results in the release of too much epineph...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Too much caffeine
-
Disorder in which there is too much copper in the body (Wilson disease)
Wilson disease
Wilson disease is an inherited disorder in which there is too much copper in the body's tissues. The excess copper damages the liver and nervous sys...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Blood tests and imaging tests (such as a CT scan of the head, brain MRI, and x-rays) are usually normal.
CT scan of the head
A head computed tomography (CT) scan uses many x-rays to create pictures of the head, including the skull, brain, eye sockets, and sinuses.

Brain MRI
A head MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is an imaging test that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the brain and surrounding...

x-rays
A skull x-ray is a picture of the bones surrounding the brain, including the facial bones, the nose, and the sinuses.

Treatment
Drug-induced tremor often goes away when you stop taking the medicine that is causing the shaking.
You may not need treatment or changes in the medicine if the tremor is mild and does not interfere with your daily activity.
If the benefit of the medicine is greater than the problems caused by the tremor, your provider may have you try different dosages of the medicine. Or, you may be prescribed another medicine to treat your condition. In rare cases, a medicine such as propranolol may be added to help control the tremor.
Do not stop taking any medicine without first talking to your provider.
Possible Complications
Severe tremor can interfere with daily activities, especially fine motor skills such as writing, and other activities such as eating or drinking.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you are taking a medicine and a tremor develops that interferes with your activity or is accompanied by other symptoms.
Prevention
Always tell your provider about the medicines you take. Ask your provider if it is OK to take over-the-counter medicines that contain stimulants or theophylline. Theophylline is a medicine used to treat wheezing and shortness of breath.
Caffeine can cause tremor and make tremor caused by other medicines worse. If you have a tremor, avoid caffeinated drinks such as coffee, tea, and soda. Also avoid other stimulants.
References
Mastaglia FL. Drug-induced disorders of the nervous system. In: Aminoff MJ, Josephson SA, eds. Aminoff's Neurology and General Medicine. 6th ed. Waltham, MA: Elsevier Academic Press; 2021:chap 32.
Morgan JC, Kurek JA, Davis JL, Sethi KD. Insights into pathophysiology from medication-induced tremor. Tremor Other Hyperkinet Mov (N Y). 2017;7:442. PMID: 29204312 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29204312/.
Okun MS, Ostrem JL. Other movement disorders. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 379.
Ul Haq Ihtsham, Liebenow B, Okun MS. Clinical overview of movement disorders. In: Winn HR, ed. Youmans and Winn Neurological Surgery. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 105.
-
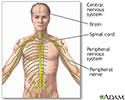
Central nervous system and peripheral nervous system - illustration
The central nervous system is made up of the brain and the spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system includes nerves outside the brain and spinal cord.
Central nervous system and peripheral nervous system
illustration
-
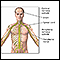
Brain - illustration
The major areas of the brain have one or more specific functions.
Brain
illustration
-
Central nervous system and peripheral nervous system - illustration
The central nervous system is made up of the brain and the spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system includes nerves outside the brain and spinal cord.
Central nervous system and peripheral nervous system
illustration
-
Brain - illustration
The major areas of the brain have one or more specific functions.
Brain
illustration
Review Date: 6/13/2024
Reviewed By: Joseph V. Campellone, MD, Department of Neurology, Cooper Medical School at Rowan University, Camden, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.