Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome
Korsakoff psychosis; Alcoholic encephalopathy; Encephalopathy - alcoholic; Wernicke's disease; Alcohol use - Wernicke; Alcoholism - Wernicke; Thiamine deficiency - WernickeWernicke-Korsakoff syndrome is a brain disorder due to vitamin B1 (thiamine) deficiency.
Vitamin B1 (thiamine) deficiency
Beriberi is a disease in which the body does not have enough thiamine (vitamin B1).
Causes
Wernicke encephalopathy and Korsakoff syndrome are different conditions that often occur together. Both are due to brain damage caused by a lack of vitamin B1.
Lack of vitamin B1 is common in people who have alcohol use disorder. It is also common in people whose bodies do not absorb food properly (malabsorption). This can sometimes occur with a chronic illness or after weight-loss (bariatric) surgery.
Alcohol use disorder
Alcohol use disorder is when your drinking causes serious problems in your life, yet you keep drinking. You may also need more and more alcohol to f...
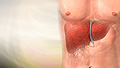
Malabsorption
Malabsorption involves problems with the body's ability to take in (absorb) nutrients from food.

Korsakoff syndrome, or Korsakoff psychosis, tends to develop as Wernicke encephalopathy as symptoms go away. Wernicke encephalopathy causes brain damage in lower parts of the brain called the thalamus and hypothalamus. Korsakoff psychosis results from permanent damage to areas of the brain involved with memory.
Symptoms
Symptoms of Wernicke encephalopathy include:
- Confusion and loss of mental activity that can progress to coma and death
Coma
Decreased alertness is a state of reduced awareness and is often a serious condition. A coma is the most severe state of decreased alertness in which...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Loss of muscle coordination (ataxia) that can cause leg tremor
Loss of muscle coordination
Uncoordinated movement is due to a muscle control problem that causes an inability to coordinate movements. It leads to a jerky, unsteady, to-and-fr...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Vision changes such as
abnormal eye movements (back and forth movements called nystagmus),
double vision, eyelid drooping
Abnormal eye movements
Nystagmus is a term to describe uncontrollable movements of the eyes that may be:Side to side (horizontal nystagmus)Up and down (vertical nystagmus)R...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleDouble vision
There are many types of eye problems and vision disturbances, such as: Halos Blurred vision (the loss of sharpness of vision and the inability to see...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleEyelid drooping
Eyelid drooping is excess sagging of the upper eyelid. The edge of the upper eyelid may be lower than it should be (ptosis) or there may be excess b...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Alcohol withdrawal
Alcohol withdrawal
Alcohol withdrawal refers to symptoms that may occur when a person who has been drinking too much alcohol on a regular basis suddenly stops drinking ...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article
Symptoms of Korsakoff syndrome include:
- Inability to form new memories
- Loss of memory, can be severe
- Making up stories (confabulation)
- Seeing or hearing things that are not really there (hallucinations)
Hallucinations
Hallucinations involve sensing things such as visions, sounds, or smells that seem real but are not. These things are created by the mind.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Exams and Tests
Examination of the nervous/muscular system may show damage to many nerve systems:
- Abnormal eye movement
- Decreased or abnormal reflexes
- Fast pulse (heart rate)
- Low blood pressure
- Low body temperature
-
Muscle weakness and atrophy (loss of muscle mass)
Loss of muscle mass
Muscle atrophy is the wasting (thinning) or loss of muscle tissue.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Problems with walk (gait) and coordination
The person may appear poorly nourished. The following tests are used to check a person's nutrition level:
-
Serum albumin (relates to person's general nutrition)
Serum albumin
Albumin is a protein made by the liver. A serum albumin test measures the amount of this protein in the clear liquid portion of the blood. Albumin c...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Serum vitamin B1 levels
- Transketolase activity in red blood cells (reduced in people with thiamine deficiency)
Liver enzymes may be high in people with a history of long-term alcohol abuse.
Other conditions that may cause vitamin B1 deficiency include:
-
HIV/AIDS
HIV/AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is the virus that causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). When a person becomes infected with HIV, the ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Chemotherapy or cancers that have spread throughout the body
- Extreme nausea and vomiting during pregnancy (hyperemesis gravidarum)
Hyperemesis gravidarum
Hyperemesis gravidarum is extreme, persistent nausea and vomiting during pregnancy. It can lead to dehydration, weight loss, and electrolyte imbalan...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Heart failure (when treated with long-term diuretic therapy)
Heart failure
Heart failure is a condition in which the heart is no longer able to pump oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body efficiently. This causes symptom...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Long periods of intravenous (IV) nutrition without receiving thiamine supplements
Intravenous
Intravenous means "within a vein. " Most often it refers to giving medicines or fluids through a needle or tube inserted into a vein. This allows th...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Long-term dialysis
- Very high thyroid hormone levels (thyrotoxicosis)
Thyrotoxicosis
Hyperthyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland makes too much thyroid hormone. The condition is often called overactive thyroid.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
A brain MRI may show changes in the tissue of the brain. But if Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome is suspected, treatment should start immediately. Usually a brain MRI exam is not needed.
MRI
A head MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is an imaging test that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the brain and surrounding...

Treatment
The goals of treatment are to control symptoms and to prevent the disorder from getting worse. Some people may need to stay in the hospital early in the condition to help control symptoms.
Monitoring and special care may be needed if the person is:
- In a coma
-
Lethargic
Lethargic
Fatigue is a feeling of weariness, tiredness, or lack of energy.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Unconscious
Vitamin B1 is usually given by injection into a vein or a muscle as soon as possible. This may improve symptoms of:
-
Confusion or delirium
Confusion
Confusion is the inability to think as clearly or quickly as you normally do. You may feel disoriented and have difficulty paying attention, remembe...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleDelirium
Delirium is sudden severe confusion due to rapid changes in brain function that can occur with physical or mental illness.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Difficulties with vision and eye movement
- Lack of muscle coordination
Vitamin B1 often does not improve loss of memory and intellect that occur with Korsakoff syndrome.
Stopping alcohol use can prevent more loss of brain function and damage to nerves. A well-balanced, nourishing diet can help, but it is not a substitute for stopping alcohol use.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Without treatment, Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome gets steadily worse, and can be life threatening. With treatment, it is possible to control symptoms (such as uncoordinated movement and vision difficulties). This disorder can also be slowed or stopped.
Possible Complications
Complications that may result include:
- Alcohol withdrawal
- Difficulty with personal or social interaction
- Injury caused by falls
- Permanent alcoholic neuropathy
Alcoholic neuropathy
Alcoholic neuropathy is damage to the nerves that results from excessive drinking of alcohol.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Permanent loss of thinking skills
- Permanent loss of memory
- Shortened life span
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your health care provider or go to the emergency room if you have symptoms of Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome, or if you have been diagnosed with the condition and your symptoms get worse or return.
Prevention
Not drinking alcohol or drinking in moderation and getting enough nutrition reduce the risk of developing Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome. If a heavy drinker will not quit, thiamine supplements and a good diet may reduce the chance of getting this condition, but the risk is not eliminated.
References
Koppel BS, Weimer LH, Daras M. Nutritional and alcohol-related neurologic disorders. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 384.
So YT. Deficiency diseases of the nervous system. In: Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC, Pomeroy SL, Newman NJ, eds. Bradley and Daroff's Neurology in Clinical Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 85.
-
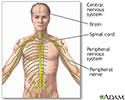
Central nervous system and peripheral nervous system - illustration
The central nervous system is made up of the brain and the spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system includes nerves outside the brain and spinal cord.
Central nervous system and peripheral nervous system
illustration
-
Brain - illustration
The major areas of the brain have one or more specific functions.
Brain
illustration
-
Brain structures - illustration
The structures of the brain include the brainstem, consisting of the spinal cord, the medulla oblongata, the pons and the midbrain; the cerebellum; the cerebrum (one half, or hemisphere shown), and the diencephalon.
Brain structures
illustration
-
Central nervous system and peripheral nervous system - illustration
The central nervous system is made up of the brain and the spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system includes nerves outside the brain and spinal cord.
Central nervous system and peripheral nervous system
illustration
-
Brain - illustration
The major areas of the brain have one or more specific functions.
Brain
illustration
-
Brain structures - illustration
The structures of the brain include the brainstem, consisting of the spinal cord, the medulla oblongata, the pons and the midbrain; the cerebellum; the cerebrum (one half, or hemisphere shown), and the diencephalon.
Brain structures
illustration
Review Date: 3/31/2024
Reviewed By: Joseph V. Campellone, MD, Department of Neurology, Cooper Medical School at Rowan University, Camden, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.