Bell palsy
Facial palsy; Idiopathic peripheral facial palsy; Cranial mononeuropathy - Bell palsy; Bell's palsyBell palsy is a disorder of the nerve that controls movement of the muscles in the face. This nerve is called the facial or seventh cranial nerve.
Damage to this nerve causes weakness or paralysis of these muscles. Paralysis means that you cannot use the muscles at all.
Paralysis
Facial paralysis means that a person is no longer able to move some or all of the muscles on one or both sides of the face.
Causes
Bell palsy can affect people of any age, most commonly those over age 65 years. It can also affect children younger than 10 years. Males and females are equally affected.
Bell palsy is thought to be due to swelling (inflammation) of the facial nerve in the area where it travels through the bones of the skull. This nerve controls movement of the muscles of the face.
Swelling
Swelling is the enlargement of organs, skin, or other body parts. It is caused by a buildup of fluid in the tissues. The extra fluid can lead to a ...

The cause is often not clear. A type of herpes infection called herpes simplex or herpes zoster might be involved. Other conditions that may affect the seventh cranial nerve include:
Herpes zoster
Shingles is a painful, blistering skin rash. It is caused by the varicella-zoster virus, a member of the herpes family of viruses. This is the viru...
-
HIV/AIDS infection
HIV/AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is the virus that causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). When a person becomes infected with HIV, the ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
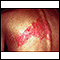
Lyme disease
Lyme disease
Lyme disease is a bacterial infection that is spread through the bite of one of several types of ticks.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
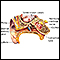
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Middle ear infection
Ear infection
Otitis is a term for infection or inflammation of the ear.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Sarcoidosis (inflammation of the lymph nodes, lungs, liver, eyes, skin, or other tissues)
Sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis is a disease in which inflammation occurs in the lymph nodes, lungs, liver, eyes, skin, and other tissues.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Having diabetes and being pregnant may increase the risk for Bell palsy.
Symptoms
Sometimes, you may have a cold shortly before the symptoms of Bell palsy begin.
Symptoms most often start suddenly, but may take 2 to 3 days to become fully developed. They do not become more severe after that.
Symptoms are almost always on one side of the face only. They may range from mild to severe.
Many people feel discomfort behind the ear before weakness is noticed. The face feels stiff or pulled to one side and may look different. Other signs can include:
- Difficulty closing one eye
- Difficulty eating and drinking because food falls out of one side of the mouth
- Drooling due to lack of control over the muscles of the face
- Slurring your words (dysarthria) due to lip weakness
- Drooping of the face, such as the eyelid or corner of the mouth
- Problems smiling, grimacing, or making facial expressions
- Twitching or weakness of the muscles in the face
Other symptoms that may occur:
- Dry eye, which may lead to eye sores or infections
- Dry mouth
- Headache if there is an infection such as Lyme disease
-
Loss of sense of taste
Loss of sense of taste
Taste impairment means there is a problem with your sense of taste. Problems range from distorted taste to a complete loss of the sense of taste. A...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Sound that is louder in one ear (hyperacusis)
Exams and Tests
Often, Bell palsy can be diagnosed just by taking a health history and doing a complete physical exam.
Blood tests may be done to look for medical problems such as Lyme disease, which may cause Bell palsy.
Sometimes, a test is needed to check the nerves that supply the muscles of the face:
-
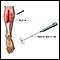
Electromyography (EMG) to check the health of the facial muscles and the nerves that control the muscles
Electromyography
Electromyography (EMG) is a test that checks the health of the muscles and the nerves that control the muscles.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
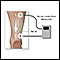
Nerve conduction test to check how fast electrical signals move through a nerve
Nerve conduction test
Nerve conduction velocity (NCV) is a test to see how fast electrical signals move through a nerve. This test is done along with electromyography (EM...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
If your health care provider is worried there is another cause for your symptoms, they may suggest:
-
CT scan of the head
CT scan of the head
A head computed tomography (CT) scan uses many x-rays to create pictures of the head, including the skull, brain, eye sockets, and sinuses.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the head
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the...
A head MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is an imaging test that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the brain and surrounding...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Lumbar puncture (spinal tap)
Lumbar puncture
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) collection is a test to look at the fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. CSF acts as a cushion, protecting the b...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
Often, no treatment is needed. Symptoms often begin to improve right away. But, it may take weeks or even months for the muscles to get stronger.
Your provider may give you lubricating eye drops or eye ointments to keep the surface of the eye moist if you can't close it completely. You may need to wear an eye patch while you sleep.
Often, medicines may be used to improve the chances of recovery, but they must be started right away. Common medicines are:
- Corticosteroids, which may reduce swelling around the facial nerve
- Medicines such as valacyclovir to fight the virus that may be causing Bell palsy
Surgery to relieve pressure on the nerve (decompression surgery) has not been shown to benefit most people with Bell palsy.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Most cases go away completely within a few weeks to months.
If you did not lose all of your nerve function and symptoms began to improve within 3 weeks, you are more likely to regain all or most of the strength in your facial muscles.
Sometimes, the following symptoms may still be present:
- Long-term changes in taste
- Spasms of muscles or eyelids
- Weakness that remains in facial muscles
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
- Eye surface becoming dry, leading to eye sores, infections, and vision loss
- Swelling in the muscles due to loss of nerve function
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider right away if your face droops or you have other symptoms of Bell palsy. Your provider can rule out other, more serious conditions, such as stroke.
Prevention
There is no known way to prevent Bell palsy.
References
National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke website. Bell's palsy. www.ninds.nih.gov/health-information/disorders/bells-palsy. Updated May 2, 2024. Accessed July 1, 2024.
Ryan MM. Bell palsy. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 22nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 657.
Smith G, Shy ME. Peripheral neuropathies. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 388.
Wallenstein J. Brain and cranial nerve disorders. In: Walls RM, ed. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 91.
-
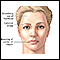
Facial drooping - illustration
Facial drooping can be caused by a disorder such as Bell's palsy. This disorder is a mononeuropathy (involvement of a single nerve) that damages the seventh cranial (facial) nerve. The facial nerve controls movement of the muscles of the face.
Facial drooping
illustration
-
Facial drooping - illustration
Facial drooping can be caused by a disorder such as Bell's palsy. This disorder is a mononeuropathy (involvement of a single nerve) that damages the seventh cranial (facial) nerve. The facial nerve controls movement of the muscles of the face.
Facial drooping
illustration
Review Date: 6/13/2024
Reviewed By: Joseph V. Campellone, MD, Department of Neurology, Cooper Medical School at Rowan University, Camden, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.



