Osmotic demyelination syndrome
ODS; Central pontine demyelination; Central pontine myelinolysisOsmotic demyelination syndrome (ODS) leads to brain cell dysfunction. It is caused by the destruction of the layer (myelin sheath) covering nerve cells in the brain, most often the middle of the brainstem (pons).
Myelin sheath
Myelin is an insulating layer, or sheath that forms around nerves, including those in the brain and spinal cord. It is made up of protein and fatty ...

Causes
When the myelin sheath that covers nerve cells is destroyed, signals from one nerve to another aren't properly transmitted. Although the brainstem is mainly affected, other areas of the brain can also be involved.
The most common cause of ODS is a quick change in the body's blood sodium levels. This most often occurs when someone is being treated for low blood sodium (hyponatremia) and the sodium is replaced too fast. Sometimes, it occurs when a high level of sodium in the body (hypernatremia) is corrected too quickly.
Hyponatremia
Low blood sodium is a condition in which the sodium level in the blood is lower than normal. The medical name of this condition is hyponatremia....
ODS does not usually occur on its own. Most often, it's a complication of treatment for other problems, or from the other problems themselves.
Risks include:
-
Alcohol use
Alcohol use
Alcohol use disorder is when your drinking causes serious problems in your life, yet you keep drinking. You may also need more and more alcohol to f...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
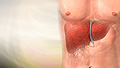
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Liver disease
-
Malnutrition from serious illnesses
Malnutrition
Malnutrition is the condition that occurs when your body does not get enough nutrients.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Radiation treatment of the brain
- Severe nausea and vomiting during pregnancy
Symptoms
Symptoms may include any of the following:
-
Confusion, delirium, hallucinations
Confusion
Confusion is the inability to think as clearly or quickly as you normally do. You may feel disoriented and have difficulty paying attention, remembe...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleDelirium
Delirium is sudden severe confusion due to rapid changes in brain function that can occur with physical or mental illness.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleHallucinations
Hallucinations involve sensing things such as visions, sounds, or smells that seem real but are not. These things are created by the mind.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Balance problems, tremor
Tremor
A tremor is a type of shaking movement. A tremor is most often noticed in the hands and arms. It may affect any body part, including the head, tong...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Problem swallowing
Problem swallowing
Difficulty with swallowing is the feeling that food or liquid is stuck in the throat or at any point before the food enters the stomach. This proble...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Reduced alertness, drowsiness or sleepiness, lethargy, poor responses
Reduced alertness
Decreased alertness is a state of reduced awareness and is often a serious condition. A coma is the most severe state of decreased alertness in which...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleDrowsiness or sleepiness
Drowsiness refers to feeling more sleepy than normal during the day. People who are drowsy may fall asleep when they do not want to or at times whic...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleLethargy
Fatigue is a feeling of weariness, tiredness, or lack of energy.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Slurred speech (dysarthria)
Slurred speech
Dysarthria is a condition in which you have difficulty saying words because of problems with the muscles that help you talk.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Weakness in the face, arms, or legs, usually affecting both sides of the body
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will perform a physical exam and ask about the symptoms.
A head MRI scan may reveal a problem in the brainstem (pons) or other parts of the brain. This is the main diagnostic test.
Head MRI
A head MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is an imaging test that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the brain and surrounding...

Other tests may include:
-
Blood sodium level and other blood tests
Blood sodium level
The sodium blood test measures the concentration of sodium in the blood. Sodium can also be measured using a urine test.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Brainstem auditory evoked response (BAER)
Brainstem auditory evoked response
Brainstem auditory evoked response (BAER) is a test to measure the brain wave activity that occurs in response to sounds such as clicks or certain to...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
ODS is an emergency disorder that needs to be treated in the hospital though most people with this condition are already in the hospital for another problem.
There is no known cure for central pontine myelinolysis. Treatment is focused on relieving symptoms.
Physical therapy may help maintain muscle strength, mobility, and function in weakened arms and legs.
Outlook (Prognosis)
The nerve damage caused by central pontine myelinolysis is often long-lasting. The disorder can cause serious long-term (chronic) disability.
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
- Decreased ability to interact with others
- Decreased ability to work or care for self
- Inability to move, other than to blink eyes ("locked in" syndrome)
- Permanent nervous system damage
When to Contact a Medical Professional
There is no real guideline on when to seek medical attention, because ODS is rare in the general community.
Prevention
In the hospital, slow, controlled treatment of a low sodium level may reduce the risk for nerve damage in the pons. Being aware of how some medicines can change sodium levels can prevent the level from changing too quickly.
References
Weissenborn K, Lockwood AH. Toxic and metabolic encephalopathies. In: Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC, Pomeroy SL, Newman NJ, eds. Bradley and Daroff's Neurology in Clinical Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 84.
Yaqoob MM, McCafferty K. Water balance, fluids and electrolytes. In: Feather A, Randall D, Waterhouse M, eds. Kumar and Clark's Clinical Medicine. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 9.
-
Brain structures - illustration
The structures of the brain include the brainstem, consisting of the spinal cord, the medulla oblongata, the pons and the midbrain; the cerebellum; the cerebrum (one half, or hemisphere shown), and the diencephalon.
Brain structures
illustration
Review Date: 6/13/2024
Reviewed By: Joseph V. Campellone, MD, Department of Neurology, Cooper Medical School at Rowan University, Camden, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.


