Neurofibromatosis 2
NF2; Bilateral acoustic neurofibromatosis; Bilateral vestibular schwannomas; Central neurofibromatosisNeurofibromatosis 2 (NF2) is a disorder in which tumors form on the nerves of the brain and spine (the central nervous system). It may be passed down (inherited) in families.
Although it has a similar name to neurofibromatosis type 1, it is a different and separate condition.
Neurofibromatosis type 1
Neurofibromatosis-1 (NF1) is an inherited disorder in which nerve tissue tumors (neurofibromas) form in the:Upper and lower layers of the skinNerves ...
Causes
NF2 is caused by a change in the gene NF2. NF2 can be passed down through families in an autosomal dominant pattern. This means that if one parent has NF2, any child of that parent has a 50% chance of inheriting the condition. Once someone carries the genetic change, their children have a 50% chance of inheriting it.
Autosomal dominant
Autosomal dominant is one of many ways that a genetic trait or disorder can be passed down through families. In an autosomal dominant disease, if you...

Some cases of NF2 occur when the gene mutates on its own. This is called sporadic and is not inherited. Once someone carries the genetic change, their children have a 50% chance of inheriting it.
Symptoms
Symptoms of NF2 include:
- Balance problems
- Cataracts at a young age
- Changes in vision
- Coffee-colored marks on the skin (café-au-lait), less common
- Headaches
- Hearing loss
- Ringing and noises in the ears
- Weakness of the face
Exams and Tests
Signs of NF2 include:
- Brain and spinal tumors
- Hearing-related (acoustic) tumors
- Skin tumors
Tests include:
- Physical examination
- Medical history
-
MRI
MRI
A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan is an imaging test that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the body. It does not us...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
CT scan
CT scan
A computed tomography (CT) scan is an imaging method that uses x-rays to create pictures of cross-sections of the body. Related tests include:Abdomin...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Genetic testing
Genetic testing
An epidermoid cyst is a closed sac under the skin, or a skin lump, filled with dead skin cells.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
Acoustic nerve tumors can be observed or treated with surgery or radiation.
Radiation
Radiation therapy uses high-powered radiation (such as x-rays or gamma rays), particles, or radioactive seeds to kill cancer cells.
People with this disorder may benefit from genetic counseling.
People with NF2 should be regularly evaluated with these tests:
- MRI of the brain and spinal cord
- Hearing and speech evaluation
Speech evaluation
A speech disorder is a condition in which a person has problems creating or forming the speech sounds needed to communicate with others. This can ma...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Eye exam
Eye exam
A standard eye exam is a series of tests done to check your vision and the health of your eyes. This exam is performed by an ophthalmologist or opto...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Support Groups
More information and support for people with NF2 and their families can be found at:
- Children's Tumor Foundation -- www.ctf.org
- Neurofibromatosis Network -- www.nfnetwork.org
References
Goldblum JR, Folpe AL, Weiss SW. Benign tumors of peripheral nerves. In: Goldblum JR, Folpe AL, Weiss SW, eds. Enzinger and Weiss's Soft Tissue Tumors. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 26.
Safier RA, Cleves-Bayon C, Gaesser J. Neurology. In: Zitelli BJ, McIntire SC, Nowalk AJ, Garrison J, eds. Zitelli and Davis' Atlas of Pediatric Physical Diagnosis. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 16.
Sahin M, Ullrich N, Srivastava S, Pinto AL. Neurocutaneous syndromes. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 22nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 636.
-
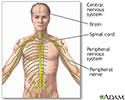
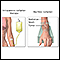
Central nervous system and peripheral nervous system - illustration
The central nervous system is made up of the brain and the spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system includes nerves outside the brain and spinal cord.
Central nervous system and peripheral nervous system
illustration
Review Date: 12/31/2023
Reviewed By: Anna C. Edens Hurst, MD, MS, Associate Professor in Medical Genetics, The University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, AL. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.