Folliculitis
Pseudofolliculitis barbae; Tinea barbae; Barber's itchFolliculitis is inflammation of one or more hair follicles. It can occur anywhere on the skin.
Causes
Folliculitis starts when hair follicles are damaged or when the follicle is blocked. For example, this may occur from rubbing against clothing or shaving. Most of the time, the damaged follicles become infected with staphylococci (staph) bacteria.
Barber's itch is a staph infection of the hair follicles in the beard area, usually the upper lip. Shaving makes it worse. Tinea barbae is similar to barber's itch, but the infection is caused by a fungus.
Pseudofolliculitis barbae is a disorder that occurs mainly in African American men. If curly beard hairs are cut too short, they may curve back into the skin and cause inflammation.
Folliculitis can affect people of all ages.
Symptoms
Common symptoms include a rash, itching, and pimples or pustules near a hair follicle in the neck, groin, or genital area. The pimples may crust over.
Rash
Rashes involve changes in the color, feeling or texture of your skin.

Pimples
Acne is a skin condition that causes pimples or "zits. " Whiteheads, blackheads, and red, inflamed bumps or patches of skin (such as cysts) may devel...

Pustules
Pustules are small, inflamed, pus-filled, blister-like sores (lesions) on the skin surface.
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider can diagnose this condition by looking at your skin. Lab tests may show which bacteria or fungus is causing the infection.
Treatment
Warm, moist compresses may help drain the affected follicles.
Treatment may include antibiotics applied to the skin or taken by mouth, or an antifungal medicine.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Folliculitis often responds well to treatment, but it may come back.
Possible Complications
Folliculitis may return or spread to other body areas.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Apply home treatment and contact your provider if your symptoms:
- Come back often
- Get worse
- Last longer than 2 or 3 days
Prevention
To prevent further damage to the hair follicles and infection:
- Reduce friction from clothing.
- Avoid shaving the area, if possible. If shaving is necessary, use a clean, new razor blade or an electric razor each time.
- Keep the area clean.
- Avoid contaminated clothing and washcloths.
References
Dinulos JGH. Bacterial infections. In: Dinulos JGH, ed. Habif's Clinical Dermatology: A Color Guide in Diagnosis and Therapy. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 9.
James WD, Elston DM, Treat JR, Rosenbach MA, Neuhaus IM. Bacterial infections. In: James WD, Elston DM, Treat JR, Rosenbach, MA, Neuhaus IM, eds. Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. 13th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 14.
James WD, Elston DM, Treat JR, Rosenbach MA, Neuhaus IM. Diseases of the skin appendages. In: James WD, Elston DM, Treat JR, Rosenbach, MA, Neuhaus IM, eds. Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. 13th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 33.
Marks JG, Miller JJ. Pustules. In: Marks JG, Miller JJ, Hollins C, eds. Lookingbill and Marks' Principles of Dermatology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 12.
-
Folliculitis - decalvans on the scalp - illustration
Folliculitis, decalvans causes scarring with hair loss (alopecia). There are areas of corn stalking (grouped hairs arising within the area of alopecia), redness (erythema), crusting, and pustules. Due to severe scarring, permanent hair loss occurs in the involved sites.
Folliculitis - decalvans on the scalp
illustration
-
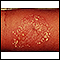
Folliculitis on the leg - illustration
Folliculitis has caused redness (erythema) and pus-filled blisters (pustules) to form around the hair follicles on this person's leg. This condition may be caused by infection or an irritation, such as shaving.
Folliculitis on the leg
illustration
-
Folliculitis - decalvans on the scalp - illustration
Folliculitis, decalvans causes scarring with hair loss (alopecia). There are areas of corn stalking (grouped hairs arising within the area of alopecia), redness (erythema), crusting, and pustules. Due to severe scarring, permanent hair loss occurs in the involved sites.
Folliculitis - decalvans on the scalp
illustration
-
Folliculitis on the leg - illustration
Folliculitis has caused redness (erythema) and pus-filled blisters (pustules) to form around the hair follicles on this person's leg. This condition may be caused by infection or an irritation, such as shaving.
Folliculitis on the leg
illustration
Review Date: 10/9/2024
Reviewed By: Linda J. Vorvick, MD, Clinical Professor, Department of Family Medicine, UW Medicine, School of Medicine, University of Washington, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.



