Ovarian cancer
Cancer - ovariesOvarian cancer is cancer that starts in the ovaries. The ovaries are the female reproductive organs that produce eggs.
Cancer
Cancer is the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the body. Cancerous cells are also called malignant cells.
Causes
Ovarian cancer is the fifth most common cancer among women. It causes more deaths than any other type of female reproductive organ cancer.
The cause of ovarian cancer is unknown.
Risks of developing ovarian cancer include any of the following:
- The fewer children a woman has and the later in life she gives birth, the higher her risk for ovarian cancer.
- Women who have had breast cancer or have a family history of breast or ovarian cancer have an increased risk for ovarian cancer (due to variants in genes such as BRCA1 or BRCA2).
- Women who take estrogen replacement only (not with progesterone) for 5 years or more may have a higher risk for ovarian cancer. Birth control pills, though, decrease the risk for ovarian cancer.
- Fertility treatment with medicines probably does not increase the risk for ovarian cancer.
- In vitro fertilization (IVF) may increase the risk of borderline or low malignant potential ovarian tumors.
- Older women are at the highest risk of developing ovarian cancer. Most deaths from ovarian cancer occur in women age 65 to 74.
Symptoms
Ovarian cancer symptoms are often vague. Women and their health care providers often blame the symptoms on other, more common conditions. Sometimes, by the time the cancer is diagnosed, the tumor has spread beyond the ovaries.
See your provider if you have the following symptoms on a daily basis for more than a few weeks:
-
Bloating or swelling in the belly area
Bloating
Abdominal bloating is a condition in which the belly (abdomen) feels full and tight. Your belly may look swollen (distended).
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Difficulty eating or feeling full quickly (early satiety)
Feeling full quickly
Satiety is the satisfied feeling of being full after eating. Early satiety is feeling full sooner than normal or after eating less than usual....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Pelvic or lower abdominal pain (area may feel heavy)
- Back pain
- Swollen lymph nodes in groin
Other symptoms that can occur:
-
Excessive hair growth that is coarse and dark
Excessive hair growth
Most of the time, women have fine hair above their lips and on their chin, chest, abdomen, or back. The growth of coarse dark hair in these areas (m...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Sudden urge to urinate
- Needing to urinate more often than usual (urinary frequency or urgency)
Urinary frequency or urgency
Frequent urination means needing to urinate more often than usual. Urgent urination is a sudden, strong need to urinate. This causes a discomfort i...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Constipation
Exams and Tests
A physical exam may often be normal. With advanced ovarian cancer, your provider may find a swollen abdomen often due to accumulation of fluid (ascites).
Ascites
Ascites is the build-up of fluid in the space between the lining of the abdomen and abdominal organs.

A pelvic exam may reveal an ovarian or abdominal mass.
Abdominal mass
An abdominal mass is swelling in one part of the belly area (abdomen).
A CA-125 blood test is not considered a good screening test for ovarian cancer. But, it may be done if a woman has:
CA-125 blood test
The CA-125 blood test measures the level of the protein CA-125 in the blood.

- Symptoms of ovarian cancer
- Already been diagnosed with ovarian cancer to determine how well treatment is working
Other tests that may be done include:
-
Complete blood count and blood chemistry
Complete blood count
A complete blood count (CBC) test measures the following:The number of white blood cells (WBC count)The number of red blood cells (RBC count)The numb...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Pregnancy test (serum HCG)
-
CT, positron emission tomography (PET) scan, or MRI of the pelvis or abdomen
CT
A computed tomography (CT) scan of the pelvis is an imaging method that uses x-rays to create cross-sectional pictures of the area between the hip bo...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticlePositron emission tomography
A positron emission tomography (PET) scan is a type of imaging test. It uses a radioactive substance called a tracer to look for disease in the body...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleMRI
A pelvis MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) scan is an imaging test that uses a machine with powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Ultrasound of the pelvis
Ultrasound
Transvaginal ultrasound is a test used to look at a woman's uterus, ovaries, tubes, cervix, and pelvic area. Transvaginal means across or through the...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Surgery, such as laparoscopy or exploratory laparotomy, may be required to find the cause of symptoms. A biopsy will be done to help make the diagnosis.
Laparoscopy
Pelvic laparoscopy is surgery to examine the pelvic organs. It uses a viewing tool called a laparoscope. The surgery is also used to treat certain ...
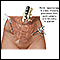
Laparotomy
Abdominal exploration is surgery to look at the organs and structures in your belly area (abdomen). This includes your:AppendixBladderGallbladderIn...

Biopsy
A biopsy is the removal of a small piece of tissue for lab examination.
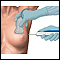
No lab or imaging test has ever been shown to be able to successfully screen for or diagnose ovarian cancer in its early stages, so no standard screening tests are recommended at this time.
Treatment
Surgery is used to treat virtually all stages of ovarian cancer. For early stages, surgery may be the only treatment needed. Surgery may involve removing both ovaries and fallopian tubes, the uterus, or other structures in the belly or pelvis. The goals of surgery for ovarian cancer are:
- Sample normal appearing areas to see if the cancer has spread (staging)
Staging
Cancer staging is a way to describe how much cancer is in your body and where it is located. Staging helps determine where the original tumor is, ho...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Remove any areas of tumor spread (debulking)
Chemotherapy is used after surgery to treat any cancer that remains. Chemotherapy can also be used if the cancer comes back (relapses). Chemotherapy is typically given intravenously (through an IV). It can also be injected directly into the abdominal cavity (intraperitoneal, or IP).
Chemotherapy
The term chemotherapy is used to describe cancer-killing drugs. Chemotherapy may be used to:Cure the cancerShrink the cancerPrevent the cancer from ...
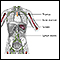
Intravenously
Intravenous means "within a vein. " Most often it refers to giving medicines or fluids through a needle or tube inserted into a vein. This allows th...
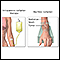
Radiation therapy is rarely used to treat ovarian cancer.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-powered radiation (such as x-rays or gamma rays), particles, or radioactive seeds to kill cancer cells.
After surgery and chemotherapy, follow instructions about how often you should see your oncologist and the tests you should have.
Support Groups
You can ease the stress of illness by joining a cancer support group. Sharing with others who have common experiences and problems can help you not feel alone.
Cancer support group
The following organizations are good resources for information on cancer:American Cancer Society. Support and online communities. www. cancer. org/...
Outlook (Prognosis)
Ovarian cancer is rarely diagnosed in its early stages. It is usually quite advanced by the time diagnosis is made:
- Nearly one half of women live longer than 5 years after diagnosis
- If the diagnosis is made early in the disease and treatment is received before the cancer spreads outside the ovary, the 5-year survival rate is high
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Make an appointment with your provider if you have symptoms of ovarian cancer. Experts differ on the effectiveness of routine pelvic exams for finding early stage ovarian cancer.
Prevention
There are no standard recommendations for screening women without symptoms (asymptomatic) for ovarian cancer. Pelvic ultrasound or a blood test, such as CA-125, have not been found to be effective and are not recommended.
Genetic testing for the BRCA1 or BRCA2, or other cancer-related genes, may be recommended for women at high risk for ovarian cancer. These are women who have a personal or family history of breast or ovarian cancer or have other family members with these genetic changes.
Genetic testing for the BRCA1 or BRCA2
The BRCA1 and BRCA2 gene test is a blood test that can tell you if you have a higher risk of getting cancer. The name BRCA comes from the first two ...
Removing the ovaries and fallopian tubes and possibly the uterus in women who have a proven mutation in the BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene may reduce the risk of developing ovarian cancer. But, ovarian cancer may still develop in other areas of the pelvis.
References
Coleman RL, Liu J, Matsuo K, Thaker PH, Westin SN, Sood AK. Carcinoma of the ovaries and fallopian tubes. In: Niederhuber JE, Armitage JO, Kastan MB, Doroshow JH, Tepper JE, eds. Abeloff's Clinical Oncology. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 86.
Coleman RL, Westin SN, Ramirez PT, Salvo G, Gershenson DM. Malignant diseases of the ovary, fallopian tube, and peritoneum. In: Lobo RA, Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA, eds. Comprehensive Gynecology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 33.
National Cancer Institute website. BRCA gene changes: cancer risk and genetic testing. www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/causes-prevention/genetics/brca-fact-sheet. Updated July 19, 2024. Accessed October 16, 2024.
-
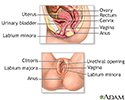
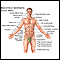
Female reproductive anatomy - illustration
Internal structures of the female reproductive anatomy include the uterus, ovaries, and cervix. External structures include the labium minora and majora, the vagina and the clitoris.
Female reproductive anatomy
illustration
-
Ascites with ovarian cancer - CT scan - illustration
This CT scan of the lower abdomen shows a massive amount of free abdominal fluid (ascites) in a patient with ovarian cancer.
Ascites with ovarian cancer - CT scan
illustration
-
Peritoneal and ovarian cancer, CT scan - illustration
A CT scan series of the lower abdomen showing ovarian cancer that has metastasized (spread) to the peritoneum.
Peritoneal and ovarian cancer, CT scan
illustration
-
Ovarian cancer dangers - illustration
Ovarian cancer is particularly dangerous because its presence is difficult to detect until it has spread beyond the ovaries.
Ovarian cancer dangers
illustration
-
Ovarian growth worries - illustration
Prior to menopause, a mass on the ovary that is smaller than 2 centimeters is probably a follicle cyst that will go away on its own. However, if the growth is larger and doesn't go away over the course of a few menstrual cycles, then it may need to be removed.
Ovarian growth worries
illustration
-
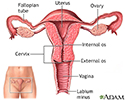
Uterus - illustration
The uterus is a hollow muscular organ located in the female pelvis between the bladder and rectum. The ovaries produce the eggs that travel through the fallopian tubes. Once the egg has left the ovary it can be fertilized and implant itself in the lining of the uterus. The main function of the uterus is to nourish the developing fetus prior to birth.
Uterus
illustration
-
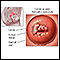
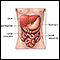
Ovarian cancer - illustration
Cancer of the ovaries is considered very dangerous because the ovaries are in close proximity to many other abdominal organs and the risk of metastasis is high.
Ovarian cancer
illustration
-
Ovarian cancer metastasis - illustration
A malignant neoplasm (abnormal growth) located on the ovaries.
Ovarian cancer metastasis
illustration
-
Female reproductive anatomy - illustration
Internal structures of the female reproductive anatomy include the uterus, ovaries, and cervix. External structures include the labium minora and majora, the vagina and the clitoris.
Female reproductive anatomy
illustration
-
Ascites with ovarian cancer - CT scan - illustration
This CT scan of the lower abdomen shows a massive amount of free abdominal fluid (ascites) in a patient with ovarian cancer.
Ascites with ovarian cancer - CT scan
illustration
-
Peritoneal and ovarian cancer, CT scan - illustration
A CT scan series of the lower abdomen showing ovarian cancer that has metastasized (spread) to the peritoneum.
Peritoneal and ovarian cancer, CT scan
illustration
-
Ovarian cancer dangers - illustration
Ovarian cancer is particularly dangerous because its presence is difficult to detect until it has spread beyond the ovaries.
Ovarian cancer dangers
illustration
-
Ovarian growth worries - illustration
Prior to menopause, a mass on the ovary that is smaller than 2 centimeters is probably a follicle cyst that will go away on its own. However, if the growth is larger and doesn't go away over the course of a few menstrual cycles, then it may need to be removed.
Ovarian growth worries
illustration
-
Uterus - illustration
The uterus is a hollow muscular organ located in the female pelvis between the bladder and rectum. The ovaries produce the eggs that travel through the fallopian tubes. Once the egg has left the ovary it can be fertilized and implant itself in the lining of the uterus. The main function of the uterus is to nourish the developing fetus prior to birth.
Uterus
illustration
-
Ovarian cancer - illustration
Cancer of the ovaries is considered very dangerous because the ovaries are in close proximity to many other abdominal organs and the risk of metastasis is high.
Ovarian cancer
illustration
-
Ovarian cancer metastasis - illustration
A malignant neoplasm (abnormal growth) located on the ovaries.
Ovarian cancer metastasis
illustration
Review Date: 10/8/2024
Reviewed By: Howard Goodman, MD, Gynecologic Oncology, Florida Cancer Specialists & Research Institute, West Palm Beach, FL. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.