Peritonsillar abscess
Quinsy; Abscess - peritonsillar; Tonsillitis - abscessPeritonsillar abscess is a collection of infected material in the area around the tonsils.
Causes
Peritonsillar abscess is a complication of tonsillitis. It is most often caused by a type of bacteria called group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus.
Tonsillitis
Tonsillitis is inflammation (swelling) of the tonsils.
Peritonsillar abscess most often occurs in older children, adolescents, and young adults. The condition is rare now that antibiotics are used to treat tonsillitis.
Symptoms
One or both tonsils become infected. The infection may spread to the area around the tonsil. It can then spread down into the neck and chest. Swollen tissues can block the airway. This is a life-threatening medical emergency.
The abscess can break open (rupture) into the throat. The contents of the abscess can travel into the lungs and cause pneumonia.
Symptoms of peritonsillar abscess include:
- Fever and chills
- Severe throat pain that is usually on one side
- Ear pain on the side of the abscess
- Difficulty opening the mouth, and pain with opening the mouth
- Swallowing problems
- Drooling or inability to swallow saliva
- Facial or neck swelling
-
Fever
Fever
Fever is the temporary increase in the body's temperature in response to a disease or illness. A child has a fever when the temperature is at or abov...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Headache
Headache
A headache is pain or discomfort in the head, scalp, or neck. Serious causes of headaches are rare. Most people with headaches can feel much better...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Muffled voice
- Tender glands of the jaw and throat
- Neck stiffness
Exams and Tests
An exam of the throat often shows swelling on one side and on the roof of the mouth.
The uvula in the back of the throat may be shifted away from the swelling. The neck and throat may be red and swollen on one or both sides.
The following tests may be done:
-
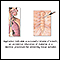
Aspiration of the abscess using a needle
Aspiration
Aspiration means to draw in or out using a sucking motion. It has two meanings:Breathing in a foreign object (for example, sucking food into the air...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
CT scan
CT scan
A computed tomography (CT) scan is an imaging method that uses x-rays to create pictures of cross-sections of the body. Related tests include:Abdomin...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Fiberoptic endoscopy to check if the airway is blocked
Fiberoptic endoscopy
Endoscopy is a way of looking inside the body using a flexible tube that has a small camera and light on the end of it. This instrument is called an...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
The infection can be treated with antibiotics if it is caught early. If an abscess has developed, it will need to be drained with a needle or by cutting it open. You will be given pain medicine before this is done.
If the infection is very severe, the tonsils will be removed at the same time the abscess is drained, but this is rare. In this case, you will have general anesthesia so you will be asleep and pain-free.
Outlook (Prognosis)
In most cases, peritonsillar abscess goes away with treatment. The infection may return in the future.
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
-
Airway obstruction
Airway obstruction
Breathing difficulty may involve:Difficult breathing Uncomfortable breathingFeeling like you are not getting enough air
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
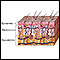
Cellulitis of the jaw, neck, or chest
Cellulitis
Cellulitis is a common skin infection caused by bacteria. It affects the middle layer of the skin (dermis) and the tissues below. Sometimes, muscle...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Endocarditis (rare)
Endocarditis
Endocarditis is inflammation of the inside lining of the heart chambers and heart valves (endocardium). It is most often caused by a bacterial or, r...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Fluid around the lungs (pleural effusion)
Pleural effusion
A pleural effusion is a buildup of fluid between the layers of tissue that line the lungs and chest cavity.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
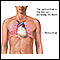
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Inflammation around the heart (pericarditis)
Pericarditis
Pericarditis is a condition in which the sac-like covering around the heart (pericardium) becomes inflamed.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Pneumonia
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is inflamed or swollen lung tissue due to infection with a germ. This article covers community-acquired pneumonia (CAP). This type of pneu...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Sepsis (infection in the blood)
Sepsis
Sepsis is an illness in which the body has a severe, inflammatory response to bacteria or other germs.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your health care provider right away if you have had tonsillitis and you develop symptoms of peritonsillar abscess.
Get medical help right away if you have:
- Breathing trouble
- High-pitched breathing sounds (stridor)
- Retraction of the muscles between the ribs when breathing
- Difficulty turning the head
- Difficulty swallowing
Prevention
Quick treatment of tonsillitis, especially if it is caused by bacteria, may help prevent this condition.
References
Pappas DE, Boggs SR. Retropharyngeal abscess, lateral pharyngeal (parapharyngeal) abscess, and peritonsillar cellulitis/abscess. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 22nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 432.
Roginski MA, Atchinson PR. Upper respiratory tract infections. In: Walls RM, ed. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 61.
Waage RK. Peritonsillar abscess drainage. In: Fowler GC, ed. Pfenninger and Fowler's Procedures for Primary Care. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 206.
-
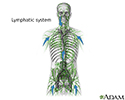
Lymphatic system - illustration
The lymphatic system filters fluid from around cells. It is an important part of the immune system. When people refer to swollen glands in the neck, they are usually referring to swollen lymph nodes. Common areas where lymph nodes can be easily felt, especially if they are enlarged, are the groin, armpits (axilla), above the clavicle (supraclavicular), in the neck (cervical), and the back of the head just above hairline (occipital).
Lymphatic system
illustration
-
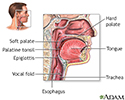
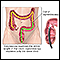
Throat anatomy - illustration
Structures of the throat include the esophagus, trachea, epiglottis and tonsils.
Throat anatomy
illustration
-
Lymphatic system - illustration
The lymphatic system filters fluid from around cells. It is an important part of the immune system. When people refer to swollen glands in the neck, they are usually referring to swollen lymph nodes. Common areas where lymph nodes can be easily felt, especially if they are enlarged, are the groin, armpits (axilla), above the clavicle (supraclavicular), in the neck (cervical), and the back of the head just above hairline (occipital).
Lymphatic system
illustration
-
Throat anatomy - illustration
Structures of the throat include the esophagus, trachea, epiglottis and tonsils.
Throat anatomy
illustration
Review Date: 10/28/2024
Reviewed By: Ashutosh Kacker, MD, FACS, Professor of Clinical Otolaryngology, Weill Cornell Medical College, and Attending Otolaryngologist, New York-Presbyterian Hospital, New York, NY. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.