Retinal detachment
Detached retinaRetinal detachment is a separation of the light-sensitive membrane (retina) in the back of the eye from its supporting layers.
Causes
The retina is the clear tissue that lines the inside of the back of the eye. Light rays that enter the eye are focused by the cornea and lens into images that are formed on the retina.
Retina
The retina is the light-sensitive layer of tissue at the back of the eyeball. Images that come through the eye's lens are focused on the retina. Th...
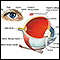
- The most common type of retinal detachment is often due to a tear or hole in the retina. This type of detachment is called a rhegmatogenous retinal detachment. Eye fluid may leak through this opening. This causes the retina to separate from the underlying tissues, much like a bubble under wallpaper. This is most often caused by a condition called posterior vitreous detachment. It can also be caused by trauma and severe nearsightedness. A family history of retinal detachment also increases your risk.
- Another type of retinal detachment is called tractional detachment. This type occurs in people who have uncontrolled diabetes, had retinal surgery before, or have long-term (chronic) inflammation.
When the retina becomes detached, bleeding from nearby blood vessels can cloud the inside of the eye so that you may not see clearly or at all. Central vision becomes severely affected if the macula becomes detached. The macula is the part of the retina responsible for sharp, detailed vision.
Macula
When an eye is looking directly at an object, light rays from that object are focused on the macula lutea. This is a yellow oval spot ("lutea" is La...
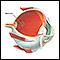
Symptoms
Symptoms of detached retina can include:
- Bright flashes of light, especially in peripheral vision.
Peripheral
Peripheral means "away from the center. " It refers to areas away from the center of the body or a body part. For example, the hands are peripheral ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Blurred vision.
Blurred vision
There are many types of eye problems and vision disturbances, such as: Halos Blurred vision (the loss of sharpness of vision and the inability to see...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - New floaters in the eye that appear suddenly.
- Shadowing or decreased peripheral vision that seems like a curtain or shade across your vision.
There is usually no pain in or around the eye.
Exams and Tests
The ophthalmologist (eye doctor) will examine your eyes. Tests to check the retina and pupil may include:
- Using special dye and a camera to look at blood flow in the retina (fluorescein angiography)
- Checking pressure inside the eye (tonometry)
Tonometry
Tonometry is a test to measure the pressure inside your eyes. The test is used to screen for glaucoma. It is also used to measure how well glaucoma...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Examining the back part of the eye, including the retina (ophthalmoscopy)
Ophthalmoscopy
Ophthalmoscopy is an examination of the back part of the eye (fundus), which includes the retina, optic disc, choroid, and blood vessels.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Checking eyeglass prescription (refraction test)
Refraction test
A refraction is an eye exam that measures a person's prescription for eyeglasses or contact lenses.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Checking color vision
Color vision
A color vision test checks your ability to distinguish between different colors.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Checking the smallest letters that can be read (visual acuity)
Visual acuity
The visual acuity test is used to determine the smallest letters you can read on a standardized chart (Snellen chart) or a card held 20 feet (6 meter...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Checking structures at the front of the eye (slit-lamp examination)
Slit-lamp examination
The slit-lamp examination looks at structures that are at the front of the eye.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
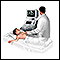
Ultrasound of the eye
Ultrasound
Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to make images of organs and structures inside the body.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
Most people with a retinal detachment need surgery. Surgery may be done right away or within a short time after diagnosis. Some types of surgery can be done in your eye doctor's office.
Surgery
Retinal detachment repair is eye surgery to place a retina back into its normal position. The retina is the light-sensitive tissue in the back of th...
- Lasers may be used to seal tears or holes in the retina before a retinal detachment occurs.
- If you have a small detachment, your eye doctor may place a gas bubble in the eye. This is called pneumatic retinopexy. It helps the retina float back into place. The hole is sealed with a laser.
Severe detachments require surgery in a hospital. These procedures include:
- Scleral buckle to gently push the eye wall up against the retina
- Vitrectomy to remove gel or scar tissue pulling on the retina, used for the largest tears and detachments
Tractional retinal detachments may be watched for a while before surgery. If surgery is needed, a vitrectomy is usually done.
Outlook (Prognosis)
How well you do after a retinal detachment depends on the location and extent of the detachment and early treatment. If the macula was not damaged, the outlook with treatment can be excellent.
Successful repair of the retina does not always fully restore vision.
Some detachments cannot be repaired.
Possible Complications
A retinal detachment causes loss of vision. Surgery to repair it may help restore some or all of your vision.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
A retinal detachment is an urgent problem that requires medical attention within 24 hours of the first symptoms of new flashes of light and floaters.
Prevention
Use protective eye wear to prevent eye trauma, especially when playing racquet sports. Control your blood sugar carefully if you have diabetes. See your eye care professional once a year. You may need more frequent visits if you have risk factors for retinal detachment. Be alert to symptoms of new flashes of light and floaters.
References
AAO PPP Retina/Vitreous Committee, Hoskins Center for Quality Eye Care. American Academy of Ophthalmology website. Preferred Practice Pattern Guidelines. Posterior vitreous detachment, retinal breaks, and lattice degeneration PPP 2019. www.aao.org/preferred-practice-pattern/posterior-vitreous-detachment-retinal-breaks-latti. Published October 2019. Accessed August 7, 2023.
Salmon JF. Retinal detachment. In: Salmon JF, ed. Kanski's Clinical Ophthalmology. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 16.
Wickham L, Aylward GW. Optimal procedures for retinal detachment repair. In: Sadda SVR, Sarraf D, Freund KB, et al, eds. Ryan's Retina. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 108.
Yorston D, Donachie PHJ, Laidlaw DA, et al. Factors affecting visual recovery after successful repair of macula-off retinal detachments: findings from a large prospective UK cohort study. Eye (Lond). 2021;35(5):1431-1439. PMID: 32581389 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32581389/.
-
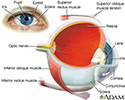
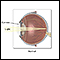
Eye - illustration
The eye is the organ of sight, a nearly spherical hollow globe filled with fluids (humors). The outer layer (sclera, or white of the eye, and cornea) is fibrous and protective. The middle layer (choroid, ciliary body and the iris) is vascular. The innermost layer (retina) is sensory nerve tissue that is light sensitive. The fluids in the eye are divided by the lens into the vitreous humor (behind the lens) and the aqueous humor (in front of the lens). The lens itself is flexible and suspended by ligaments which allow it to change shape to focus light on the retina, which is composed of sensory neurons.
Eye
illustration
-
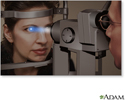
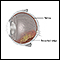
Slit-lamp exam - illustration
A slit-lamp, which is a specialized magnifying microscope, is used to examine the structures of the eye (including the cornea, iris, vitreous, and retina). The slit-lamp is used to examine, treat (with a laser), and photograph (with a camera) the eye.
Slit-lamp exam
illustration
-
Eye - illustration
The eye is the organ of sight, a nearly spherical hollow globe filled with fluids (humors). The outer layer (sclera, or white of the eye, and cornea) is fibrous and protective. The middle layer (choroid, ciliary body and the iris) is vascular. The innermost layer (retina) is sensory nerve tissue that is light sensitive. The fluids in the eye are divided by the lens into the vitreous humor (behind the lens) and the aqueous humor (in front of the lens). The lens itself is flexible and suspended by ligaments which allow it to change shape to focus light on the retina, which is composed of sensory neurons.
Eye
illustration
-
Slit-lamp exam - illustration
A slit-lamp, which is a specialized magnifying microscope, is used to examine the structures of the eye (including the cornea, iris, vitreous, and retina). The slit-lamp is used to examine, treat (with a laser), and photograph (with a camera) the eye.
Slit-lamp exam
illustration
Review Date: 8/4/2023
Reviewed By: Franklin W. Lusby, MD, Ophthalmologist, Lusby Vision Institute, La Jolla, CA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.