Retinal artery occlusion
Central retinal artery occlusion; CRAO; Branch retinal artery occlusion; BRAO; Vision loss - retinal artery occlusion; Blurry vision - retinal artery occlusionRetinal artery occlusion is a blockage in one of the small arteries that carry blood to the retina. The retina is a layer of tissue in the back of the eye that is able to sense light.
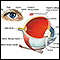
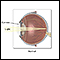
Retina
The retina is the light-sensitive layer of tissue at the back of the eyeball. Images that come through the eye's lens are focused on the retina. Th...
Causes
Retinal arteries may become blocked when a blood clot or fat deposits get stuck in the arteries. These blockages are more likely if there is hardening of the arteries (atherosclerosis) in the eye.
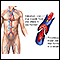
Blood clot
Blood clots are clumps that occur when blood hardens from a liquid to a solid. A blood clot that forms inside one of your veins or arteries is calle...
Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis, sometimes called "hardening of the arteries," occurs when fat, cholesterol, and other substances build up in the walls of arteries. ...
Clots may travel from other parts of the body and block an artery in the retina. The most common sources of clots are the heart and carotid artery in the neck.
Most blockages occur in people with conditions such as:
-
Carotid artery disease, in which the two large blood vessels in the neck become narrowed or blocked
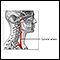
Carotid artery disease
Carotid artery disease causes the carotid arteries to become narrowed or blocked. The carotid arteries provide part of the main blood supply to your ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Diabetes
Diabetes
Diabetes is a long-term (chronic) disease in which the body cannot regulate the amount of sugar in the blood.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Heart rhythm problem (mainly atrial fibrillation)
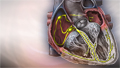
Atrial fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation (AFib) and atrial flutter are common types of abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmias) which affect the upper chambers (atria) of the...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Heart valve problem
- High levels of fat in the blood (hyperlipidemia)
-
High blood pressure
High blood pressure
Blood pressure is a measurement of the force exerted against the walls of your arteries as your heart pumps blood to your body. Hypertension is the ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Intravenous drug abuse
-
Temporal arteritis (inflammation of arteries due to an immune response)
Temporal arteritis
Giant cell arteritis (GCA) is inflammation and damage to the blood vessels that supply blood to the head, neck, upper body and arms. It is also call...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
If a branch of the retinal artery is blocked, part of the retina will not receive enough blood and oxygen. If this happens, you may lose part of your vision.
Symptoms
Sudden blurring or loss of vision may occur in:
- All of one eye (central retinal artery occlusion or CRAO)
- Part of one eye (branch retinal artery occlusion or BRAO)
The retinal artery occlusion may last for only a few seconds or minutes, or it may be permanent.
A blood clot in the eye may be a warning sign of clots elsewhere. A clot in the brain may cause a stroke.
Exams and Tests
Tests to evaluate the retina may include:
- Examination of the retina after dilating the pupil
-
Fluorescein angiography
Fluorescein angiography
Fluorescein angiography is an eye test that uses a special dye and camera to look at blood flow in the retina and choroid. These are the two layers ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Intraocular pressure
Intraocular pressure
Tonometry is a test to measure the pressure inside your eyes. The test is used to screen for glaucoma. It is also used to measure how well glaucoma...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Pupil reflex response
-
Refraction
Refraction
A refraction is an eye exam that measures a person's prescription for eyeglasses or contact lenses.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Retinal photography
Retinal photography
Fluorescein angiography is an eye test that uses a special dye and camera to look at blood flow in the retina and choroid. These are the two layers ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Slit lamp examination
Slit lamp examination
The slit-lamp examination looks at structures that are at the front of the eye.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Testing of side vision (visual field examination)
-
Visual acuity
Visual acuity
The visual acuity test is used to determine the smallest letters you can read on a standardized chart (Snellen chart) or a card held 20 feet (6 meter...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
General tests should include:
- Blood pressure
- Blood tests, including cholesterol and triglyceride levels and the erythrocyte sedimentation rate
Triglyceride levels
The triglyceride level is a blood test to measure the amount of triglycerides in your blood. Triglycerides are a type of fat. Your body makes some t...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleErythrocyte sedimentation rate
ESR stands for erythrocyte sedimentation rate. It is commonly called a "sed rate. "It is a test that indirectly measures the level of certain protei...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Physical examination
Tests to identify the source of a clot from another part of the body:
-
Echocardiogram
Echocardiogram
An echocardiogram is a test that uses sound waves to create pictures of the heart. The picture and information it produces is more detailed than a s...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
Electrocardiogram
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a test that records the electrical activity of the heart.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Heart monitor for abnormal heart rhythm
- Duplex Doppler ultrasound of the carotid arteries
Treatment
There is no proven treatment for vision loss that involves the whole eye, unless it is caused by another illness that can be treated.
Several treatments may be tried. To be helpful, these treatments must be given within 2 to 4 hours after symptoms begin. However, the benefit of these treatments has never been proven, and they are rarely used.
- Breathing in (inhaling) a carbon dioxide-oxygen mixture. This treatment causes the arteries of the retina to widen (dilate).
- Massage of the eye.
- Removal of fluid from within the eye. An eye doctor uses a needle to drain a small amount of fluid from the front of the eye. This causes a sudden drop in eye pressure, which can sometimes cause the clot to move into a smaller branch artery where it will cause less damage.
- The clot-busting drug, tissue plasminogen activator (tPA).
The health care provider should look for the cause of the blockage. Blockages may be signs of a life-threatening medical problem.
Outlook (Prognosis)
People with blockages of the retinal artery may not get their vision back.
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
-
Glaucoma (CRAO only)
Glaucoma
Glaucoma is a group of eye conditions that can damage the optic nerve. This nerve sends the images you see to your brain. Most often, optic nerve da...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Partial or complete loss of vision in the affected eye
- Stroke (due to the same factors that contribute to retinal artery occlusion, not due to the occlusion itself)
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you have sudden blurring or vision loss.
Prevention
Measures used to prevent other blood vessel (vascular) diseases, such as coronary artery disease, may decrease the risk for retinal artery occlusion. These include:
Coronary artery disease
Stable angina is chest pain or discomfort that most often occurs with activity or emotional stress. Angina is due to poor blood flow through the blo...
- Eating a low-fat diet
- Exercising
- Stopping smoking
- Losing weight if you are overweight
Sometimes, blood thinners may be used to prevent the artery from becoming blocked again. Aspirin or other anti-clotting drugs are used if the problem is in the carotid arteries. Warfarin or other more potent blood thinners are used if the problem is in the heart.
References
Cioffi GA, Liebmann JM. Diseases of the visual system. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 391.
Duker JS, Duker JS. Retinal arterial obstruction. In: Yanoff M, Duker JS, eds. Ophthalmology. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 6.15.
Guluma K, Lee JE. Ophthalmology. In: Walls RM, ed. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 57.
Mac Grory B, Schrag M, Biousse V, et al. American Heart Association Stroke Council; Council on Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis and Vascular Biology; Council on Hypertension; and Council on Peripheral Vascular Disease. Management of central retinal artery occlusion: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Stroke. 2021;52(6):e309. PMID: 33677974 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33677974/.
Patel PS, Sadda SR, Sarraf D. Retinal artery and capillary occlusions. In: Sadda SR, Sarraf D, Freund KB, et al, eds. Ryan's Retina. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 53.
Salmon JF. Retinal vascular disease. In: Salmon JF, ed. Kanski's Clinical Ophthalmology. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 13.
-
Retina - illustration
The retina is the internal layer of the eye that receives and transmits focused images. The retina is normally red due to its rich blood supply.
Retina
illustration
Review Date: 1/29/2024
Reviewed By: Audrey Tai, DO, MS, Athena Eye Care, Mission Viejo, CA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.


