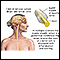
Labyrinthitis
Bacterial labyrinthitis; Serous labyrinthitis; Neuronitis - vestibular; Vestibular neuronitis; Viral neurolabyrinthitis; Vestibular neuritis; Labyrinthitis - vertigo: Labyrinthitis - dizziness; Labyrinthitis - vertigo; Labyrinthitis - hearing lossLabyrinthitis is irritation and swelling of the inner ear. It can cause vertigo and hearing loss.
Causes
Labyrinthitis is usually caused by a virus but sometimes by bacteria. Having a cold or flu can trigger the condition. Less often, an ear infection may lead to labyrinthitis. Other causes include allergies or certain medicines that are bad for the inner ear.
Cold
The common cold most often causes a runny nose, nasal congestion, and sneezing. You may also have a sore throat, cough, headache, or other symptoms....

Flu
The flu (influenza) is a viral respiratory illness that causes fever, chills, runny nose, body aches, and cough. It spreads easily from person to pe...
Ear infection
Suspected ear infections are one of the most common reasons parents take their children to their health care provider. The most common type of ear i...
Your inner ear is important for both hearing and balance. When you have labyrinthitis, the parts of your inner ear become irritated and swollen. This can make you lose your balance and cause hearing loss.
These factors raise your risk for labyrinthitis:
- Drinking large amounts of alcohol
-
Fatigue
Fatigue
Fatigue is a feeling of weariness, tiredness, or lack of energy.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - History of allergies
Allergies
An allergy is an immune response or reaction to substances that are usually not harmful.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Recent viral illness, respiratory infection, or ear infection
Respiratory infection
The common cold most often causes a runny nose, nasal congestion, and sneezing. You may also have a sore throat, cough, headache, or other symptoms....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Smoking
-
Stress
Stress
Stress is a feeling of emotional or physical tension. It can come from any event or thought that makes you feel frustrated, angry, or nervous. Stres...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Using certain prescription or nonprescription medicines (such as aspirin)
Symptoms
Symptoms may include any of the following:
- Feeling like you are spinning, even when you are still (vertigo).
-
Your eyes moving on their own, making it hard to focus them.
Your eyes moving on their own,
Nystagmus is a term to describe uncontrollable movements of the eyes that may be:Side to side (horizontal nystagmus)Up and down (vertical nystagmus)R...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Dizziness.
Dizziness
Dizziness is a term that is often used to describe 2 different symptoms: lightheadedness and vertigo. Lightheadedness is a feeling that you might fai...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Hearing loss in one ear.
Hearing loss
Hearing loss is being partly or totally unable to hear sound in one or both ears.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Loss of balance -- you may fall toward one side.
-
Nausea and vomiting.
Nausea and vomiting
Nausea is feeling an urge to vomit. It is often called "being sick to your stomach. "Vomiting or throwing-up forces the contents of the stomach up t...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Ringing or other noises in your ears (tinnitus).
Tinnitus
Tinnitus is the medical term for "hearing" noises in your ears. It occurs when there is no outside source of the sounds. Tinnitus is often called "r...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will give you a physical exam. You may also have tests of your nervous system (neurological exam).
Tests can check for other causes of your symptoms. These may include:
-
Electronystagmography,(ENG) and warming and cooling the inner ear with air or water to test eye reflexes (caloric stimulation)
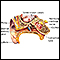
Electronystagmography
Electronystagmography is a test that looks at eye movements to see how well nerves in the brain are working. These nerves are:Vestibular nerve (eigh...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleCaloric stimulation
Caloric stimulation is a test that uses differences in temperature to diagnose damage to the acoustic nerve. This is the nerve that is involved in h...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Head CT scan
Head CT scan
A head computed tomography (CT) scan uses many x-rays to create pictures of the head, including the skull, brain, eye sockets, and sinuses.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Hearing test
Hearing test
An audiometry exam tests your ability to hear sounds. Sounds vary, based on their loudness (intensity) and the speed of sound wave vibrations (tone)...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
MRI of the head
MRI of the head
A head MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is an imaging test that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the brain and surrounding...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
Labyrinthitis usually goes away within a few weeks. Treatment can help reduce vertigo and other symptoms. Physical therapy focused on balance can be helpful for some people. Medicines that may help include:
- Antihistamines
- Medicines to control nausea and vomiting, such as prochlorperazine
- Medicines to relieve dizziness, such as meclizine or scopolamine
- Sedatives, such as diazepam (Valium)
- Corticosteroids
- Antiviral medicines
If you have severe vomiting, you may be admitted to the hospital.
Follow your provider's instructions for taking care of yourself at home. Doing these things can help you manage vertigo:
Taking care of yourself at home
You may have seen your health care provider because you have had labyrinthitis. This inner ear problem can cause you to feel like you are spinning (...
- Stay still and rest.
- Avoid sudden movements or position changes.
- Rest during severe episodes. Slowly resume activity. You may need help walking when you lose your balance during attacks.
- Avoid bright lights, TV, and reading during attacks.
- Ask your provider about balance therapy. This may help once nausea and vomiting have passed.
You should avoid the following for one week after symptoms disappear:
- Driving
- Operating heavy machinery
- Climbing
A sudden dizzy spell during these activities can be dangerous. Avoid other activities with a similar danger.
Outlook (Prognosis)
It takes time for labyrinthitis symptoms to go away completely.
- Severe symptoms usually go away within a week.
- Most people are completely better within 2 to 3 months.
- Older adults are more likely to have dizziness that lasts longer.
In very rare cases, hearing loss is permanent.
Possible Complications
People with severe vertigo may get dehydrated due to frequent vomiting.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if:
- You have dizziness, vertigo, loss of balance, or other symptoms of labyrinthitis
- You have hearing loss
Call 911 or the local emergency number if you have any of the following severe symptoms:
-
Convulsions
Convulsions
A seizure is the physical changes in behavior that occurs during an episode of specific types of abnormal electrical activity in the brain. The term ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Double vision
Double vision
There are many types of eye problems and vision disturbances, such as: Halos Blurred vision (the loss of sharpness of vision and the inability to see...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Fainting
- Vomiting a lot
-
Slurred speech
Slurred speech
Speech and language impairment may be any of several problems that make it difficult to communicate.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Vertigo that occurs with a fever of more than 101°F (38.3°C)
- Weakness or paralysis
Prevention
There is no known way to prevent labyrinthitis.
References
Baloh RW, Jen JC. Hearing and equilibrium. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 396.
Goddard JC, Slattery WH. Infections of the labyrinth. In: Flint PW, Francis HW, Haughey BH, et al, eds. Cummings Otolaryngology: Head and Neck Surgery. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 155.
Holste K, Patil PG. Treatment of intractable vertigo. In: Winn HR, ed. Youmans and Winn Neurological Surgery. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 128.
-
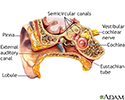
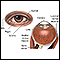
Ear anatomy - illustration
The ear consists of external, middle, and inner structures. The eardrum and the 3 tiny bones conduct sound from the eardrum to the cochlea.
Ear anatomy
illustration
Review Date: 7/17/2025
Reviewed By: Joseph V. Campellone, MD, Department of Neurology, Cooper Medical School at Rowan University, Camden, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.