Ear barotrauma
Barotitis media; Barotrauma; Ear popping - barotrauma; Pressure-related ear pain; Eustachian tube dysfunction - barotrauma; Barotitis; Ear squeezeEar barotrauma causes discomfort in the ear due to pressure differences between the inside and outside of the eardrum. It may include damage to the ear.
Causes
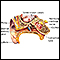
The air pressure in the middle ear is most often the same as the air pressure outside of the body. The eustachian tube is a connection between the middle ear and the back of the nose and upper throat.
Swallowing or yawning opens the eustachian tube and allows air to flow into or out of the middle ear. This helps equalize pressure on either side of the ear drum. If the eustachian tube is blocked, the air pressure in the middle ear is different than the pressure on the outside of the eardrum. This can cause barotrauma.
Many people have barotrauma at some time. The problem often occurs with altitude changes, such as flying, scuba diving, or driving in the mountains. If you have a congested nose from allergies, colds, or an upper respiratory infection, you are more likely to develop barotrauma.
Blockage of the eustachian tube could also be present before birth (congenital). It may also be caused by swelling in the throat.
Symptoms
Common symptoms include:
- Dizziness
-
Ear discomfort or pain in one or both ears
Ear discomfort
An earache is a sharp, dull, or burning pain in one or both ears. The pain may last a short time or be ongoing. Related conditions include:Otitis m...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Hearing loss (slight)
Hearing loss
Hearing loss is being partly or totally unable to hear sound in one or both ears.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Sensation of fullness or stuffiness in the ears
Other symptoms may develop if the condition is very bad or goes on for a long time, such as:
- Ear pain
- Feeling of pressure in the ears (as if underwater)
- Moderate to severe hearing loss
- Nosebleed
Exams and Tests
During an exam of the ear, the health care provider may see a slight outward bulge or inward pull of the eardrum. If the condition is severe, there may be blood or bruising behind the eardrum.
Severe barotrauma may cause the eardrum to look similar to an ear infection.
Ear infection
Otitis is a term for infection or inflammation of the ear.

Treatment
To relieve ear pain or discomfort, you can take steps to open the eustachian tube and relieve the pressure, such as:
- Chew gum
- Inhale, and then gently exhale while holding the nostrils closed and the mouth shut
- Suck on candy
- Yawn
When flying, DO NOT sleep as the plane prepares to land. Repeat the listed steps to open the eustachian tube. For infants and small children, nursing or taking sips of a drink may help.
Scuba divers should go down and come up slowly. Diving while you have congestion from allergies or a respiratory infection is dangerous. Barotrauma may be severe in these situations.
If self-care steps do not ease discomfort within a few hours or the problem is severe, you may need to see a provider.
You may need medicine to relieve nasal congestion and allow the eustachian tube to open. These include:
- Decongestants taken by mouth, or by a nose spray
- Steroids taken by mouth, or by a nose spray
You may need antibiotics to prevent or treat an ear infection if barotrauma is severe.
Rarely, surgery may be needed if other treatments do not work to open the tube. In this procedure, a surgical cut is made in the eardrum to allow pressure to become equal and fluid to drain (myringotomy).
Myringotomy
Ear tube insertion involves placing tubes through the eardrums. The eardrum is the thin layer of tissue that separates the outer and middle ear. No...
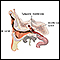
If you must change altitude often or you are prone to barotrauma, you may need to have surgery to place tubes in the ear drum. This is not an option for scuba diving.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Barotrauma is usually a benign, self-limited condition that responds to self-care. Hearing loss is almost always temporary.
Benign
Benign refers to a condition, tumor, or growth that is not cancerous. This means that it does not spread to other parts of the body. It does not in...
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
-
Acute ear infection
Acute ear infection
Suspected ear infections are one of the most common reasons parents take their children to their health care provider. The most common type of ear i...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Hearing loss
-
Ruptured or perforated eardrum
Ruptured or perforated eardrum
A ruptured eardrum is an opening or hole in the eardrum. The eardrum is a thin piece of tissue that separates the outer and middle ear. Damage to t...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Vertigo
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Try home care measures first. Contact your provider if the discomfort does not ease after a few hours.
Contact your provider if you have barotrauma and new symptoms develop, especially:
-
Drainage or bleeding from the ear
Drainage or bleeding from the ear
Ear discharge is drainage of blood, ear wax, pus, or fluid from the ear.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Fever
Fever
Fever is the temporary increase in the body's temperature in response to a disease or illness. A child has a fever when the temperature is at or abov...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Severe ear pain
Prevention
You can use nasal decongestants (spray or pill form) before altitude changes. Try to avoid altitude changes while you have an upper respiratory infection or active allergy symptoms.
Talk to your provider about using decongestants if you plan to scuba dive.
References
Peak DA. Scuba diving and dysbarism. In: Walls RM, ed. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 131.
Van Hoesen KB, Lang MA. Diving medicine. In: Auerbach PS, Cushing TA, Harris NS, eds. Auerbach's Wilderness Medicine. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2017:chap 71.
-
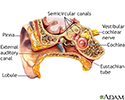
Ear anatomy - illustration
The ear consists of external, middle, and inner structures. The eardrum and the 3 tiny bones conduct sound from the eardrum to the cochlea.
Ear anatomy
illustration
Review Date: 5/2/2024
Reviewed By: Josef Shargorodsky, MD, MPH, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.