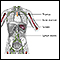
SVC obstruction
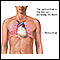
Superior vena cava obstruction; Superior vena cava syndromeSVC obstruction is a narrowing or blockage of the superior vena cava (SVC), which is the second largest vein in the human body. The superior vena cava moves blood from the upper parts of the body to the heart.
Causes
SVC obstruction is a rare condition.
It is most often caused by cancer or a tumor in the mediastinum (the area of the chest under the breastbone and between the lungs).
Cancer
Cancer is the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the body. Cancerous cells are also called malignant cells.
Tumor
Mediastinal tumors are growths that form in the mediastinum. This is an area in the middle of the chest that separates the lungs.

Types of cancer that can lead to this condition include:
-
Breast cancer
Breast cancer
Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the tissues of the breast. There are two main types of breast cancer:Ductal carcinoma starts in the tubes (du...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Lung cancer
- Lymphoma
-
Metastatic cancer to the lung (cancer that has spread to the lungs)
Metastatic cancer to the lung
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is a fast-growing type of lung cancer. It tends to spread more quickly than non-small cell lung cancer. There are two ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
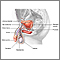
Testicular cancer
Testicular cancer
Testicular cancer is cancer that starts in the testicles. The testicles are the male reproductive glands located in the scrotum.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Thyroid cancer
Thyroid cancer
Thyroid cancer is a cancer that starts in the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland is located in the front of your lower neck.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Thymus tumor
SVC obstruction can also be caused by noncancerous conditions that cause scarring near the SVC. These conditions include:
-
Histoplasmosis (a type of fungal infection)
Histoplasmosis
Histoplasmosis is an infection that occurs from breathing in the spores of the fungus Histoplasma capsulatum.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Inflammation of a vein (thrombophlebitis)
Thrombophlebitis
Thrombophlebitis is swelling (inflammation) of a vein. A blood clot (thrombus) in the vein is the most common cause of this swelling.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Lung infections (such as tuberculosis)
Tuberculosis
Pulmonary tuberculosis (TB) is a contagious bacterial infection that involves the lungs. It may spread to other organs.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Other causes of SVC obstruction include:
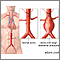
- Widening of the artery that leaves the heart (aortic aneurysm)
Aortic aneurysm
An aneurysm is an abnormal widening or ballooning of a portion of an artery due to weakness in the wall of the blood vessel. A thoracic aortic aneury...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Blood clots in the SVC
- Tightening of the thin lining of the heart (constrictive pericarditis)
Constrictive pericarditis
Constrictive pericarditis is a process in which the sac-like covering of the heart (the pericardium) becomes thickened and scarred. Related conditio...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Effects of radiation therapy for certain medical conditions
- Enlargement of the thyroid gland (goiter)
Catheters placed in the large veins of the upper arm and neck may cause blood clots in the SVC.
Symptoms
Symptoms occur when something blocks the blood flowing back to the heart. Symptoms may begin suddenly or gradually, and may worsen when you bend over or lie down.
Early signs include:
- Swelling around the eyes
- Swelling of the face
- Swelling of the whites of the eyes
- Distended veins in the neck
The swelling may be worse or more prominent when lying down than when upright. It may be worse in the early morning hours and may go away by mid-morning.
The most common symptoms are shortness of breath (dyspnea) and swelling of the face, neck, trunk, and arms.
Shortness of breath
Breathing difficulty may involve:Difficult breathing Uncomfortable breathingFeeling like you are not getting enough air

Other possible symptoms include:
-
Decreased alertness
Decreased alertness
Decreased alertness is a state of reduced awareness and is often a serious condition. A coma is the most severe state of decreased alertness in which...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Dizziness, fainting
Dizziness
Dizziness is a term that is often used to describe 2 different symptoms: lightheadedness and vertigo. Lightheadedness is a feeling that you might fai...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Headache
- Reddish face or cheeks
- Reddish palms
- Reddish mucous membranes (inside the nose, mouth, and other places)
- Redness changing to blueness later
- Sensation of head or ear fullness
- Vision changes
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will perform a physical exam, which may show enlarged veins of the face, neck, and upper chest. Blood pressure is often high in the arms and low in the legs.
If lung cancer is suspected, a bronchoscopy may be done. During this procedure, a camera is used to view inside the airways and lungs.
Bronchoscopy
Bronchoscopy is a test to view the airways and diagnose lung disease. It may also be used during the treatment of some lung conditions.

Blockage of the SVC may be visible on:
-
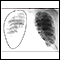
Chest x-ray
Chest x-ray
A chest x-ray is an x-ray of the chest, lungs, heart, large arteries, ribs, and diaphragm.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
CT scan of the chest or MRI of chest
CT scan of the chest
A chest CT (computed tomography) scan is an imaging method that uses x-rays to create cross-sectional pictures of the chest and upper abdomen....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
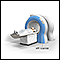
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleMRI of chest
A chest MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) scan is an imaging test that uses powerful magnetic fields and radio waves to create pictures of the chest (...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Coronary angiography (a heart blood vessel study)
Coronary angiography
Coronary angiography is a procedure that uses a special dye (contrast material) and x-rays to see how blood flows through the arteries in your heart....
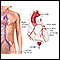 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Doppler ultrasound (sound wave test of the blood vessels)
Doppler ultrasound
This test uses ultrasound to look at the blood flow in the large arteries and veins in the arms or legs.
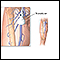 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Radionuclide ventriculography (nuclear study of heart motion)
Radionuclide ventriculography
Nuclear ventriculography is a test that uses radioactive materials called tracers to show the heart chambers. The procedure is noninvasive. The ins...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
The goal of treatment is to relieve the blockage.
Diuretics (water pills) or steroids (anti-inflammatory medicines) may be used to temporarily relieve swelling.
Swelling
Swelling is the enlargement of organs, skin, or other body parts. It is caused by a buildup of fluid in the tissues. The extra fluid can lead to a ...

Other treatment options may include radiation therapy or chemotherapy to shrink the tumor, or surgery to remove the tumors. Surgery to bypass the obstruction is rarely performed. Placement of a stent (tube placed inside a blood vessel) to open up the SVC may be performed.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-powered radiation (such as x-rays or gamma rays), particles, or radioactive seeds to kill cancer cells.
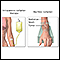
Chemotherapy
The term chemotherapy is used to describe cancer-killing drugs. Chemotherapy may be used to:Cure the cancerShrink the cancerPrevent the cancer from ...
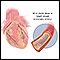
Stent
A stent is a tiny tube placed into a hollow structure in your body. This structure can be an artery, a vein, or another structure, such as the tube ...
Outlook (Prognosis)
The outcome varies, depending on the cause and the amount of blockage.
SVC obstruction caused by a tumor is a sign that the tumor has spread, and it indicates a poorer long-term outlook.
Possible Complications
The throat could become blocked, which can block the airways.
Increased pressure may develop in the brain, leading to changed levels of consciousness, nausea, vomiting, or vision changes.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you develop symptoms of SVC obstruction. Complications are serious and can sometimes be fatal.
Prevention
Prompt treatment of other medical disorders may reduce the risk of developing SVC obstruction.
References
Gupta A, Kim DN, Kalva S, Reznik S, Johnson DH. Superior vena cava syndrome. In: Niederhuber JE, Armitage JO, Kastan MB, Doroshow JH, Tepper JE, eds. Abeloff's Clinical Oncology. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 53.
Kinlay S, Bhatt DL. Treatment of noncoronary obstructive vascular disease. In: Libby P, Bonow RO, Mann DL, Tomaselli GF, Bhatt DL, Solomon SD, eds. Braunwald's Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 44.
-
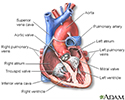
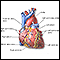
Heart - section through the middle - illustration
The interior of the heart is composed of valves, chambers, and associated vessels.
Heart - section through the middle
illustration
Review Date: 2/13/2025
Reviewed By: Jacob Berman, MD, MPH, Clinical Assistant Professor of Medicine, Division of General Internal Medicine, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.