Crigler-Najjar syndrome
Glucuronyl transferase deficiency (type I Crigler-Najjar); Arias syndrome (type II Crigler-Najjar)Crigler-Najjar syndrome is a very rare inherited disorder in which bilirubin cannot be broken down. Bilirubin is a substance made by the liver.
Causes
An enzyme converts bilirubin into a form that can easily be removed from the body. Crigler-Najjar syndrome occurs when this enzyme does not work correctly. Without this enzyme, bilirubin can build up in the body and lead to:
- Jaundice (yellow discoloration of skin and eyes)
- Damage to the brain, muscles, and nerves
Type I Crigler-Najjar is the form of the disease that starts early in life. Type II Crigler-Najjar syndrome may start later in life.
The syndrome runs in families (inherited). A child must receive a copy of the variant gene from both parents to develop the severe form of the condition. Parents who are carriers (with just one variant gene) have about one half the enzyme activity of a normal adult, but do not have symptoms.
Symptoms
Symptoms may include:
-
Confusion and changes in thinking
Confusion
Confusion is the inability to think as clearly or quickly as you normally do. You may feel disoriented and have difficulty paying attention, remembe...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Yellow skin (jaundice) and yellow in the whites of the eyes (icterus), which begin a few days after birth and get worse over time
- Lethargy
- Poor feeding
- Vomiting
Exams and Tests
Tests of liver function include:
- Conjugated (bound) bilirubin
- Total bilirubin level
- Unconjugated (unbound) bilirubin in blood.
-
Enzyme assay
Enzyme assay
ELISA stands for enzyme-linked immunoassay. It is a commonly used laboratory test to detect antibodies in the blood. An antibody is a protein produ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Liver biopsy
Liver biopsy
A liver biopsy is a test that takes a sample of tissue from the liver for examination.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
Light treatment (phototherapy) is needed throughout a person's life. In infants, this is done using bilirubin lights (bili or 'blue' lights). Phototherapy does not work as well after age 4, because thickened skin blocks the light.
A liver transplant can be done in some people with type I disease.
Blood transfusions may help control the amount of bilirubin in blood. Calcium compounds are sometimes used to remove bilirubin in the gut.
The drug phenobarbitol is sometimes used to treat type II Crigler-Najjar syndrome.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Milder forms of the disease (type II) do not cause liver damage or changes in thinking during childhood. People who are affected with a mild form still have jaundice, but they have fewer symptoms and less organ damage.
Infants with the severe form of the disease (type I) may continue to have jaundice into adulthood, and may need daily treatment. If not treated, this severe form of the disease will lead to death in childhood.
People with this condition who reach adulthood will develop brain damage due to jaundice (kernicterus), even with regular treatment. The life expectancy for someone with type I disease is 30 years.
Kernicterus
Bilirubin encephalopathy is a rare neurological condition that occurs in some newborns with severe jaundice.

Possible Complications
Possible complications include:
- A form of brain damage caused by jaundice (kernicterus)
- Chronic yellow skin/eyes
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Seek genetic counseling if you are planning to have children and have a personal or family history of Crigler-Najjar.
Contact your health care provider if you or your newborn infant has jaundice that does not go away.
Prevention
Genetic counseling is recommended for people with a personal or family history of Crigler-Najjar syndrome who want to have children. Blood tests can identify people who carry the genetic variant.
References
Bonn J, Balistreri WF. Metabolic diseases of the liver. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 22nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 405.
Kaplan M, Wong RJ, Bensen R, Sibley E, Stevenson DK. Neonatal jaundice and liver diseases. In: Martin RJ, Fanaroff AA, Walsh MC, eds. Fanaroff and Martin's Neonatal-Perinatal Medicine. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 95.
Lidofsky SD. Jaundice. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 21.
-
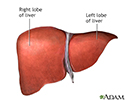
Liver anatomy - illustration
The liver serves a wide variety of body functions, including detoxifying blood and producing bile that aids in digestion.
Liver anatomy
illustration
Review Date: 8/18/2024
Reviewed By: Anna C. Edens Hurst, MD, MS, Associate Professor in Medical Genetics, The University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, AL. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.