Agammaglobulinemia
Bruton's agammaglobulinemia; X-linked agammaglobulinemia; Immunosuppression - agammaglobulinemia; Immunodepressed - agammaglobulinemia; Immunosuppressed - agammaglobulinemiaAgammaglobulinemia is an inherited disorder in which a person has very low levels of protective immune system proteins called immunoglobulins. Immunoglobulins are a type of antibody. Low levels of these antibodies make you more likely to get infections.
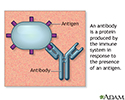
Antibody
An antibody is a protein produced by the body's immune system when it detects harmful substances, called antigens. Examples of antigens include micr...
Causes
This is a rare disorder that mainly affects males. It is caused by a gene defect that blocks the growth of normal, mature immune cells called B lymphocytes.
As a result, the body makes very little (if any) immunoglobulins. Immunoglobulins play a major role in the immune response, which protects against illness and infection.
Immune response
The immune response is how your body recognizes and defends itself against bacteria, viruses, and substances that appear foreign and harmful....
People with this disorder develop infections again and again. Common infections include ones that are due to bacteria such as Haemophilus influenzae, pneumococci (Streptococcus pneumoniae), and staphylococci. Common sites of infection include:
- Gastrointestinal tract
- Joints
- Lungs
- Skin
- Upper respiratory tract
Respiratory
The words "respiratory" and "respiration" refer to the lungs and breathing.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Agammaglobulinemia is inherited, which means other people in your family may have the condition.
Symptoms
Symptoms include frequent episodes of:
-
Bronchitis (airway infection)
Bronchitis
Acute bronchitis is swelling and inflamed tissue in the bronchi, the main passages that carry air to the lungs. This swelling narrows the airways, w...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Conjunctivitis (eye infection)
Conjunctivitis
The conjunctiva is a clear layer of tissue lining the eyelids and covering the white of the eye. Conjunctivitis occurs when the conjunctiva becomes ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Diarrhea
-
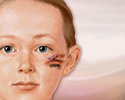
Otitis media (middle ear infection)
Otitis media
Suspected ear infections are one of the most common reasons parents take their children to their health care provider. The most common type of ear i...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Pneumonia (lung infection)
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is inflamed or swollen lung tissue due to infection with a germ. This article covers community-acquired pneumonia (CAP). This type of pneu...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
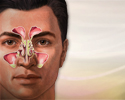
Sinusitis (sinus infection)
Sinusitis
Sinusitis is present when the tissue lining the sinuses become swollen or inflamed. It occurs as the result of an inflammatory reaction or an infect...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Skin infections
- Upper respiratory tract infections
Infections typically appear in the first 4 years of life.
Other symptoms include:
-
Bronchiectasis (a disease in which the bronchial tubes in the lungs become damaged and enlarged)
Bronchiectasis
Bronchiectasis is a disease in which the large airways in the lungs are damaged. This causes the airways to become permanently wider. Bronchiectasis...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Asthma without a known cause
Asthma
Asthma is a chronic disease that causes the airways of the lungs to swell and become narrow. It leads to breathing difficulty such as wheezing, shor...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Exams and Tests
The disorder is confirmed by blood tests that measure levels of immunoglobulins.
Tests include:
- Flow cytometry to measure circulating B lymphocytes
-
Immunoelectrophoresis - serum
Immunoelectrophoresis - serum
Serum immunoelectrophoresis is a lab test that measures proteins called immunoglobulins in the blood. Immunoglobulins are proteins that function as ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Quantitative immunoglobulins - IgG, IgA, IgM (usually measured by nephelometry)
Quantitative immunoglobulins
Quantitative nephelometry is a lab test to quickly and accurately measure levels of certain proteins called immunoglobulins in the blood. Immunoglob...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
Treatment involves taking steps to reduce the number and severity of infections. Antibiotics are often needed to treat bacterial infections.
Immunoglobulins are given through a vein or by injection to boost the immune system.
A bone marrow transplant may be considered.
Support Groups
More information and support for people with agammaglobulinemia and their families can be found at:
- Immune Deficiency Foundation -- primaryimmune.org
- National Organization for Rare Disorders -- rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/agammaglobulinemia/
- NIH Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center -- rarediseases.info.nih.gov/diseases/1033/x-linked-agammaglobulinemia
Outlook (Prognosis)
Treatment with immunoglobulins has greatly improved the health of those who have this disorder.
Without treatment, most severe infections are deadly.
Possible Complications
Health problems that may result include:
- Arthritis
-
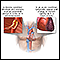
Chronic sinus or pulmonary disease
Chronic
Chronic refers to something that continues over an extended period of time. A chronic condition is usually long-lasting and does not easily or quick...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
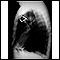
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticlePulmonary disease
Lung disease is any problem in the lungs that prevents the lungs from working properly. There are three main types of lung disease:Airway diseases -...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Eczema
Eczema
Atopic dermatitis is a long-term (chronic) skin disorder that involves scaly and itchy rashes. It is a type of eczema. Other forms of dermatitis inc...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Intestinal malabsorption syndromes
Malabsorption
Malabsorption involves problems with the body's ability to take in (absorb) nutrients from food.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your health care provider for an appointment if:
- You or your child has experienced frequent infections.
- You have a family history of agammaglobulinemia or another immunodeficiency disorder and you are planning to have children. Ask the provider about genetic counseling.
Prevention
Genetic counseling should be offered to prospective parents with a family history of agammaglobulinemia or other immunodeficiency disorders.
Immunodeficiency disorders
Immunodeficiency diseases occur when the body's immune response is reduced or absent.

References
Cunningham-Rundles C. Primary immunodeficiency diseases. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 231.
Hernandez-Trujillo VP, Ortega C. B-cell and antibody deficiencies. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 22nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 166.
Pai SY, Notarangelo LD. Congenital disorders of lymphocyte function. In: Hoffman R, Benz EJ, Silberstein LE, et al, eds. Hematology: Basic Principles and Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 52.
-
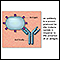
Antibodies - illustration
Antigens are large molecules (usually proteins) on the surface of cells, viruses, fungi, bacteria, and some non-living substances such as toxins, chemicals, drugs, and foreign particles. The immune system recognizes antigens and produces antibodies that destroy substances containing antigens.
Antibodies
illustration
-
Antibodies - illustration
Antigens are large molecules (usually proteins) on the surface of cells, viruses, fungi, bacteria, and some non-living substances such as toxins, chemicals, drugs, and foreign particles. The immune system recognizes antigens and produces antibodies that destroy substances containing antigens.
Antibodies
illustration
Review Date: 3/31/2024
Reviewed By: Deborah Pedersen, MD, MS, Allergy & Asthma Care, PC, Taunton, MA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.