Graft-versus-host disease
GVHD; Bone marrow transplant - graft-versus-host disease; Stem cell transplant - graft-versus-host disease; Allogeneic transplant - GVHDGraft-versus-host disease (GVHD) is a potentially life-threatening complication that can occur after certain stem cell or bone marrow transplants.
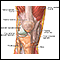
Bone marrow transplants
A bone marrow transplant is a procedure to replace damaged or diseased bone marrow with healthy bone marrow stem cells. Bone marrow is the soft, fatt...

Causes
GVHD may occur after a bone marrow or stem cell transplant in which someone receives bone marrow tissue or cells from a donor. This type of transplant is called allogeneic. The new, transplanted cells regard the recipient's body as foreign. When this happens, the cells attack the recipient's body.
GVHD does not occur when people receive their own cells. This type of transplant is called autologous.
Before a transplant, tissue and cells from possible donors are checked to see how closely they match the recipient. GVHD is less likely to occur, or symptoms will be milder, when the match is close. The chance of GVHD is:
- Around 35% to 45% when the donor and recipient are related
- Around 60% to 80% when the donor and recipient are not related
Symptoms
There are two types of GVHD: acute and chronic. Symptoms in both acute and chronic GVHD range from mild to severe.
Acute GVHD usually happens within days or as late as 6 months after a transplant. The immune system, skin, liver, and intestines are mainly affected. Common acute symptoms include:
- Abdominal pain or cramps, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea
-
Jaundice (yellow coloring of the skin or eyes) or other liver problems
Jaundice
Jaundice is a yellow color of the skin, mucus membranes, or eyes. The yellow coloring comes from bilirubin, a byproduct of old red blood cells. Jau...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Skin rash, itching, redness on areas of the skin
Skin rash,
Rashes involve changes in the color, feeling or texture of your skin.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Increased risk for infections
Chronic GVHD usually starts more than 3 months after a transplant, and can last a lifetime. Chronic symptoms may include:
-
Dry eyes, burning sensation, or vision changes
Dry eyes
You need tears to moisten your eyes and to wash away particles that have gotten into your eyes. A healthy tear film on the eye is necessary for good...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Dry mouth, white patches inside the mouth, and sensitivity to spicy foods
Dry mouth
Dry mouth occurs when you don't make enough saliva. This causes your mouth to feel dry and uncomfortable. Dry mouth that is ongoing may be a sign o...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Fatigue, muscle weakness, and chronic pain
Fatigue
Fatigue is a feeling of weariness, tiredness, or lack of energy.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Joint pain or stiffness
- Skin rash with raised, discolored areas, as well as skin tightening or thickening
- Shortness of breath due to lung damage
-
Vaginal dryness
Vaginal dryness
Vaginal dryness is present when the tissues of the vagina are not well-lubricated and healthy.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Weight loss
Weight loss
Unexplained weight loss is a decrease in body weight, when you did not try to lose the weight on your own. Many people gain and lose weight. Uninten...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Reduced bile flow from the liver
- Brittle hair and premature graying
- Damage to sweat glands
- Cytopenia (decrease in number of mature blood cells)
-
Pericarditis (inflammation in the membrane surrounding the heart; causes chest pain)
Pericarditis
Pericarditis is a condition in which the sac-like covering around the heart (pericardium) becomes inflamed.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Exams and Tests
Several lab and imaging tests can be done to diagnose and monitor problems caused by GVHD. These may include:
-
X-ray abdomen
X-ray abdomen
An abdominal x-ray is an imaging test to look at organs and structures in the abdomen. Organs include the liver, spleen, stomach, and intestines. T...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
CT scan abdomen and CT chest
CT scan abdomen
An abdominal CT scan is an imaging test that uses x-rays to create cross-sectional pictures of the belly area. CT stands for computed tomography....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleCT chest
A chest CT (computed tomography) scan is an imaging method that uses x-rays to create cross-sectional pictures of the chest and upper abdomen....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Liver function tests
Liver function tests
Liver function tests are common tests that are used to see how well the liver is working. Tests include:AlbuminAlpha-1 antitrypsinAlkaline phosphata...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
PET scan
PET scan
A positron emission tomography (PET) scan is a type of imaging test. It uses a radioactive substance called a tracer to look for disease in the body...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
MRI
MRI
A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan is an imaging test that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the body. It does not us...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Capsule endoscopy
Capsule endoscopy
Endoscopy is a way of looking inside the body. Endoscopy is often done with a tube put into the body that the doctor can use to look inside. Anothe...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Liver biopsy
Liver biopsy
A liver biopsy is a test that takes a sample of tissue from the liver for examination.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
A biopsy of the skin, mucous membranes in the mouth, may also help to confirm the diagnosis.
Biopsy
A biopsy is the removal of a small piece of tissue for lab examination.
Treatment
After a transplant, the recipient usually takes medicines, such as prednisone (a steroid), which suppress the immune system. This helps reduce the chances (or severity) of GVHD.
You'll continue taking the medicines until your transplant health care provider thinks the risk for GVHD is low. Many of these medicines have side effects, including kidney and liver damage. You'll have regular tests to watch for these problems.
Outlook (Prognosis)
The outlook depends on the severity of GVHD. People who receive closely matched bone marrow tissue and cells usually do better.
Some cases of GVHD can damage the liver, lungs, digestive tract, or other body organs. There is also a risk for severe infections.
Many cases of acute or chronic GVHD can be treated successfully. But this doesn't guarantee that the transplant itself will succeed in treating the original disease.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
If you have had a bone marrow transplant, contact your transplant provider right away if you develop any symptoms of GVHD or other unusual symptoms.
References
Chao NJ, Keating A. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 163.
Im A, Pavletic SZ. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. In: Niederhuber JE, Armitage JO, Kastan MB, Doroshow JH, Tepper JE, eds. Abeloff's Clinical Oncology. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 28.
Riwes M, Ferrara JL, Reddy P, Magenau JM. Graft-versus-host disease and graft-versus-leukemia responses. In: Hoffman R, Benz EJ, Silberstein LE, et al, eds. Hematology: Basic Principles and Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 109.
-
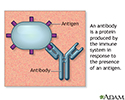
Antibodies - illustration
Antigens are large molecules (usually proteins) on the surface of cells, viruses, fungi, bacteria, and some non-living substances such as toxins, chemicals, drugs, and foreign particles. The immune system recognizes antigens and produces antibodies that destroy substances containing antigens.
Antibodies
illustration
-
Antibodies - illustration
Antigens are large molecules (usually proteins) on the surface of cells, viruses, fungi, bacteria, and some non-living substances such as toxins, chemicals, drugs, and foreign particles. The immune system recognizes antigens and produces antibodies that destroy substances containing antigens.
Antibodies
illustration
Review Date: 6/17/2024
Reviewed By: Todd Gersten, MD, Hematology/Oncology, Florida Cancer Specialists & Research Institute, Wellington, FL. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.