Congenital toxoplasmosis
Congenital toxoplasmosis is a group of symptoms that occur when an unborn baby (fetus) is infected with the parasite Toxoplasma gondii.
Causes
Toxoplasmosis infection can be passed to a developing baby if the mother becomes infected while pregnant. The infection spreads to the developing baby across the placenta. Most of the time, the infection is mild in the mother. The woman may not be aware she has the parasite. However, infection of the developing baby can cause serious problems. Problems are worse if the infection occurs in early pregnancy.
Symptoms
Up to half of babies who become infected with toxoplasmosis during the pregnancy are born early (prematurely). The infection can damage the baby's eyes, nervous system, skin, and ears.
Often, there are signs of infection at the time of birth. However, babies with mild infections may not have symptoms for months or years after birth. If not treated, most children with this infection develop problems in their teens. Eye problems are common.
Symptoms may include:
- Enlarged liver and spleen
- Vomiting
- Eye damage from inflammation of the retina or other parts of the eye
- Feeding problems
- Hearing loss
-
Jaundice (yellow skin)
Jaundice
Jaundice is a yellow color of the skin, mucus membranes, or eyes. The yellow coloring comes from bilirubin, a byproduct of old red blood cells. Jau...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Low birth weight (intrauterine growth restriction)
- Skin rash (tiny red spots or bruising) at birth
- Vision problems
Brain and nervous system damage ranges from very mild to severe, and may include:
-
Seizures
Seizures
A seizure is the physical changes in behavior that occurs during an episode of specific types of abnormal electrical activity in the brain. The term ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Intellectual disability
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will examine the baby. The baby may have:
- Swollen spleen and liver
- Yellow skin (jaundice)
- Inflammation of the eyes
- Fluid on the brain (hydrocephalus)
Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is a buildup of fluid inside the skull that leads to the brain pushing against the skull. Hydrocephalus means "water on the brain. "...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Swollen lymph nodes (lymphadenopathy)
Lymphadenopathy
Lymphofollicular hyperplasia is an increase in the number of cells found in a lymph node. These follicles contain normal white blood cells called ly...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
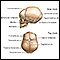
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Large head size (macrocephaly) or smaller-than-normal head size (microcephaly)
Macrocephaly
Increased head circumference is when the measured distance around the widest part of the skull is larger than expected for the child's age and backgr...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleMicrocephaly
Microcephaly is a condition in which a person's head size is much smaller than that of others of the same age and sex. Head size is measured as the ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Tests that may be done during pregnancy include:
-
Amniotic fluid testing and fetal blood testing
Amniotic fluid
Amniotic fluid is a clear, slightly yellowish liquid that surrounds the unborn baby (fetus) during pregnancy. It is contained in the amniotic sac....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleFetal blood testing
Fetal scalp pH testing is a procedure performed when a woman is in active labor to determine if the baby is getting enough oxygen.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Antibody titer
Antibody titer
Antibody titer is a laboratory test that measures the level of antibodies in a blood sample.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Ultrasound of the abdomen
Ultrasound of the abdomen
Abdominal ultrasound is a type of imaging test. It is used to look at organs in the abdomen, including the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, and kidneys...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
After birth, the following tests may be done on the baby:
- Antibody tests on cord blood and cerebrospinal fluid
Cord blood
Cord blood refers to a sample of blood collected from the umbilical cord when a baby is born. The umbilical cord is the cord connecting the baby to ...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
CT scan of the brain
CT scan
A head computed tomography (CT) scan uses many x-rays to create pictures of the head, including the skull, brain, eye sockets, and sinuses.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
MRI scan of the brain
MRI scan
A head MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is an imaging test that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the brain and surrounding...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Neurological exams
-
Standard eye exam
Standard eye exam
A standard eye exam is a series of tests done to check your vision and the health of your eyes. This exam is performed by an ophthalmologist or opto...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Toxoplasmosis test
Treatment
Spiramycin can treat infection in the pregnant mother.
Pyrimethamine and sulfadiazine can treat a fetal infection (diagnosed during the pregnancy).
Treatment of infants with congenital toxoplasmosis most often includes pyrimethamine, sulfadiazine, and leucovorin for one year. Infants are also sometimes given steroids if their vision is threatened or if their protein level in the spinal fluid is high.
Outlook (Prognosis)
The outcome depends on the extent of the condition.
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
-
Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is a buildup of fluid inside the skull that leads to the brain pushing against the skull. Hydrocephalus means "water on the brain. "...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Blindness or severe visual disability
Blindness
Blindness is a lack of vision. It may also refer to a loss of vision that cannot be corrected with glasses or contact lenses. Partial blindness mean...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Severe intellectual disability or other neurological problems
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you are pregnant and think you are at risk for the infection. (For example, toxoplasmosis infection can be passed from cats if you clean the cat's litter box.) Contact your provider if you are pregnant and have not had prenatal care.
Prevention
Women who are pregnant or planning to become pregnant can be tested to find out if they are at risk for the infection.
Pregnant women who have cats as house pets may be at higher risk. They should avoid contact with cat feces, or things that could be contaminated by insects exposed to cat feces (such as cockroaches and flies).
Also, cook meat until it is well done, and wash your hands after handling raw meat to avoid getting the parasite.
References
Boudova S, Silverman NS. Bacterial and parasitic infections in pregnancy. In: Landon MB, Galan HL, Jauniaux ERM, et al, eds. Gabbe's Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 58.
Kim K, Boothroyd JC, Kovacs JA. Toxoplasma gondii. In: Bennett JE, Cohen JI, Holland SM, et, al, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2026:chap 284.
McLeod R, Boyer KM. Toxoplasmosis (Toxoplasma gondii). In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 22nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 336.
-
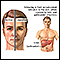
Congenital toxoplasmosis - illustration
Human infection with the toxoplasma gondii protozoan results from ingesting contaminated raw meat or soil, or careless handling of the contents of an infected cat's litter box. An infected pregnant woman can transmit the infection to her fetus (congenital toxoplasmosis).
Congenital toxoplasmosis
illustration
-
Congenital toxoplasmosis - illustration
Human infection with the toxoplasma gondii protozoan results from ingesting contaminated raw meat or soil, or careless handling of the contents of an infected cat's litter box. An infected pregnant woman can transmit the infection to her fetus (congenital toxoplasmosis).
Congenital toxoplasmosis
illustration
Review Date: 4/6/2025
Reviewed By: Neil K. Kaneshiro, MD, MHA, Clinical Professor of Pediatrics, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.


