Ataxia - telangiectasia
Louis-Bar syndromeAtaxia-telangiectasia is a rare childhood disease. It affects the brain and other parts of the body.
Ataxia refers to uncoordinated movements, such as walking. Telangiectasias are enlarged blood vessels (capillaries) just below the surface of the skin. Telangiectasias appear as tiny, red, spider-like blood vessels.
Causes
Ataxia-telangiectasia is inherited. This means it is passed down through families. It is an autosomal recessive trait. Both parents must provide a copy of a nonworking gene for the child to have symptoms of the disorder.
Autosomal recessive
Autosomal recessive is one of several ways that a genetic trait, disorder, or disease can be passed down through families. An autosomal recessive dis...

The disease results from a variant in the ATM gene. This gene provides instructions for making a protein that helps control the rate at which cells grow and divide. Defects in this gene can lead to abnormal cell death in many sites of the body, including the part of the brain that helps coordinate movement.
Boys and girls are equally affected.
Symptoms
Symptoms include:
- Decreased coordination of movements (ataxia) in late childhood that can include ataxic gait (cerebellar ataxia), jerky gait, unsteadiness
Ataxia
Uncoordinated movement is due to a muscle control problem that causes an inability to coordinate movements. It leads to a jerky, unsteady, to-and-fr...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Decreasing mental development, slows or stops after age 10 to 12
- Delayed walking
- Discoloration of skin areas exposed to sunlight
- Discoloration of skin (coffee-with-milk-colored spots)
- Enlarged blood vessels in skin of nose, ears, and inside of the elbow and knee
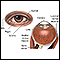
- Enlarged blood vessels in the whites of the eyes
- Jerky or abnormal eye movements (nystagmus) late in the disease
Nystagmus
Nystagmus is a term to describe uncontrollable movements of the eyes that may be:Side to side (horizontal nystagmus)Up and down (vertical nystagmus)R...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Premature graying of the hair
- Seizures
- Sensitivity to radiation, including x-rays
- Severe respiratory infections that keep coming back (recurring)
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will perform a physical exam. The exam may show signs of the following:
- Tonsils, lymph nodes, and spleen below normal size
- Decreased to absent deep tendon reflexes
- Delayed or absent physical and sexual development
-
Growth failure
Growth failure
Failure to thrive refers to children whose current weight or rate of weight gain is much lower than that of other children of similar age and sex....
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Mask-like face
- Multiple skin coloring and texture changes
Possible tests include:
-
Alpha fetoprotein
Alpha fetoprotein
Alpha fetoprotein (AFP) is a protein produced by the liver and yolk sac of a developing baby during pregnancy. AFP levels go down soon after birth. ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
B and T cell screen
B and T cell screen
B and T cell screen is a lab test to determine the amount of B and T lymphocytes in the blood.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Carcinoembryonic antigen
Carcinoembryonic antigen
The carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) test measures the level of CEA in the blood. CEA is a protein normally found in the tissue of a developing baby i...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Genetic testing to look for changes in the ATM gene
- Glucose tolerance test
- Serum immunoglobulin levels (IgE, IgA)
- X-ray or CT scan to look at the size of the thymus gland
Treatment
There is no specific treatment for ataxia-telangiectasia. Treatment is directed at specific symptoms.
Support Groups
More information and support for people with ataxia-telangiectasia condition and their families can be found at:
- Ataxia Telangiectasia Children's Project: www.atcp.org
- National Ataxia Foundation (NAF): www.ataxia.org
Outlook (Prognosis)
Early death is common, but life expectancy varies.
Because people with this condition are very sensitive to radiation, they should never be given radiation therapy, and no unnecessary x-rays should be done.
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
- Cancer, such as lymphoma
Lymphoma
Hodgkin lymphoma is a cancer of lymph tissue. Lymph tissue is found in the lymph nodes, spleen, liver, bone marrow, and other sites.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Diabetes
Diabetes
Diabetes is a long-term (chronic) disease in which the body cannot regulate the amount of sugar in the blood.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Kyphosis
Kyphosis
Kyphosis is a curving of the spine that causes a bowing or rounding of the back. This leads to a hunchback or slouching posture.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Progressive movement disorder that leads to wheelchair use
-
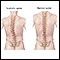
Scoliosis
Scoliosis
Scoliosis is an abnormal curving of the spine. Your spine is your backbone. It runs straight down your back. Everyone's spine naturally curves a b...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
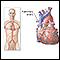
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Severe, recurrent lung infections
Lung infections
Pulmonary angiography is a test to see how blood flows through the lung. Angiography is an imaging test that uses x-rays and a special dye to see th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if your child develops symptoms of this disorder.
Prevention
Couples with a family history of this condition who are considering pregnancy may consider genetic counseling.
Parents of a child with this disorder may have a slight increased risk for cancer. They should have genetic counseling and increased cancer screenings.
References
Cunningham-Rundles C. Primary immunodeficiency diseases. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 231.
Martin KL. Vascular disorders. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 669.
National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences. Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center website. Ataxia-telangiectasia. rarediseases.info.nih.gov/diseases/5862/ataxia-telangiectasia. Updated February 2023. Accessed October 17, 2023.
Safier RA, Cleves-Bayon C, Gaesser J. Neurology. In: Zitelli BJ, McIntire SC, Nowalk AJ, eds. Zitelli and Davis' Atlas of Pediatric Physical Diagnosis. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 16.
-
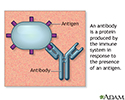
Antibodies - illustration
Antigens are large molecules (usually proteins) on the surface of cells, viruses, fungi, bacteria, and some non-living substances such as toxins, chemicals, drugs, and foreign particles. The immune system recognizes antigens and produces antibodies that destroy substances containing antigens.
Antibodies
illustration
-
Telangiectasia - illustration
Telangiectasia is the dilation of small superficial vessels and capillaries that cause numerous flat red marks on the hands, face and tongue. Telangiectasia can be a symptom of scleroderma or other systemic diseases.
Telangiectasia
illustration
-
Antibodies - illustration
Antigens are large molecules (usually proteins) on the surface of cells, viruses, fungi, bacteria, and some non-living substances such as toxins, chemicals, drugs, and foreign particles. The immune system recognizes antigens and produces antibodies that destroy substances containing antigens.
Antibodies
illustration
-
Telangiectasia - illustration
Telangiectasia is the dilation of small superficial vessels and capillaries that cause numerous flat red marks on the hands, face and tongue. Telangiectasia can be a symptom of scleroderma or other systemic diseases.
Telangiectasia
illustration
Review Date: 9/18/2023
Reviewed By: Anna C. Edens Hurst, MD, MS, Associate Professor in Medical Genetics, The University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, AL. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.