Neuralgia
Nerve pain; Painful neuropathy; Neuropathic painNeuralgia is a sharp, shocking pain that follows the path of a nerve and is due to irritation or damage to the nerve.
Common neuralgias include:
-
Postherpetic neuralgia (pain that continues after a bout of shingles)
Postherpetic neuralgia
Shingles is a painful, blistering skin rash. It is caused by the varicella-zoster virus, a member of the herpes family of viruses. This is the viru...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Trigeminal neuralgia (stabbing or electric-shock-like pain in parts of the face)
Trigeminal neuralgia
Trigeminal neuralgia (TN) is a nerve disorder. It causes a stabbing or electric shock-like pain in parts of the face.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Alcoholic neuropathy
- Peripheral neuropathy
Causes
Causes of neuralgia include:
- Chemical irritation
-
Chronic kidney disease
Chronic kidney disease
Chronic kidney disease is the slow loss of kidney function over time. The main job of the kidneys is to remove wastes and excess water from the body...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Diabetes
Diabetes
Diabetes is a long-term (chronic) disease in which the body cannot regulate the amount of sugar in the blood.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Infections, such as herpes zoster (shingles), HIV/AIDS, Lyme disease, and syphilis
Shingles
Shingles is a painful, blistering skin rash. It is caused by the varicella-zoster virus, a member of the herpes family of viruses. This is the viru...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleHIV/AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is the virus that causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). When a person becomes infected with HIV, the ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleLyme disease
Lyme disease is a bacterial infection that is spread through the bite of one of several types of ticks.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleSyphilis
Syphilis is a bacterial infection that is most often spread through sexual contact.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Chemotherapy medicines such as cisplatin, paclitaxel, or vincristine
-
Porphyria (blood disorder)
Porphyria
Porphyrias are a group of rare disorders in which an important part of hemoglobin, called heme, is not made properly. Hemoglobin is a protein in red...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Pressure on nerves by nearby bones, ligaments, blood vessels, or tumors
- Trauma (including surgery)
- Underlying nervous system disorder (such as multiple sclerosis)
Multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease that affects the brain and spinal cord (central nervous system).
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
In many cases, the cause is unknown.
Postherpetic neuralgia and trigeminal neuralgia are the two most common forms of neuralgia. A related but less common neuralgia affects the glossopharyngeal nerve, which provides feeling to the throat.
Glossopharyngeal nerve
Glossopharyngeal neuralgia (GPN) is a rare condition in which there are repeated episodes of severe pain in the tongue, throat, ear, and tonsils. Th...

Neuralgia is more common in older people, but it may occur at any age.
Symptoms
Symptoms may include any of the following:
- Increased sensitivity of the skin along the path of the damaged nerve, so that any touch or pressure is felt as pain
- Pain along the path of the nerve that is sharp or stabbing, in the same location each episode, comes and goes (intermittent) or is constant and burning, and may get worse when the area is moved
- Weakness or complete paralysis of muscles supplied by the same nerve
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will perform a physical exam, and ask about your symptoms.
The exam may show:
- Abnormal sensation in the skin
- Reflex problems
- Loss of muscle mass
- Lack of sweating (sweating is controlled by nerves)
- Tenderness along a nerve
- Trigger points (areas where even a slight touch triggers pain)
You may also need to see a dentist if the pain is in your face or jaw. A dental exam can check for dental disorders that may cause facial pain (such as a tooth abscess).
Facial pain
Face pain may be dull and throbbing or an intense, stabbing discomfort in the face or forehead. It can occur in one or both sides.
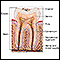
Tooth abscess
A tooth abscess is a pocket of pus caused by a bacterial infection.
Other symptoms (such as redness or swelling) may indicate other conditions such as infections, bone fractures, or rheumatoid arthritis.
Rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a disease that leads to inflammation of the joints and surrounding tissues. It is a long-term disease. It can also aff...
There are no specific tests for neuralgia. But, the following tests may be done to find the cause of the pain:
- Blood tests to check blood sugar, kidney function, and other possible causes of neuralgia
Blood sugar
A blood sugar test measures the amount of sugar (glucose) in a sample of your blood. Glucose is a major source of energy for most cells of the body, ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
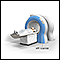
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
Magnetic resonance imaging
A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan is an imaging test that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the body. It does not us...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
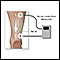
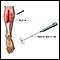
Nerve conduction study with electromyography
Nerve conduction study
Nerve conduction velocity (NCV) is a test to see how fast electrical signals move through a nerve. This test is done along with electromyography (EM...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleElectromyography
Electromyography (EMG) is a test that checks the health of the muscles and the nerves that control the muscles.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Ultrasound
- Spinal tap (lumbar puncture)
Lumbar puncture
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) collection is a test to look at the fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. CSF acts as a cushion, protecting the b...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
Treatment depends on the cause, location, and severity of the pain.
Medicines to control pain may include:
- Antidepressants
- Antiseizure medicines
- Over-the-counter or prescription pain medicines
- Pain medicines in the form of skin patches or creams
Other treatments may include:
- Shots with pain-relieving (anesthetic) medicines
- Nerve blocks
- Physical therapy (for some types of neuralgia, especially postherpetic neuralgia)
- Procedures to reduce feeling in the nerve (such as nerve ablation using radiofrequency, heat, balloon compression, or injection of chemicals)
- Surgery to take pressure off a nerve
- Alternative therapy, such as acupuncture or biofeedback
Procedures may not improve symptoms and can cause loss of feeling or abnormal sensations.
When other treatments fail, providers may try nerve or spinal cord stimulation. In rare cases, a procedure called motor cortex stimulation (MCS) is tried. An electrode is placed over part of a nerve, spinal cord, or brain and is hooked to a pulse generator under the skin. This changes how your nerves signal and it may reduce pain.
Spinal cord stimulation
Spinal cord stimulation (SCS) is a treatment for pain that uses a mild electric current to block nerve impulses in the spine.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Most neuralgias are not life threatening and are not signs of other life-threatening disorders. For severe pain that does not improve, see a pain specialist so that you can explore all treatment options.
Most neuralgias respond to treatment. Attacks of pain usually come and go. But, attacks may become more frequent in some people as they get older.
Sometimes, the condition may improve on its own or disappear with time, even when the cause is not found.
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
- Problems from surgery
- Disability caused by pain
- Side effects of medicines used to control pain
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if:
- You develop shingles
- You have symptoms of neuralgia, especially if over-the-counter pain medicines do not relieve your pain
- You have severe pain (see a pain specialist)
Prevention
Strict control of blood sugar may prevent nerve damage in people with diabetes. In the case of shingles, antiviral medicines and the herpes zoster virus vaccine may prevent neuralgia.
References
Cohen SP. Pain. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 388.
Katirji B. Disorders of peripheral nerves. In: Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC, Pomeroy SL, Newman NJ, eds. Bradley and Daroff's Neurology in Clinical Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 106.
Smith AG, Shy ME. Peripheral neuropathies. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 388.
-
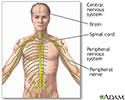
Central nervous system and peripheral nervous system - illustration
The central nervous system is made up of the brain and the spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system includes nerves outside the brain and spinal cord.
Central nervous system and peripheral nervous system
illustration
Review Date: 6/13/2024
Reviewed By: Joseph V. Campellone, MD, Department of Neurology, Cooper Medical School at Rowan University, Camden, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.